In essence, batch pyrolysis is a thermal decomposition process where a fixed quantity, or "batch," of material is loaded into a sealed reactor, heated in the absence of oxygen to break it down, and then cooled before the resulting products are removed. The entire process—from loading to unloading—is completed as one distinct cycle before another can begin.
The core distinction of batch pyrolysis is its non-continuous, cyclical nature. Unlike continuous systems designed for high-volume throughput, batch processing prioritizes simplicity, control over a single reaction, and lower initial investment, making it ideal for specific applications like research or small-scale operations.

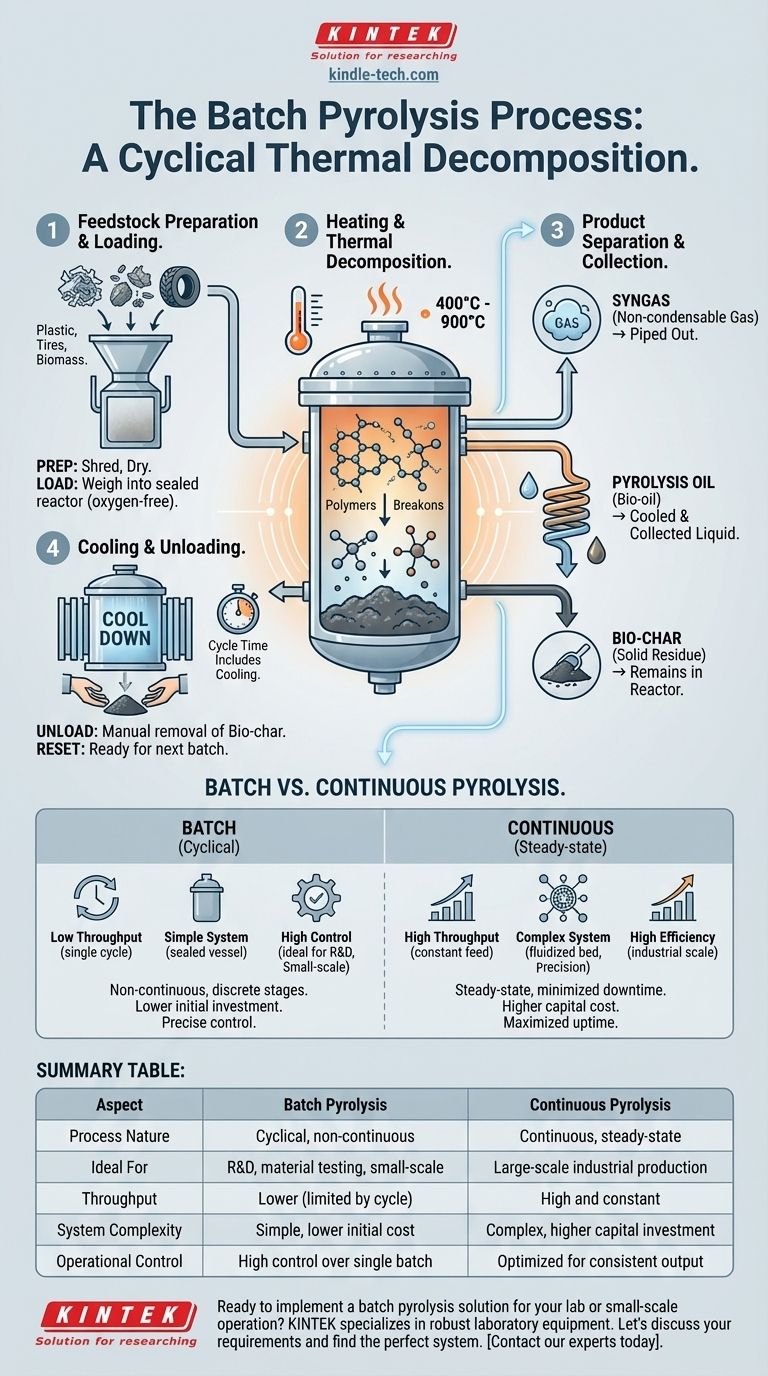
The Step-by-Step Batch Pyrolysis Process
The batch process can be understood as a sequence of discrete stages. Each stage must be completed before the next begins for that specific batch of material.
1. Feedstock Preparation and Loading
Before the process starts, the raw material (feedstock) like plastic, tires, or biomass is often pre-processed. This can involve shredding to increase surface area and drying to remove moisture.
This prepared feedstock is then weighed and loaded into the reactor vessel. Once loaded, the reactor is hermetically sealed to create an oxygen-free environment.
2. Heating and Thermal Decomposition
With the reactor sealed, heat is applied externally. The temperature is raised to a specific target, typically between 400°C and 900°C.
In this oxygen-starved, high-heat environment, the complex organic polymers in the feedstock break down (pyrolyze) into simpler, smaller molecules.
3. Product Separation and Collection
The decomposition creates three primary products:
- Syngas: A non-condensable gas mixture that is piped out of the reactor.
- Pyrolysis Oil (Bio-oil): Volatile vapors that are routed through a condensation system, where they are cooled and collected as a liquid.
- Bio-char: A solid, carbon-rich residue that remains in the reactor.
4. Cooling and Unloading
After the reaction is complete, the heating system is turned off, and the entire reactor must cool down. This is a critical safety step and represents a significant portion of the total cycle time.
Once the reactor reaches a safe temperature, it is opened, and the solid bio-char is manually removed. The system is now ready to be loaded for the next batch.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Batch vs. Continuous Systems
The decision to use a batch reactor is fundamentally a choice between simplicity and scale. This is best understood by comparing it to a continuous system, such as a fluidized-bed reactor.
Throughput and Scale
A batch system has inherently low throughput. The total output is limited by the cycle time, which includes loading, heating, cooling, and unloading.
A continuous system is designed for industrial-scale production. Feedstock is constantly fed into the reactor and products are continuously removed, eliminating downtime between cycles.
Operational Efficiency
Batch processes are less efficient for large-scale operations due to the significant non-productive time spent cooling and reloading the reactor.
Continuous reactors maintain a steady operational state, maximizing uptime and energy efficiency once at temperature.
System Complexity and Cost
Batch reactors are mechanically simple, often consisting of little more than a sealed, heated vessel. This results in lower initial capital investment and easier maintenance.
Continuous systems, like a fluidized-bed reactor, are far more complex. They require sophisticated mechanisms for continuous feeding, ash removal, and precise temperature management using agents like fluidized sand and inert gases.
Process Control and Application
The isolated nature of a batch process provides excellent control over a single reaction. This makes it ideal for research, material testing, and investigating the energy stability of different feedstocks.
Continuous systems are built for consistent, high-volume production of a standardized product, not for frequent experimentation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The optimal pyrolysis approach is dictated entirely by your operational scale, feedstock, and ultimate objective.
- If your primary focus is research and development: A batch reactor is the superior choice for its precise control over reaction conditions and its suitability for testing small, varied samples.
- If your primary focus is small-scale waste conversion: A batch system provides a lower-cost, simpler, and more manageable entry point for processing specific waste streams locally.
- If your primary focus is large-scale industrial production: A continuous reactor is essential to achieve the high throughput, efficiency, and economy of scale required for a commercial operation.
Ultimately, choosing the right method comes down to understanding the fundamental trade-off between the cyclical simplicity of a batch system and the high-volume efficiency of a continuous one.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Batch Pyrolysis | Continuous Pyrolysis |
|---|---|---|
| Process Nature | Cyclical, non-continuous | Continuous, steady-state |
| Ideal For | R&D, material testing, small-scale operations | Large-scale industrial production |
| Throughput | Lower (limited by cycle time) | High and constant |
| System Complexity | Simple, lower initial cost | Complex, higher capital investment |
| Operational Control | High control over single batch | Optimized for consistent output |
Ready to implement a batch pyrolysis solution for your lab or small-scale operation?
KINTEK specializes in providing robust and reliable laboratory equipment, including pyrolysis systems tailored for research and development. Our batch reactors offer the precise control and simplicity you need to effectively test feedstocks, optimize processes, and convert waste into valuable products like bio-oil and bio-char.
Let's discuss your specific requirements and find the perfect system for your needs.
Contact our experts today to learn more about our pyrolysis solutions and how they can enhance your work.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the conditions for biomass pyrolysis? Optimize Temperature, Heating Rate & Time
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis technology? Turn Waste into Profit and Reduce Emissions
- What are the reactions involved in pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock the Chemistry for Tailored Bio-Products
- What are the different types of pyrolysis machines? Choose the Right System for Your Output
- What are the components of biomass pyrolysis? A Complete Guide to the System, Products, and Process



















