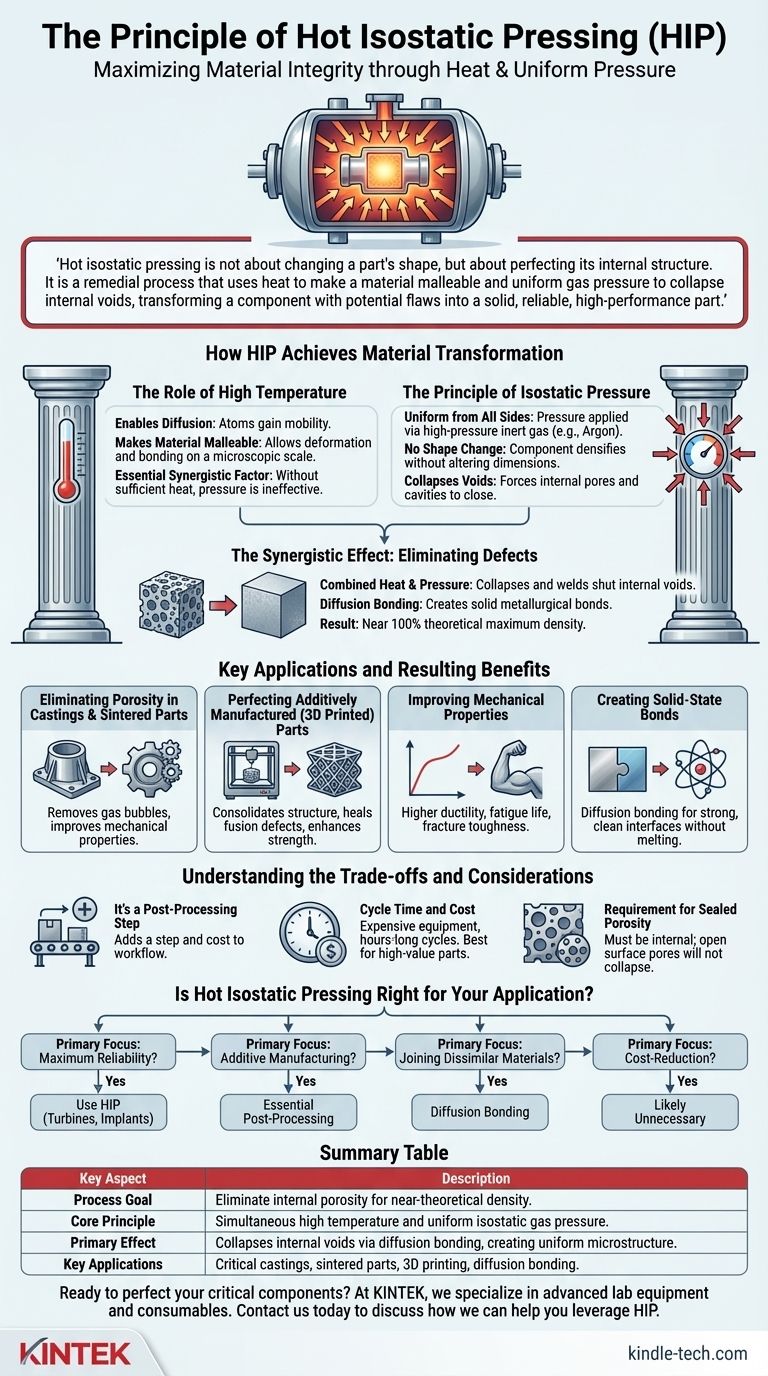
At its core, the principle of hot isostatic pressing (HIP) is a manufacturing process that subjects a component to both high temperature and extreme, uniform pressure from all sides. Using an inert gas like argon as the pressure medium, this combination of heat and pressure fundamentally improves the material by eliminating internal porosity and creating a fully dense, uniform microstructure.
Hot isostatic pressing is not about changing a part's shape, but about perfecting its internal structure. It is a remedial process that uses heat to make a material malleable and uniform gas pressure to collapse internal voids, transforming a component with potential flaws into a solid, reliable, high-performance part.

How HIP Achieves Material Transformation
The effectiveness of HIP lies in the precise, simultaneous application of heat and pressure. Each plays a distinct and critical role in transforming the material at a microscopic level.
The Role of High Temperature
The "Hot" in HIP is the enabling factor for change. Heating a component to an elevated temperature (typically below its melting point) gives the atoms within the material enough energy to move.
This increased atomic mobility, known as diffusion, makes the material soft and malleable enough to deform and bond on a microscopic scale. Without sufficient heat, the pressure alone would be ineffective.
The Principle of Isostatic Pressure
"Isostatic" means that pressure is applied uniformly from all directions. This is achieved by placing the component inside a sealed pressure vessel and introducing a high-pressure inert gas.
Unlike mechanical pressing, which applies force from one or two directions, the gas envelops the part and exerts equal pressure on every point of its surface. This ensures that the component densifies without changing its overall shape or dimensions.
The Synergistic Effect: Eliminating Defects
The combination of heat and pressure works to collapse and weld shut internal voids. Heat makes the material pliable, while the immense external pressure creates a differential that squeezes any internal pores or cavities closed.
Once the walls of these voids are forced into contact, the high temperature facilitates diffusion bonding, creating a seamless, solid metallurgical bond where the defect once was. The result is a part that approaches 100% of its theoretical maximum density.
Key Applications and Resulting Benefits
HIP is used not as a primary shaping method, but as a critical post-processing step to perfect components made by other means. Its benefits are directly tied to the elimination of internal flaws.
Eliminating Porosity in Castings and Sintered Parts
Traditional casting and powder metallurgy processes can leave behind microscopic gas bubbles or voids. HIP effectively removes this porosity, dramatically improving the mechanical properties of the finished component.
Perfecting Additively Manufactured (3D Printed) Parts
Metal 3D printing often suffers from issues like incomplete fusion between layers and trapped porosity. HIP is a near-essential step for critical 3D printed parts, as it consolidates the structure, heals these defects, and creates a uniform microstructure with superior strength and fatigue resistance.
Improving Mechanical Properties
By creating a fully dense and homogenous material, HIP significantly enhances key performance characteristics. Parts treated with HIP exhibit higher ductility, superior fatigue life, and greater fracture toughness, making them more reliable in demanding applications.
Creating Solid-State Bonds
HIP can be used to diffusion bond two or more separate parts, even if they are made of dissimilar materials. Under heat and pressure, the atoms at the interface diffuse across the boundary, creating a continuous, solid-state joint without any melting or liquid phase.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While powerful, HIP is a specialized process with specific requirements and limitations that are important to understand.
It's a Post-Processing Step
HIP does not create a part from scratch; it improves a part that is already formed into its near-net shape. This adds an extra step and associated cost to the overall manufacturing workflow.
Cycle Time and Cost
The equipment required for HIP is expensive, and the process cycles—involving controlled heating, pressurization, holding time, and cooling—can take several hours. This makes it most suitable for high-value components where performance and reliability are non-negotiable.
Requirement for Sealed Porosity
For HIP to work, any porosity must be internal to the part and not connected to the surface. If a pore is open to the surface, the pressurizing gas will simply fill the void, equalizing the pressure and preventing it from collapsing.
Is Hot Isostatic Pressing Right for Your Application?
Choosing to use HIP depends entirely on the performance requirements and value of the final component.
- If your primary focus is maximum reliability and performance: Use HIP to eliminate internal defects in critical components like turbine blades, medical implants, or high-stress structural parts to achieve theoretical density and superior mechanical properties.
- If your primary focus is producing parts via additive manufacturing: Consider HIP an essential post-processing step to overcome inherent porosity, improve layer bonding, and ensure the material integrity required for functional, end-use parts.
- If your primary focus is joining dissimilar materials without melting: Leverage HIP for diffusion bonding to create strong, clean interfaces that are impossible to achieve with conventional welding or brazing techniques.
- If your primary focus is cost-reduction on non-critical parts: HIP is likely unnecessary, as its benefits may not justify the added cost and time for components where internal microstructure is not a performance driver.
Ultimately, understanding the principle of HIP empowers you to specify its use precisely where it adds the most value, transforming good components into exceptional ones.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Process Goal | Eliminate internal porosity and defects to achieve near-theoretical density. |
| Core Principle | Simultaneous application of high temperature and uniform isostatic gas pressure. |
| Primary Effect | Collapses internal voids via diffusion bonding, creating a uniform microstructure. |
| Key Applications | Critical castings, sintered parts, additive manufacturing (3D printing), diffusion bonding. |
Ready to perfect your critical components?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing advanced lab equipment and consumables to meet your most demanding laboratory needs. If you are manufacturing high-value parts like turbine blades, medical implants, or 3D-printed components, our expertise can help you leverage Hot Isostatic Pressing to achieve unparalleled material integrity and performance.
Contact us today via our contact form to discuss how our solutions can help you eliminate internal defects and ensure the reliability of your most critical parts.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Warm Isostatic Press WIP Workstation 300Mpa for High Pressure Applications
- Anti-Cracking Press Mold for Lab Use
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
People Also Ask
- Is hot isostatic pressing a heat treatment? A Guide to Its Unique Thermomechanical Process
- What is HIP treatment for metal? Eliminate Internal Defects for Superior Part Performance
- What is HIP in material processing? Achieve Near-Perfect Density for Critical Components
- How much energy does hot isostatic pressing consume? Unlock Net Energy Savings in Your Process
- What is the HIP material process? Achieve Near-Perfect Density and Reliability



















