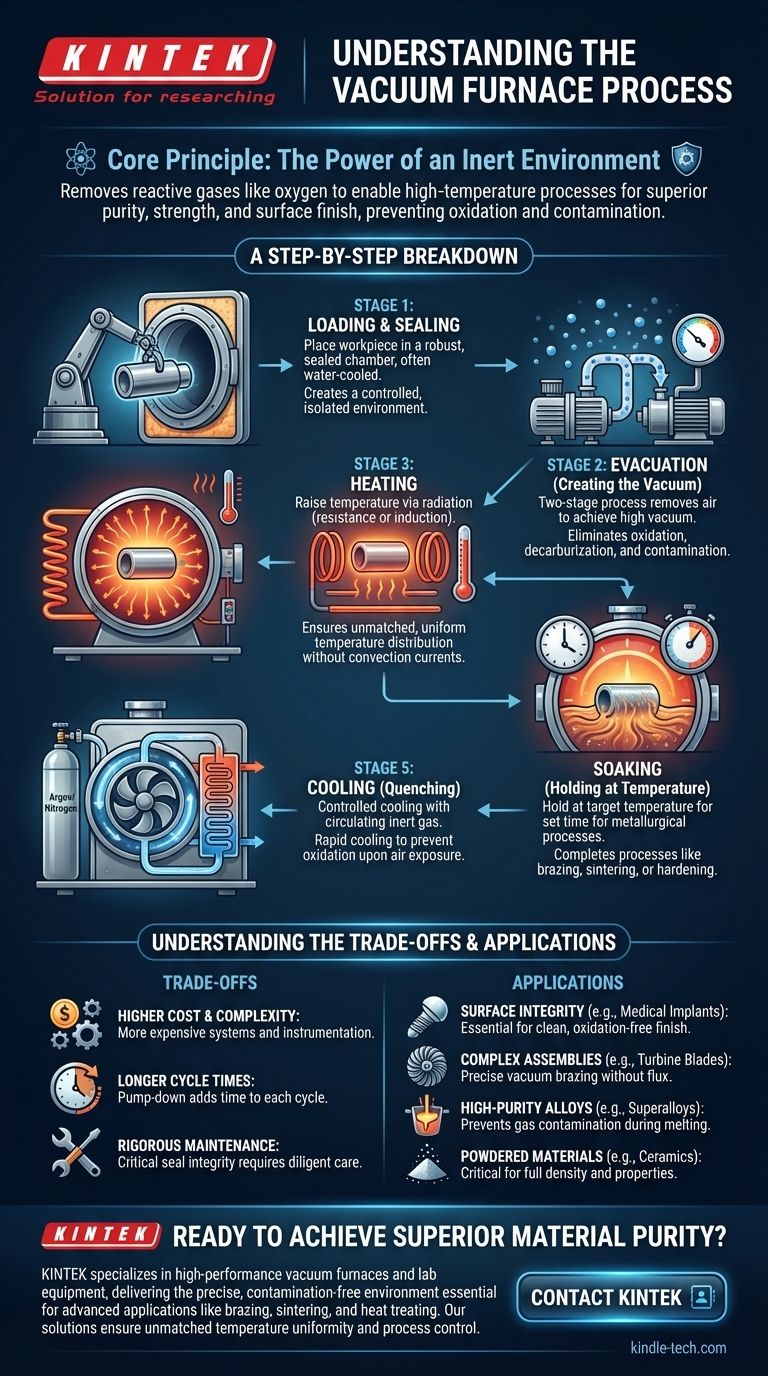
At its core, a vacuum furnace process involves heating materials inside a sealed chamber from which virtually all air has been removed. The typical sequence includes loading the material, pumping out the atmosphere to create a vacuum, heating the material to a precise temperature, holding it there for a set time, and finally cooling it in a controlled manner before exposing it to air again. This controlled, oxygen-free environment is the key to preventing unwanted chemical reactions like oxidation.
The fundamental purpose of a vacuum furnace is not just to heat materials, but to do so in an inert environment. By removing reactive gases like oxygen, the furnace enables high-temperature processes that result in superior material purity, strength, and surface finish—properties often impossible to achieve in a conventional atmospheric furnace.

The Core Principle: Why Operate in a Vacuum?
To understand the process, you must first understand the problem it solves. When materials are heated in the presence of air, they react with oxygen, nitrogen, and water vapor. A vacuum furnace eliminates this variable entirely.
Eliminating Oxidation and Contamination
The most immediate benefit is the prevention of oxidation. In a vacuum, there is no oxygen to tarnish, discolor, or form a weak oxide layer on the material's surface.
This also prevents other forms of contamination and unwanted reactions, such as decarburization (the loss of carbon from steel), which can compromise the material's structural integrity.
Enabling High-Purity Processes
For advanced materials like high-temperature superalloys, titanium, or medical-grade implants, even trace amounts of gaseous impurities can ruin their performance.
A vacuum environment ensures that the material's chemistry remains pure and precisely controlled throughout the heating and cooling cycle.
Achieving Unmatched Temperature Uniformity
In a vacuum, heat is transferred primarily through radiation, not convection. This allows for extremely uniform heating, ensuring that complex parts reach the target temperature evenly, which minimizes internal stresses and distortion.
A Step-by-Step Breakdown of the Process
While specific parameters vary by application (such as brazing, sintering, or heat treating), the fundamental operational sequence remains consistent.
Step 1: Loading and Sealing
The material or workpiece is placed inside the furnace chamber. The chamber itself is a robust, sealed vessel, often with a double wall for water cooling to protect the structure and seals from the intense internal heat.
Step 2: Evacuation (Creating the Vacuum)
This is typically a two-stage process to efficiently remove the air.
- A mechanical "roughing" pump removes the bulk of the air, bringing the pressure down significantly.
- A diffusion or turbomolecular pump then takes over to achieve the high-vacuum level required for the process, removing the remaining molecules.
Step 3: Heating
Once the target vacuum is reached, heating elements raise the temperature. The method of heating varies by furnace type:
- Resistance Heating: Graphite or refractory metal elements heat up when electricity is passed through them, radiating heat to the workpiece.
- Induction Heating: An alternating current in an induction coil generates eddy currents within the metal itself, causing it to heat from the inside out. This is common for melting metals.
Step 4: Soaking (Holding at Temperature)
The material is held at the target temperature for a predetermined amount of time. This "soaking" period allows the desired metallurgical process—such as brazing alloy flowing, atoms diffusing for hardening, or particles bonding during sintering—to complete fully.
Step 5: Cooling (Quenching)
Controlled cooling is just as critical as heating. To cool the material rapidly without exposing it to air, the furnace is backfilled with a high-purity inert gas, like argon or nitrogen.
A powerful fan circulates this gas through a heat exchanger, transferring heat away from the workpiece in a rapid and controlled manner. The material must be cooled to a safe temperature before the door is opened to prevent immediate oxidation.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, vacuum furnaces are not a universal solution. Their benefits come with specific considerations.
Higher Cost and Complexity
Vacuum systems, including pumps, seals, and advanced control instrumentation, are significantly more complex and expensive to purchase and operate than standard atmospheric furnaces.
Longer Cycle Times
The need to pump down the chamber to a deep vacuum adds considerable time to the beginning of each cycle. This can make the overall process time longer compared to conventional methods.
Rigorous Maintenance Requirements
Maintaining a perfect vacuum seal is critical. This requires diligent and proactive maintenance of door seals, pumps, valves, and feedthroughs to prevent leaks that could compromise the entire process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your specific application dictates whether the benefits of a vacuum furnace justify its complexities.
- If your primary focus is surface integrity and brightness (e.g., medical implants, aerospace parts): A vacuum furnace is essential to prevent any surface oxidation and ensure a clean finish.
- If your primary focus is joining complex assemblies without flux (e.g., turbine blades, electronics): Vacuum brazing provides a clean, strong, and precise joining method that is impossible with other techniques.
- If your primary focus is melting high-purity alloys (e.g., superalloys for jet engines): A vacuum induction furnace is the industry standard for preventing gas contamination and achieving precise chemical composition.
- If your primary focus is processing powdered materials (e.g., ceramics, tungsten carbide): Vacuum sintering is critical for achieving full density and superior material properties without introducing impurities.
By removing the atmosphere from the equation, a vacuum furnace gives you absolute control over the thermal processing environment.
Summary Table:
| Process Step | Key Action | Primary Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Loading & Sealing | Place workpiece in sealed, water-cooled chamber | Creates a controlled environment |
| 2. Evacuation | Remove air using roughing and high-vacuum pumps | Eliminates oxidation and contamination |
| 3. Heating | Heat via radiation (resistance/induction) | Ensures uniform temperature distribution |
| 4. Soaking | Hold at target temperature for set time | Completes metallurgical processes (e.g., brazing, sintering) |
| 5. Cooling | Quench with inert gas (argon/nitrogen) circulation | Rapid cooling without oxidation |
Ready to achieve superior material purity and performance in your lab?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance vacuum furnaces and lab equipment, delivering the precise, contamination-free environment essential for advanced applications like brazing, sintering, and heat treating. Our solutions ensure unmatched temperature uniformity, surface integrity, and process control for industries ranging from aerospace to medical implants.
Contact us today to discuss how a KINTEK vacuum furnace can enhance your laboratory's capabilities and meet your specific material processing goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Superior Purity and Control in Heat Treatment
- What is the maximum temperature in a vacuum furnace? It Depends on Your Materials and Process Needs
- What materials are used in a vacuum furnace? A Guide to Hot Zone Materials and Processed Metals
- What is the standard thickness of plating? Optimize Durability, Corrosion & Cost
- What are the uses of vacuum furnace? Achieve Unmatched Material Purity and Performance



















