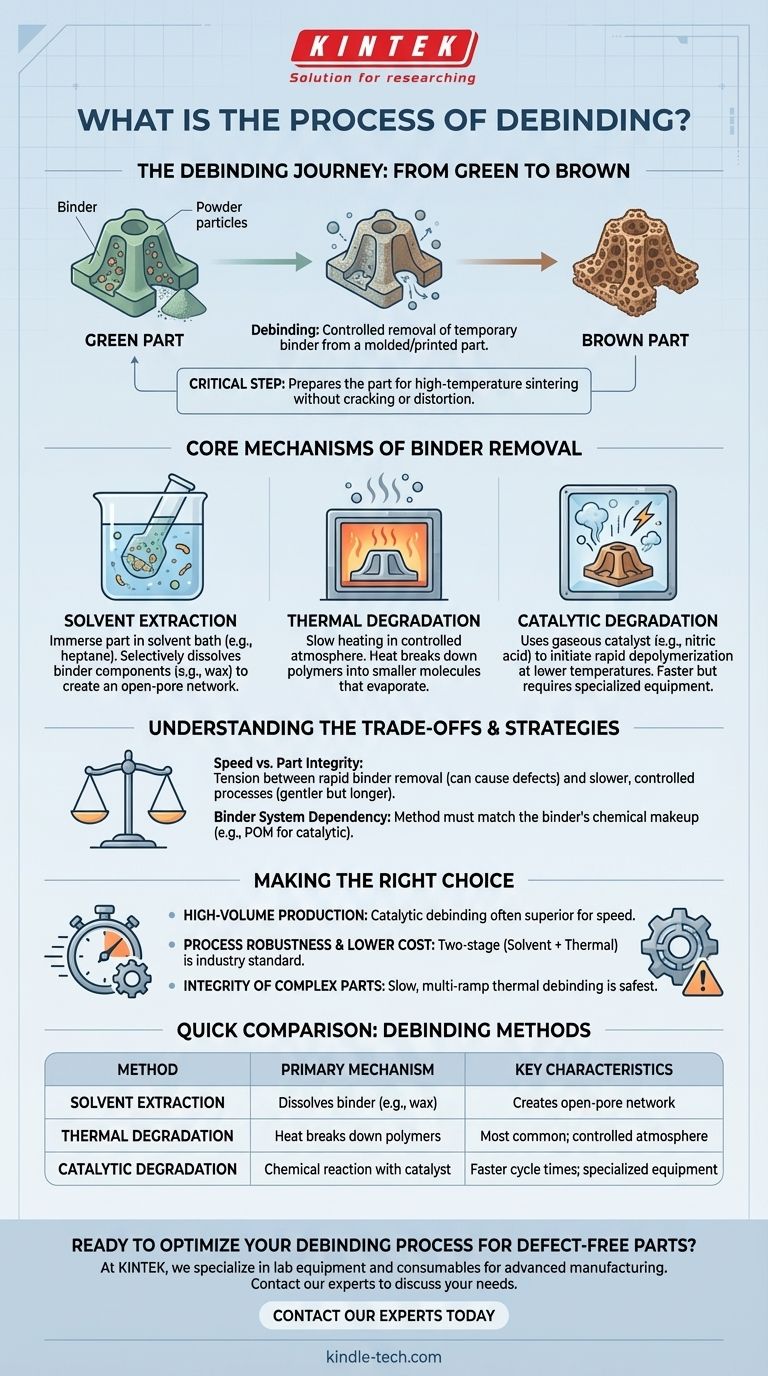
In essence, debinding is the critical manufacturing step where a temporary "binder" material is removed from a molded or printed part. This process prepares the fragile "green" part for its final, high-temperature sintering phase, where the material's particles fuse together. The binder is systematically broken down and extracted, typically through chemical reaction, thermal degradation, or solvent dissolution.
Debinding is not a single action but a carefully controlled process designed to remove the binder scaffolding without introducing stress, cracks, or distortion to the part. The success of this intermediate step is fundamental to the structural integrity of the final product.

Why Debinding is a Critical Step
Before a part can be densified into its final, solid form, the temporary material holding its shape must be completely removed. This intermediate part, full of binder, is often called a "green part."
The Role of the Binder
The binder is a mixture, often of waxes and polymers, that acts as a carrier for metal or ceramic powders. It provides the necessary flow for injection molding or the structural integrity for 3D printing, allowing complex shapes to be formed and handled.
From "Green" to "Brown" Part
Removing the binder transforms the "green part" into a porous, fragile structure known as a "brown part." This step is non-negotiable. If the binder were left in, it would combust uncontrollably during the high-temperature sintering stage, releasing gases that would crack, blister, or warp the final component.
The Core Mechanisms of Binder Removal
Debinding is not one-size-fits-all; the method is chosen based on the binder system, part geometry, and production requirements. The process often combines multiple stages.
Solvent Extraction
In many systems, the first stage involves immersing the green part in a solvent bath (like heptane or a specialized fluid). The solvent selectively dissolves some components of the binder, such as wax, creating an open-pore network throughout the part. This network allows the remaining binder to be removed more easily in subsequent stages.
Thermal Degradation
Thermal debinding is the most common method, where the part is slowly heated in a controlled atmosphere furnace. The heat breaks down the long polymer chains of the binder into smaller, lighter molecules. These smaller molecules then evaporate and are carried away by the furnace atmosphere, leaving behind only the powder structure.
Catalytic Degradation
As noted in some processes, catalytic debinding uses a gaseous catalyst, such as nitric acid vapor, to accelerate the breakdown of the binder. The catalyst initiates a chemical reaction that rapidly depolymerizes the binder at much lower temperatures than thermal debinding alone. This significantly reduces cycle times but requires specialized equipment.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a debinding strategy involves balancing speed, cost, and the risk of part defects. This is a process of careful engineering.
Speed vs. Part Integrity
The primary tension is between process speed and safety. Removing the binder too quickly can cause the gaseous byproducts to build up pressure inside the part, leading to cracks, swelling, or slumping. A slower, more controlled process is gentler but increases manufacturing time and cost.
Binder System Dependency
There is no universal debinding method. The technique is entirely dependent on the chemical makeup of the binder system used to create the green part. A binder designed for catalytic debinding (like one based on polyoxymethylene, or POM) will not respond properly to a solvent-first process, and vice versa.
Equipment and Safety
Each method carries unique requirements. Solvent debinding involves handling and disposing of volatile organic compounds (VOCs). Catalytic debinding requires furnaces capable of handling highly corrosive acids. Thermal debinding, while simpler, can be the most time-consuming.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your debinding strategy should be directly aligned with your production goals and the materials you are using.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, rapid production: Catalytic debinding is often the superior choice for its speed, assuming the higher initial equipment investment is viable.
- If your primary focus is process robustness and lower capital cost: A two-stage process combining solvent extraction with subsequent thermal debinding is a proven and widely used industry standard.
- If your primary focus is the integrity of large or complex parts: A slow, multi-ramp thermal debinding cycle is the safest method to minimize internal stresses and prevent defects.
Ultimately, a successful debinding cycle is the invisible foundation upon which a defect-free, high-density final part is built.
Summary Table:
| Debinding Method | Primary Mechanism | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Solvent Extraction | Dissolves binder components (e.g., wax) | Creates open-pore network for subsequent stages |
| Thermal Degradation | Heat breaks down polymers into gases | Most common method; requires controlled atmosphere furnace |
| Catalytic Degradation | Chemical reaction with a gaseous catalyst | Faster cycle times; requires specialized equipment |
Ready to optimize your debinding process for defect-free parts?
At KINTEK, we specialize in lab equipment and consumables for advanced manufacturing. Our expertise helps you select the right debinding strategy—whether for high-volume production with catalytic methods or robust thermal processes—ensuring your metal or ceramic parts achieve maximum structural integrity.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific needs and discover how KINTEK solutions can enhance your laboratory's efficiency and success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How do tube furnaces or muffle furnaces ensure stoichiometric accuracy during synthesis? Mastering Li4GeO4 & Li4VO4
- What is a rotary heat type furnace? The Ultimate Guide to Uniform Heating & Mixing
- What is the temperature of a rotary hearth furnace? Find the Right Heat for Your Process
- Why is a high-temperature furnace with multi-probe testing used for ABO3 perovskite? Get Precise Conductivity Data
- How are tube furnaces classified based on the orientation of the tube? Choose the Right Design for Your Process



















