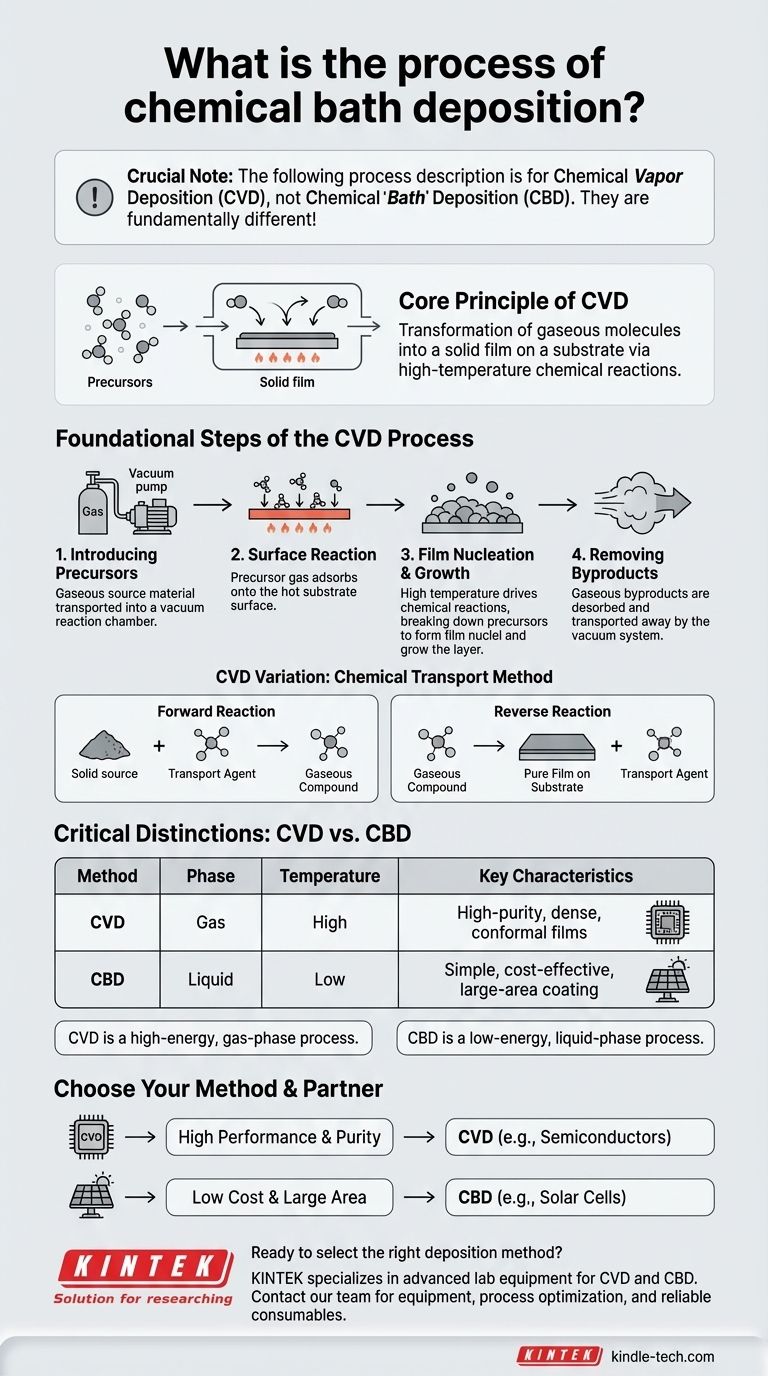
It is crucial to note that the process described in the provided materials is Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), not Chemical Bath Deposition (CBD). While both are methods for creating thin films, their principles are fundamentally different. CVD involves depositing a material from a gas or vapor phase onto a substrate, whereas CBD involves precipitating a material from a liquid chemical solution.
The core principle of Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is the transformation of gaseous molecules, known as precursors, into a solid film on the surface of a substrate through high-temperature chemical reactions.
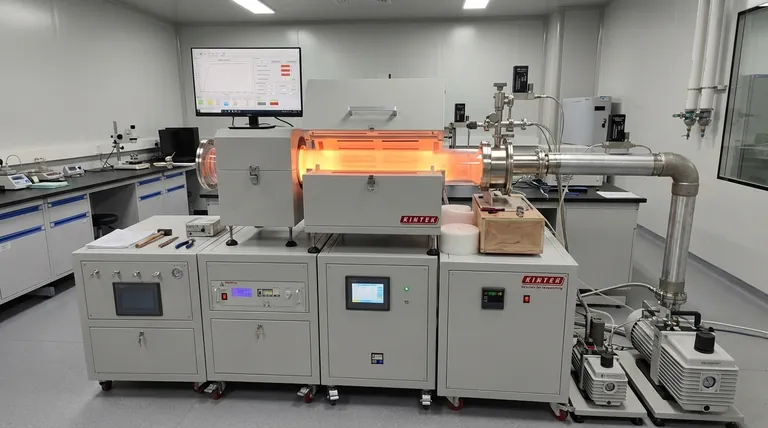

The Foundational Steps of the CVD Process
The CVD process can be understood as a carefully controlled sequence where gas is transported to a surface, reacts, and forms a solid layer. This is not a single action but a series of interconnected physical and chemical events.
Step 1: Introducing the Precursors
The process begins with the source material for the coating, which must be in a gaseous state. This is often achieved by evaporating a volatile liquid or solid compound.
This gaseous precursor is then transported into a controlled environment, typically a reaction chamber that has been vacuumed. The vacuum helps ensure purity and facilitates the transport of the reactive gas molecules.
Step 2: The Surface Reaction
The part to be coated, known as the substrate, is placed inside the chamber and heated. The gaseous precursor is then introduced.
When the reactive gas species reach the hot substrate surface, a series of events is triggered. The gas molecules are first adsorbed, meaning they physically stick to the surface.
Step 3: Film Nucleation and Growth
Once adsorbed, the high temperature of the substrate provides the energy for heterogeneous chemical reactions to occur directly on the surface. These reactions break down the precursor molecules.
The nonvolatile products of this reaction form stable nuclei on the surface, which act as seeds for the film to grow. The atoms diffuse across the surface to find these growth sites, gradually building up the desired thin film layer by layer.
Step 4: Removing Byproducts
The chemical reactions that form the solid film also produce gaseous byproducts. These waste products are desorbed (released) from the substrate surface.
Finally, the vacuum or gas flow system transports these byproducts away from the substrate, leaving behind only the pure, solid coating.
A Key Variation: The Chemical Transport Method
One specific method of CVD is known as the chemical transport method. This technique is unique in how it moves the source material.
Forward and Reverse Reactions
In this method, the solid source material reacts with a transport agent in one area to form a new gaseous compound. This is the "forward reaction."
This gas is then transported to the growth area, where a change in temperature causes the opposite reaction to occur. This "reverse reaction" breaks down the gas, redepositing the original source material as a pure film onto the substrate.
Critical Distinctions and Considerations
Understanding the context of CVD is key to appreciating its applications. The primary distinction is its reliance on a gas phase, which has significant implications compared to liquid-phase methods like Chemical Bath Deposition.
The Nature of CVD
CVD is fundamentally a high-energy, gas-phase process. The use of high temperatures and vacuum chambers allows for the creation of very high-purity, dense, and uniform coatings that can conform to complex shapes. However, these requirements also make the equipment complex and costly.
Contrast with Chemical Bath Deposition (CBD)
Chemical Bath Deposition (CBD), the topic of the original query, is fundamentally different. It is a low-energy, liquid-phase process.
In CBD, a substrate is simply immersed in a chemical solution (a "bath") at a relatively low temperature. Controlled chemical reactions within the solution cause the desired material to slowly precipitate and form a solid film on the substrate. It is often simpler and cheaper but may offer less control over film density and purity compared to CVD.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
Choosing a deposition method requires a clear understanding of your project's technical and budgetary constraints.
- If your primary focus is high performance and purity: CVD is the superior choice for creating dense, durable, and highly conformal films required in applications like semiconductors and advanced tooling.
- If your primary focus is low cost and large-area deposition at low temperatures: A liquid-based process like Chemical Bath Deposition (CBD) would be a more suitable method to investigate for applications like solar cells or certain sensors.
Ultimately, your choice depends on whether your material and substrate can withstand the high temperatures of a gas-phase reaction or are better suited to a gentle, liquid-phase precipitation.
Summary Table:
| Deposition Method | Phase | Temperature | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) | Gas | High | High-purity, dense, conformal films |
| Chemical Bath Deposition (CBD) | Liquid | Low | Simple, cost-effective, large-area coating |
Ready to select the right deposition method for your project?
KINTEK specializes in providing advanced lab equipment and consumables for all your thin film deposition needs. Whether you require the high-performance capabilities of a CVD system or are exploring simpler CBD setups, our experts can help you:
- Choose the right equipment for your specific application and budget
- Optimize your process parameters for superior film quality
- Access reliable consumables to ensure consistent results
Let us help you achieve precise, high-quality thin films. Contact our team today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Lab and Diamond Growth
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Oxygen-Free Copper Crucible and Evaporation Boat
People Also Ask
- What color diamonds are CVD? Understanding the Process from Brown Tint to Colorless Beauty
- What is the process of vacuum vapor deposition? Mastering CVD and PVD Thin-Film Coating
- How are thin films deposited? A Guide to PVD vs. CVD Methods for Your Application
- What are the methods of deposition? A Guide to PVD and CVD Thin-Film Techniques
- What is PECVD in semiconductor? Enable Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition for ICs

















