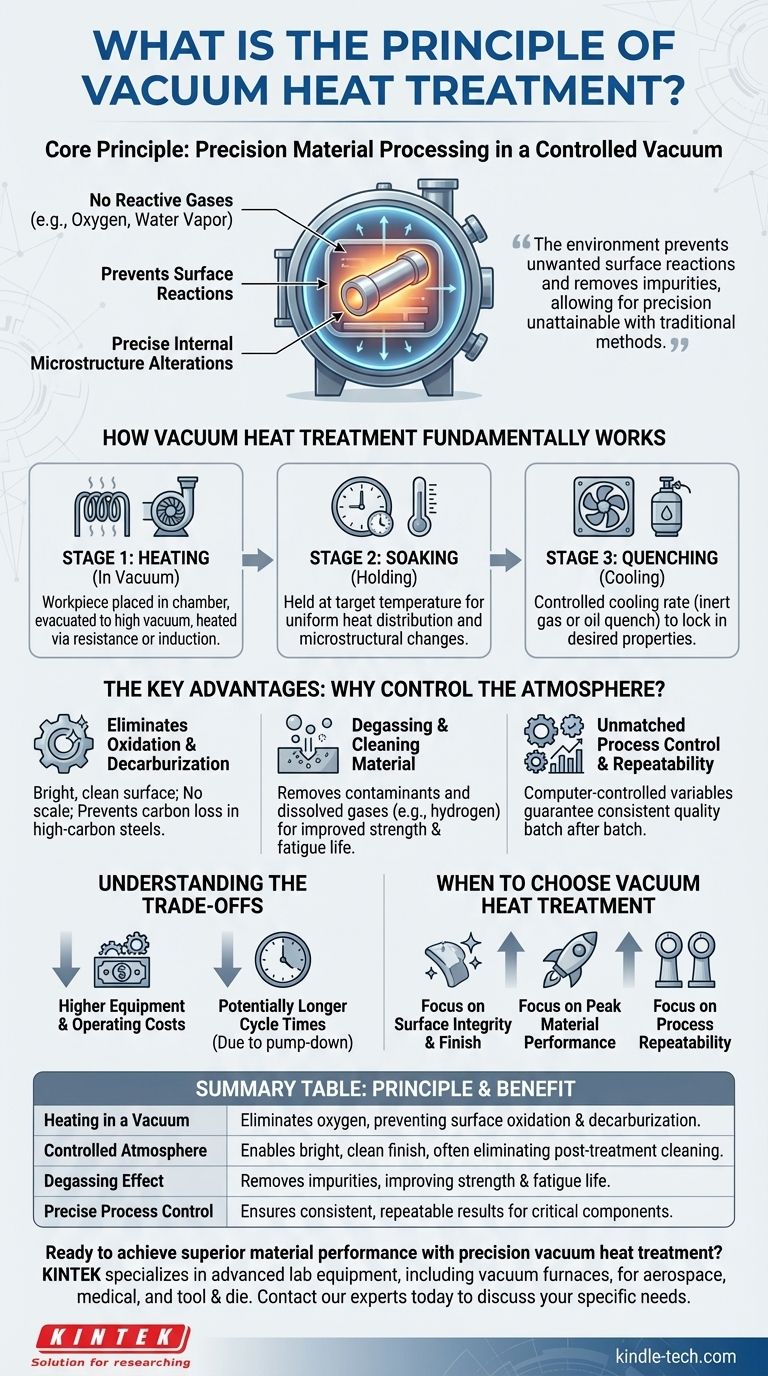
In essence, vacuum heat treatment is a material processing method where a part is heated to a specific temperature and then cooled in a controlled manner, all while inside a chamber with the air removed. By operating at pressures below atmospheric levels, the process eliminates reactive gases like oxygen, which prevents surface reactions such as oxidation and decarburization. This allows for precise, clean alterations to a material's internal microstructure to enhance its physical and mechanical properties.
The core principle is not merely heating metal, but doing so within a controlled vacuum. This environment prevents unwanted surface reactions and removes impurities, allowing for a level of precision and cleanliness that is unattainable with traditional atmospheric heat treatment methods.

How Vacuum Heat Treatment Fundamentally Works
To understand the principle, it's best to break the process down into its environment and its stages. The vacuum itself is the enabling factor for the specific heating and cooling steps.
The Principle of the Vacuum
A vacuum is a space with extremely low pressure, created by pumping out air and other gases. In heat treatment, achieving a high vacuum (low pressure) is critical because it removes the oxygen, water vapor, and other gases that would normally react with the hot metal surface.
This controlled atmosphere is the defining feature of the process. It allows for heating and cooling without causing scale, discoloration, or changes to the surface chemistry of the workpiece.
The Three Core Stages of the Process
Every vacuum heat treatment cycle follows a precise, programmed sequence of heating, holding, and cooling.
- Heating: The workpiece is placed in the vacuum furnace, the chamber is evacuated to the target vacuum level, and the part is heated. This is typically done using internal resistance or induction heating elements.
- Soaking (Holding): Once at the target temperature, the material is "soaked" for a predetermined period. This holding time, calculated based on the part's thickness and geometry, ensures that the entire workpiece reaches a uniform temperature and that the desired microstructural changes can take place.
- Quenching (Cooling): After soaking, the part is cooled at a specific, controlled rate to lock in the desired properties. This can be done by backfilling the chamber with a high-purity inert gas (like nitrogen or argon) for convection cooling, or by moving the part to an integrated oil quench tank, all while remaining under vacuum or controlled atmosphere.
Why Control the Atmosphere? The Key Advantages
Removing air from the process creates several distinct advantages that solve common problems found in traditional heat treatment.
Eliminating Surface Oxidation and Decarburization
This is the most significant benefit. Without oxygen, iron cannot form iron oxide (scale or rust) on the surface. For high-carbon steels, it also prevents carbon from being stripped from the surface (decarburization), which would otherwise create a soft outer layer.
The result is a bright, clean surface finish that often requires no subsequent cleaning or machining, saving time and cost.
Degassing and Cleaning the Material
The vacuum actively pulls contaminants off and out of the material. This includes vaporizing residual lubrication from manufacturing and removing dissolved gases, such as hydrogen, which can cause embrittlement in sensitive alloys.
This purification effect leads to materials with improved strength, ductility, and fatigue life.
Unmatched Process Control and Repeatability
Modern vacuum furnaces are computer-controlled, allowing for the precise and repeatable programming of every process variable: heating rates, temperature, soaking time, vacuum level, and cooling rates.
This guarantees that every part in a batch and every subsequent batch is processed under the exact same conditions, ensuring consistent quality for critical components.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, vacuum heat treatment is not a universal solution. Its precision comes with specific considerations.
Higher Equipment and Operating Costs
Vacuum furnaces are more complex and expensive to purchase, operate, and maintain than standard atmospheric furnaces. The need for vacuum pumps, sophisticated controls, and leak-free chambers adds to the initial investment and ongoing operational costs.
Potentially Longer Cycle Times
The time required to pump the chamber down to the target vacuum level can add to the total cycle time. While the heating and cooling can be rapid, the entire "floor-to-floor" time may be longer than for a less precise atmospheric process.
Not Always Necessary
For low-carbon steels or non-critical components where a layer of surface scale is acceptable (and may even be removed later), the added expense and complexity of vacuum processing may be unnecessary. The choice always depends on the final application requirements.
When to Choose Vacuum Heat Treatment
Use the principles of the process to guide your decision based on your primary engineering goal.
- If your primary focus is surface integrity and finish: Choose vacuum processing to produce bright, clean parts that are free of oxidation and decarburization, eliminating the need for post-treatment cleaning.
- If your primary focus is peak material performance: Use vacuum heat treatment for its ability to degas and purify sensitive alloys, which is critical for high-stress applications in aerospace, medical, and tool & die industries.
- If your primary focus is process repeatability: Choose a vacuum furnace for its precise computer control, guaranteeing that every critical component meets the exact same metallurgical specifications, batch after batch.
Ultimately, the principle of vacuum heat treatment is about achieving total environmental control to produce superior, cleaner, and more consistent material properties.
Summary Table:
| Key Principle | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Heating in a Vacuum | Eliminates oxygen, preventing surface oxidation and decarburization. |
| Controlled Atmosphere | Enables a bright, clean finish, often eliminating post-treatment cleaning. |
| Degassing Effect | Removes impurities and dissolved gases, improving strength and fatigue life. |
| Precise Process Control | Ensures consistent, repeatable results for critical components. |
Ready to achieve superior material performance with precision vacuum heat treatment?
KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment, including vacuum furnaces, to help you produce cleaner, stronger, and more consistent parts. Whether you're in aerospace, medical, or tool & die manufacturing, our solutions are designed for peak reliability and repeatability.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our vacuum heat treatment equipment can meet your specific laboratory and production needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why do you heat treat in a vacuum? Achieve Perfect Surface Finish and Material Integrity
- How does heat treatment process work? Tailor Material Properties for Your Application
- What is the difference between annealing hardening and tempering? Master Metal Properties for Your Lab
- What is a vacuum heat treatment furnace? The Ultimate Guide to Controlled Atmosphere Processing
- What is the process of vacuum quenching? Achieve Superior Hardness with a Pristine Surface Finish



















