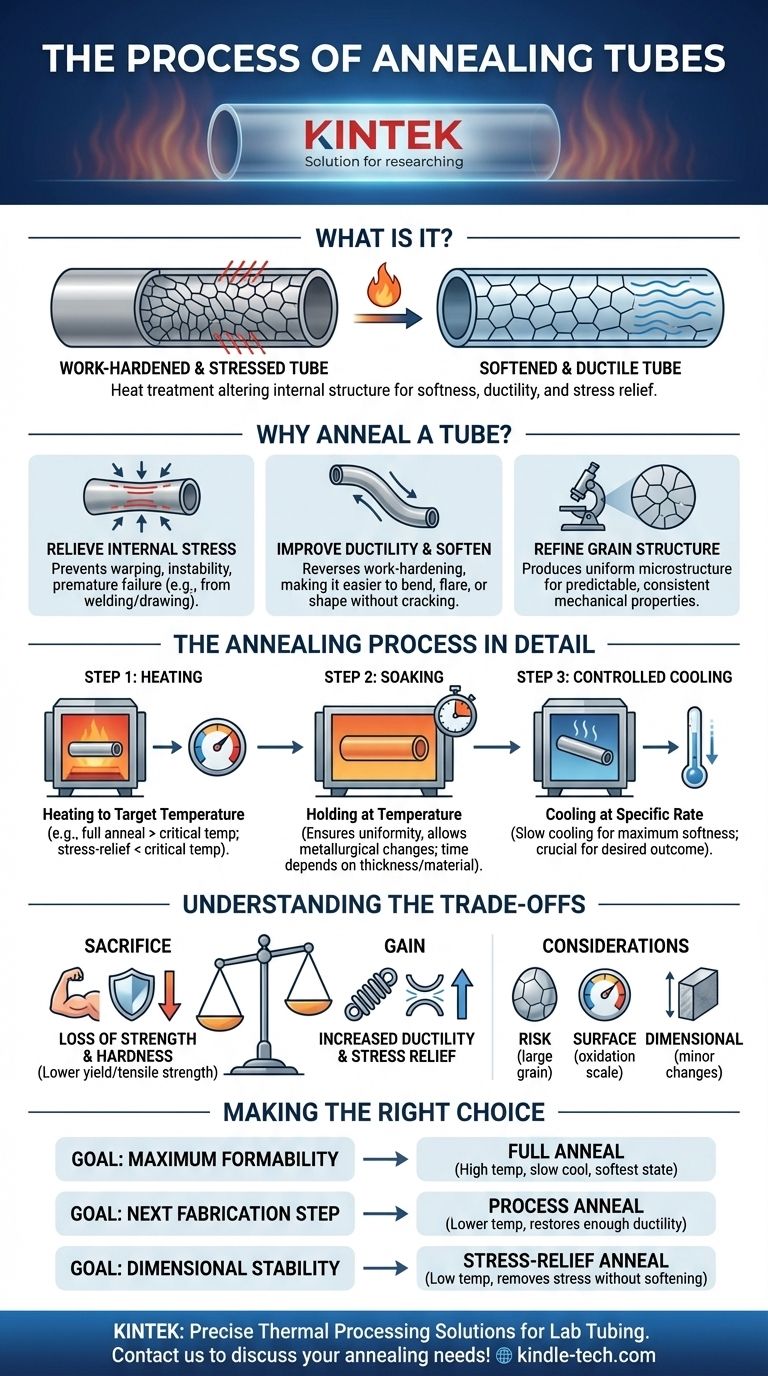
In essence, annealing is a heat treatment process that alters the internal structure of a tube to make it softer, more ductile, and easier to form. It involves heating the tube to a specific temperature, holding it there for a set duration, and then cooling it in a controlled manner. This process effectively reverses the effects of work-hardening and relieves internal stresses created during manufacturing processes like drawing or bending.
The core purpose of annealing a tube is not merely to heat and cool it, but to strategically reset its metallurgical properties. It sacrifices hardness and strength to gain crucial ductility and stress relief, enabling further fabrication or ensuring stability in its final application.

The Purpose: Why Anneal a Tube?
Annealing is performed to solve specific problems introduced during the manufacturing and fabrication of tubing. It primarily targets the material's microstructure—the internal arrangement of its crystalline grains.
To Relieve Internal Stress
Manufacturing processes like welding, drawing, or cold rolling force the metal's grains into a stressed and distorted state. This is known as internal residual stress.
These internal stresses can lead to warping, dimensional instability over time, or even premature failure through stress-corrosion cracking. Annealing provides the thermal energy for the atoms to rearrange into a more stable, lower-energy state, effectively relaxing the material like a tense muscle.
To Improve Ductility and Soften the Material
As metal is worked, it becomes harder and more brittle through a process called work-hardening or strain-hardening. While increased hardness can be desirable, it makes the material difficult to bend, flare, or shape without cracking.
Annealing reverses this effect. The heat causes new, strain-free grains to form and grow, a process called recrystallization. This new grain structure makes the material significantly softer and more ductile, allowing it to undergo severe plastic deformation.
To Refine the Grain Structure
The properties of a metal are heavily dependent on the size and shape of its grains. Inconsistent or overly large grains can lead to poor performance.
Specific annealing cycles can be designed to control grain size, producing a more uniform and refined microstructure. This leads to more predictable and consistent mechanical properties throughout the tube.
The Annealing Process in Detail
While the concept is simple (heat, soak, cool), the precise control of each variable is critical to achieving the desired outcome.
Step 1: Heating to the Target Temperature
The tube is heated in a furnace or via induction heating. The target temperature is the most critical parameter and depends entirely on the material and the desired type of annealing.
For example, a full anneal for steel requires heating above its upper critical temperature to completely transform its grain structure. A stress-relief anneal, however, uses a much lower temperature that is high enough to relieve stress but too low to cause significant microstructural change.
Step 2: Soaking (Holding at Temperature)
Once the entire tube reaches the target temperature, it is held there for a specific period. This "soaking" time ensures that the temperature is uniform throughout the tube's cross-section and allows the desired metallurgical changes (like recrystallization or stress diffusion) to complete.
Soaking time is a function of the tube's wall thickness and the material's composition. Too short a soak results in an incomplete anneal; too long can lead to undesirable grain growth.
Step 3: Controlled Cooling
After soaking, the tube is cooled. The cooling rate is just as important as the heating temperature.
For a full anneal, the goal is to produce the softest possible state, which typically requires a very slow cooling rate, often by leaving the material inside the furnace as it cools down. Faster cooling rates can produce harder, less ductile structures and are generally avoided unless a specific outcome is desired.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Annealing is not a universal solution and comes with important considerations. Misunderstanding these can lead to material that does not meet performance requirements.
Loss of Strength and Hardness
The primary trade-off is clear: you sacrifice strength and hardness for ductility. An annealed tube will have a much lower yield strength and tensile strength than its work-hardened counterpart. This must be accounted for in the engineering design.
Risk of Excessive Grain Growth
If the annealing temperature is too high or the soaking time is too long, the newly formed grains can grow excessively large. This can degrade the material's toughness and fatigue life, making it brittle, especially at low temperatures.
Surface Oxidation and Scale
Heating metal to high temperatures in the presence of oxygen will cause a layer of oxide, or "scale," to form on the surface. This can be detrimental to appearance and may need to be removed through secondary processes like pickling or abrasive blasting.
To prevent this, annealing is often performed in a controlled atmosphere furnace, using inert or reducing gases (like nitrogen, argon, or hydrogen) to displace the oxygen.
Potential for Dimensional Changes
The relief of internal stresses can cause slight changes in the tube's dimensions, including its length and straightness. For high-precision applications, this potential for movement must be anticipated and managed.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The correct annealing process is dictated entirely by your final objective.
- If your primary focus is maximum formability for severe bending or flaring: You need a full anneal that produces the softest possible material state by heating above the critical temperature and cooling very slowly.
- If your primary focus is to prepare a work-hardened tube for the next drawing or forming step: A process anneal (or "in-process anneal") at a lower temperature is sufficient to restore enough ductility to continue fabrication without causing excessive grain growth.
- If your primary focus is to ensure dimensional stability after welding or machining: A low-temperature stress-relief anneal is the correct choice, as it removes internal stresses without significantly softening the material or changing its core microstructure.
Ultimately, understanding annealing empowers you to specify not just a part, but a material condition perfectly suited for its intended function.
Summary Table:
| Purpose of Annealing | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Relieve Internal Stress | Prevents warping and premature failure |
| Improve Ductility | Enables easier bending and forming |
| Refine Grain Structure | Ensures consistent mechanical properties |
Need precise thermal processing for your lab's tubing? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, offering solutions that ensure your annealing processes are controlled and repeatable. Whether you're working with steel, copper, or other alloys, our expertise helps you achieve the perfect material properties for fabrication or stability. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's annealing needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of a tube furnace? Achieve Superior Temperature Uniformity and Control
- What temperature is alumina activated? Unlock Optimal Porosity for Adsorption
- What are the advantages of using an alumina liner in a tube furnace for biomass combustion corrosion simulations?
- What tube is used for tubular furnace? Choose the Right Material for Temperature & Atmosphere
- Why is an Alumina Ceramic Tube Support Necessary for 1100°C Experiments? Ensure Data Accuracy and Chemical Inertness



















