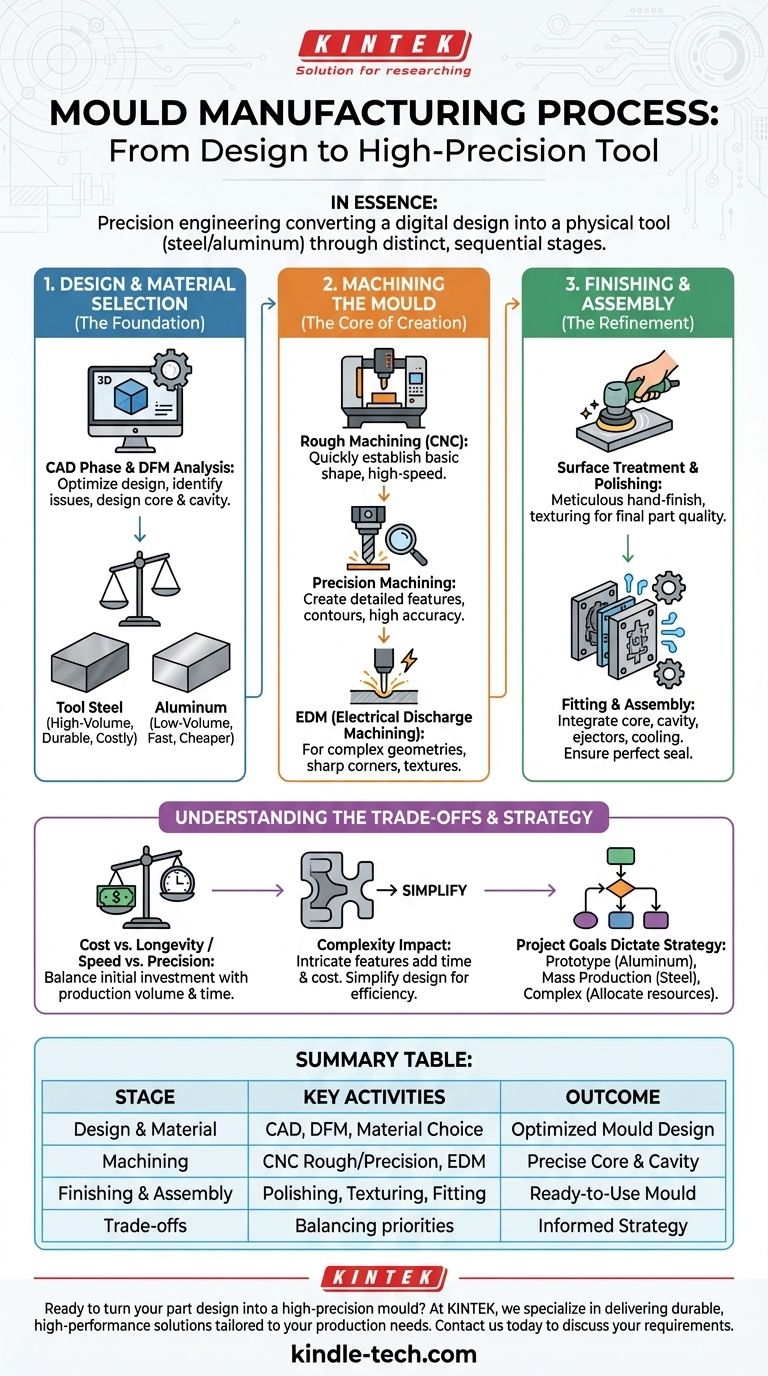
In essence, manufacturing a mould is a precision engineering process that translates a digital part design into a physical tool, typically from steel or aluminum. It involves several distinct stages, beginning with computer-aided design (CAD), followed by precise machining of the mould’s core and cavity, and concluding with meticulous finishing, polishing, and assembly to ensure the final plastic parts meet exact specifications.
The quality, cost, and speed of your final production run are determined long before the first part is moulded. Understanding the mould manufacturing process is not just a technical curiosity; it is the key to making strategic decisions about your product's design and budget.
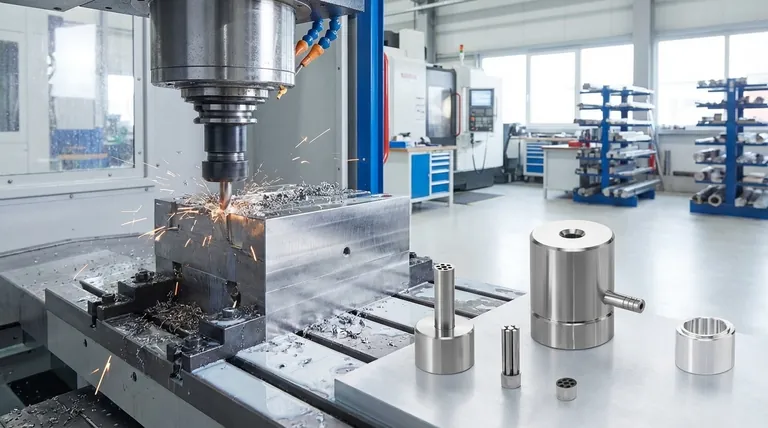

The Foundation: Design and Material Selection
The mould-making process begins on a computer, not on the factory floor. This initial digital phase is arguably the most critical, as decisions made here have cascading effects on the entire project.
From Part to Mould: The CAD Phase
First, a 3D model of the final part is analyzed for Design for Manufacturability (DFM). This analysis identifies potential issues like sharp internal corners, insufficient draft angles for part ejection, or walls that are too thin.
Once the part design is optimized, engineers design the mould itself. This involves creating the two primary halves—the core (the "male" side) and the cavity (the "female" side)—which will form the shape of the part. This design also includes crucial subsystems like the runner system that delivers plastic and the cooling channels that control temperature.
Choosing the Right Metal: Steel vs. Aluminum
The choice of material for the mould is a fundamental decision based on production volume and budget.
Tool steel is the standard for high-volume production. It is extremely durable and resistant to the high pressures and temperatures of injection moulding, capable of producing millions of parts. However, it is harder and more time-consuming to machine, making it more expensive upfront.
Aluminum is often used for prototyping and low-volume production runs. It is softer and much faster to machine, significantly reducing the initial cost and lead time of the mould. Its lower durability means it can only produce thousands, not millions, of parts.
The Core of Creation: Machining the Mould
With the design complete and material selected, the raw block of metal is transformed into a precision tool. This is a subtractive process, where material is carefully removed to create the final shape.
Rough Machining: Shaping the Block
The process starts with Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machining. A large CNC mill cuts away large volumes of metal from the block, quickly establishing the basic shape of the mould's core and cavity. This is a high-speed but lower-precision step focused on bulk material removal.
Precision Machining: Creating the Details
Following the rough cut, the mould undergoes finer, higher-precision CNC machining. Using smaller cutting tools and slower speeds, the machine creates the detailed features, contours, and final dimensions of the part's geometry with exceptional accuracy.
Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM): For Complex Geometries
For features that are impossible to create with a traditional cutting tool—such as sharp internal corners, deep and narrow ribs, or complex textures—Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM) is used. This process uses a precisely shaped electrode and electrical sparks to erode the metal, achieving intricate shapes that milling cannot.
Refinement and Assembly: The Finishing Touches
A machined mould is not yet ready for production. It requires careful hand-finishing and assembly to function correctly.
Surface Treatment and Polishing
The mould surfaces that form the part are meticulously polished by hand or with specialized equipment. The level of polish—from a matte finish to a mirror-like shine—directly translates to the surface finish of the final plastic part. Textures can also be etched onto the surface at this stage.
Fitting and Assembly
Finally, all the components of the mould are assembled: the core, the cavity, ejector pins (which push the part out), slides (for features like undercuts), and the cooling system. The two halves are carefully fitted together to ensure a perfect seal, preventing plastic from leaking out (a defect known as "flash"). The assembled mould is then tested to confirm its readiness for production.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a mould-making strategy involves balancing competing priorities. An informed decision requires understanding these compromises.
Cost vs. Longevity
An aluminum mould offers a low initial investment and fast turnaround, but it will wear out relatively quickly. A hardened steel mould costs significantly more and takes longer to make but represents a lower cost-per-part over a high-volume production run.
Speed vs. Precision
Rushing the DFM analysis or the machining process to save time often leads to a flawed mould. This can result in defective parts, costly mould rework, and significant production delays, negating any initial time savings.
The Impact of Complexity
Every complex feature in your part design—such as undercuts requiring slides, fine textures requiring EDM, or extremely tight tolerances—adds significant time and cost to the mould manufacturing process. Simplifying a design is the most effective way to reduce mould cost.
Making the Right Choice for Your Project
Your project goals should dictate your mould manufacturing strategy. Use these guidelines to align your approach with your needs.
- If your primary focus is rapid prototyping or low-volume production: Opt for an aluminum mould to minimize upfront cost and lead time.
- If your primary focus is mass production (100,000+ units): Invest in a hardened P20 or H13 steel mould for maximum durability and long-term cost-effectiveness.
- If your part has complex geometries or textures: Allocate extra budget and time for advanced processes like EDM and prioritize a thorough Design for Manufacturability review early on.
By viewing the mould not as a simple tool but as a long-term manufacturing asset, you can make smarter decisions that ensure a successful product launch.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Key Activities | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Design & Material Selection | CAD, DFM analysis, steel vs. aluminum choice | Optimized mould design for production volume |
| Machining | CNC roughing, precision machining, EDM for complex features | Precise core and cavity shapes |
| Finishing & Assembly | Polishing, texturing, fitting of ejector pins and cooling system | Ready-to-use mould for injection molding |
| Trade-offs | Cost vs. longevity, speed vs. precision, complexity impact | Informed strategy for project success |
Ready to turn your part design into a high-precision mould?
At KINTEK, we specialize in delivering durable, high-performance lab equipment and consumables tailored to your production needs. Whether you require a rapid-prototype aluminium mould or a high-volume steel mould for mass production, our expertise ensures your project is built for efficiency, accuracy, and long-term value.
Contact us today to discuss your mould manufacturing requirements and let KINTEK help you bring your product to life with precision and reliability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Special Shape Press Mold for Lab
- Polygon Press Mold for Lab
- Multi-Punch Rotary Tablet Press Mold Ring for Rotating Oval and Square Molds
- Special Heat Press Mold for Lab Use
- Assemble Lab Cylindrical Press Mold
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using high-strength graphite molds in the hot press sintering of Ti6Al4V-based composites?
- Why are custom pressure molds used during the hot pressing process for solid polymer electrolytes?
- What role do customized metal molds play in solid-state battery densification? Achieving Precision at 500 MPa
- How does a stainless steel pressure die ensure the quality of the electrolyte layer? Unlock Precision Battery Assembly
- What functions do high-purity graphite molds serve for IZO targets? Ensure Density and Prevent Sintering Cracks



















