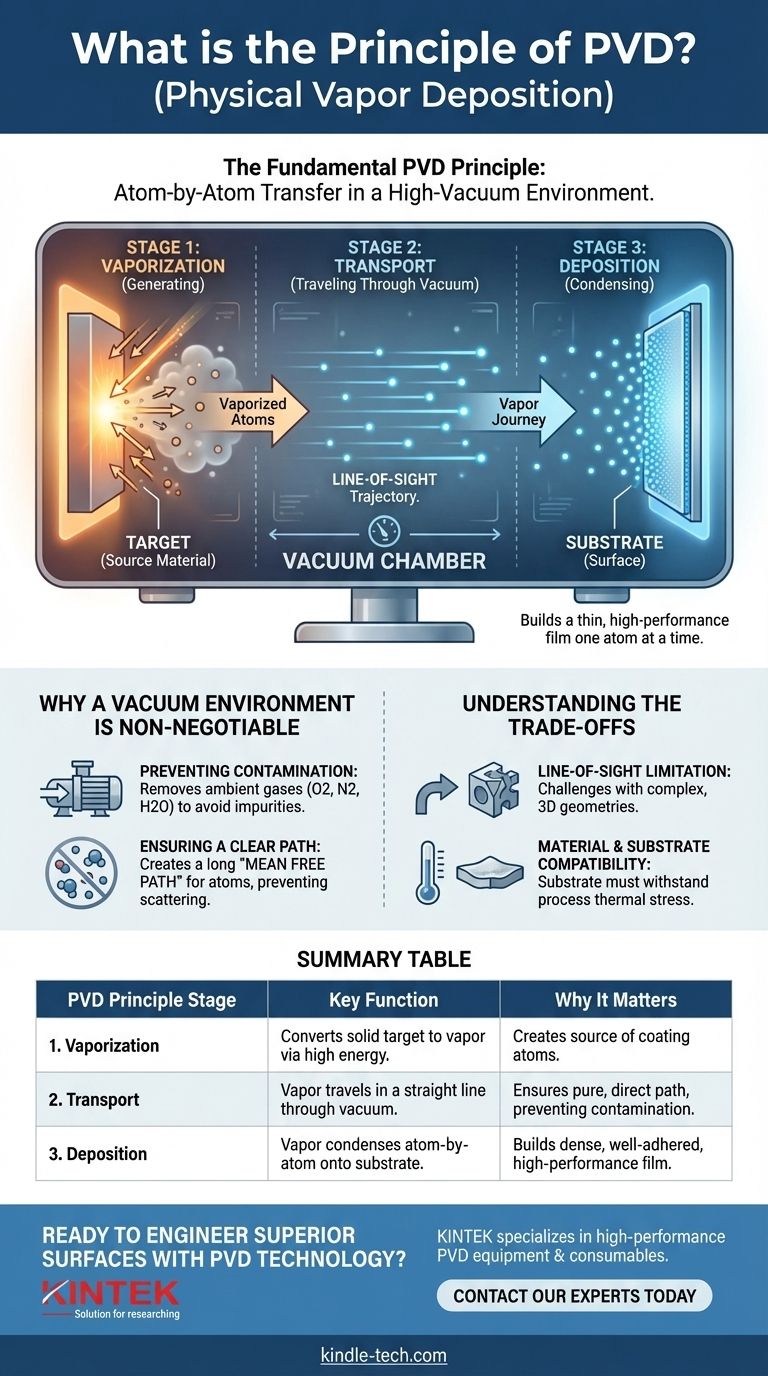
The fundamental principle of PVD is the physical transfer of material on an atom-by-atom basis. In a high-vacuum environment, a solid source material, known as the "target," is converted into a vapor. This vapor then travels through the vacuum and condenses onto a substrate, meticulously building a thin, high-performance film.
At its core, Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is a three-stage process—vaporization, transport, and deposition. It physically moves atoms from a source to a surface within a vacuum, completely avoiding chemical reactions to create exceptionally pure and dense coatings.
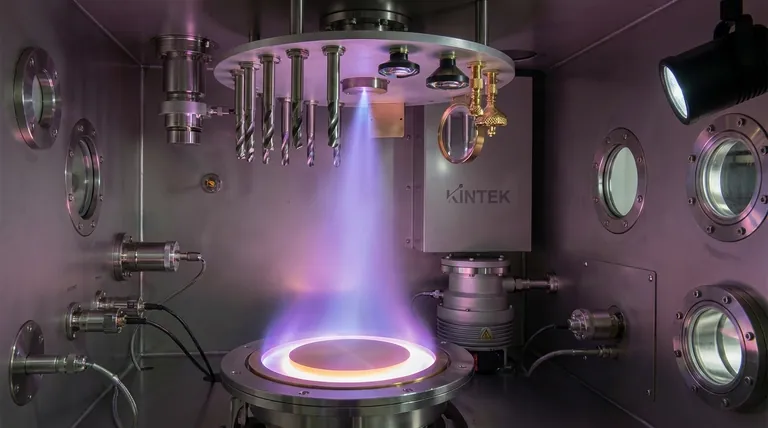

The Three Foundational Stages of PVD
To truly understand the principle, it's best to break the process down into its three distinct and sequential stages. Each stage is critical for the final quality of the coating.
Stage 1: Vaporization (Generating the Coating Material)
The process begins by converting a solid source material into a gaseous vapor. This is achieved by supplying a significant amount of energy to the target.
The specific method of vaporization is the primary way different PVD techniques are categorized. Common methods include simple heating, bombarding the target with high-energy ions (sputtering), or using a high-power electron beam or laser.
Stage 2: Transport (Traveling Through the Vacuum)
Once the atoms are vaporized, they travel through the vacuum chamber from the source to the substrate. This journey is a crucial, defining feature of the PVD process.
The high vacuum ensures there are virtually no air or gas molecules for the vaporized atoms to collide with. This allows them to travel in a straight, unimpeded path, often described as a "line-of-sight" trajectory.
Stage 3: Deposition (Condensing onto the Substrate)
When the vaporized atoms reach the cooler surface of the substrate, they condense back into a solid state. This condensation builds the coating one atom at a time.
The result is an extremely thin, well-adhered, and often very dense film. The properties of this film—such as hardness, friction, and oxidation resistance—can be precisely controlled.
Why a Vacuum Environment is Non-Negotiable
The entire PVD process is dependent on the carefully controlled, low-pressure vacuum chamber. This environment is not optional; it is fundamental to the principle.
Preventing Contamination
A primary function of the vacuum is to remove ambient gases like oxygen, nitrogen, and water vapor. If these particles were present, they would react with the vaporized material and become embedded in the film, creating impurities and compromising its performance.
Ensuring a Clear Path
The vacuum creates a long "mean free path" for the coating atoms. This means they can travel from the target to the substrate without colliding with other gas molecules, which would otherwise scatter them and prevent uniform, direct deposition.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the principles of PVD introduce specific limitations that are important to understand.
The Line-of-Sight Limitation
Because the vapor travels in a straight line, PVD is best suited for coating flat or smoothly curved surfaces. Coating complex, three-dimensional geometries with sharp corners or deep recesses can be challenging and often requires sophisticated rotating fixtures to expose all surfaces to the vapor source.
Material and Substrate Compatibility
The energy required for vaporization and the conditions within the chamber can place thermal stress on the substrate. Therefore, the substrate material must be able to withstand the process temperatures without deforming or degrading.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the core principle of PVD helps you determine where its unique capabilities can be best applied.
- If your primary focus is creating highly pure, dense films: PVD is the standard for applications like semiconductors, optical lenses, and medical implants where material purity is paramount.
- If your primary focus is enhancing surface properties: Use PVD for adding extreme hardness, wear resistance, and lubricity to cutting tools, engine components, and industrial molds.
- If your primary focus is a durable, decorative finish: The process provides precise control over color and reflectivity, making it ideal for high-end watches, faucets, and architectural hardware.
Ultimately, the principle of PVD provides a mechanism for engineering surfaces at the atomic level, delivering performance unattainable by conventional methods.
Summary Table:
| PVD Principle Stage | Key Function | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Vaporization | Converts solid target material into a vapor using high energy. | Creates the source of coating atoms. |
| 2. Transport | Vapor travels in a straight line through a high vacuum. | Ensures a pure, direct path for the atoms, preventing contamination. |
| 3. Deposition | Vapor condenses atom-by-atom onto the substrate surface. | Builds a dense, well-adhered, and high-performance thin film. |
Ready to engineer superior surfaces with PVD technology?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance PVD equipment and consumables for laboratories and industrial applications. Whether you are developing semiconductors, enhancing tool durability, or creating precise decorative finishes, our solutions deliver the purity and control your projects demand.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our PVD systems can help you achieve unparalleled coating quality and performance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
People Also Ask
- What materials are deposited in PECVD? Discover the Versatile Thin-Film Materials for Your Application
- What is the difference between CVD and PECVD? Choose the Right Thin-Film Deposition Method
- What is plasma enhanced chemical vapour deposition process? Unlock Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Films
- What is plasma in CVD process? Lowering Deposition Temperatures for Heat-Sensitive Materials
- How does plasma enhanced CVD work? Achieve Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition



















