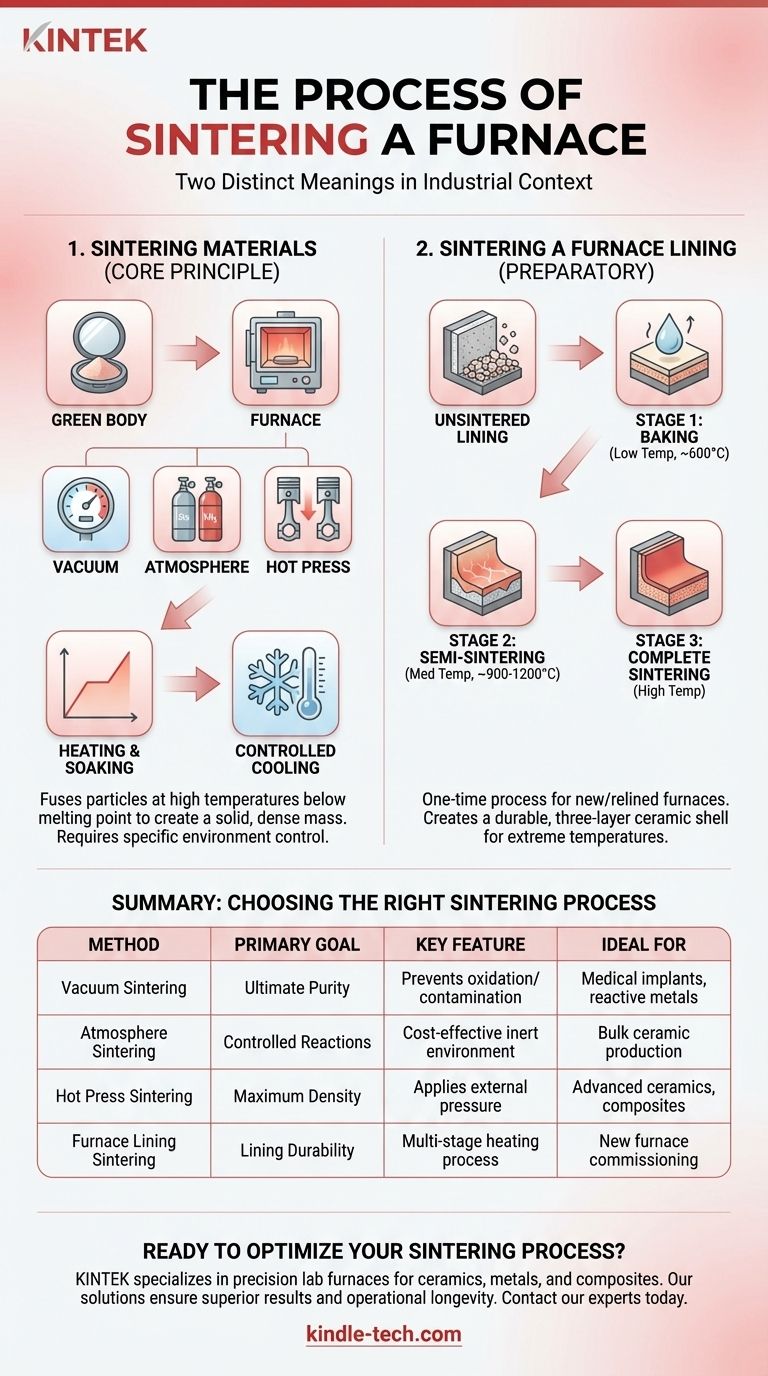
The process of "sintering a furnace" can mean two distinct things. It can refer to the process of using a furnace to sinter materials like ceramics or metal powders, or it can refer to the one-time process of preparing the refractory lining of a new furnace for use. Both involve using controlled high heat to compact and solidify a material without melting it completely.
Sintering is a high-temperature process that fuses material particles into a solid, dense mass. The specific method depends entirely on the goal: processing a component within the furnace requires controlling a vacuum, atmosphere, or pressure, while preparing the furnace itself involves a careful, multi-stage heating process to cure its protective lining.

The Two Meanings of Sintering
Before detailing the steps, it's critical to distinguish between the two primary applications of sintering in an industrial context. Your objective determines the entire process.
Sintering Materials: The Core Principle
This is the most common meaning. The goal is to take a powdery or loosely formed material and transform it into a solid, dense object.
At high temperatures, well below the material's melting point, atoms in the particles diffuse across their boundaries. This atomic migration effectively fuses the particles together, eliminating the pores between them and causing the entire mass to shrink and densify.
Sintering a Furnace Lining: Creating the Protective Shell
This is a preparatory process performed when commissioning a new induction furnace or relining an old one.
The furnace's interior is lined with a refractory material (like sand or alumina) that must be solidified into a hard, ceramic-like shell. This initial sintering creates a durable, non-reactive crucible capable of withstanding extreme temperatures during future operations.
The Process of Sintering Materials in a Furnace
When using a furnace to process a component, the process generally follows four key stages. The most critical factor is the type of environment created inside the furnace.
Step 1: Material Loading
The material, typically a compacted powder known as a "green body," is placed inside the sintering chamber. Proper placement is essential to ensure uniform heating.
Step 2: Environment Control
This is the defining step of the process. The air is removed and replaced with a specific environment to prevent contamination and control chemical reactions.
- Vacuum Sintering: The chamber is evacuated to a high vacuum. This prevents oxidation and removes trapped gases, which is crucial for reactive metals or high-purity ceramics.
- Atmosphere Sintering: The chamber is filled with a controlled gas, such as nitrogen or argon. This creates an inert environment that is often more cost-effective than a deep vacuum.
- Hot Press Sintering: In addition to heat and a vacuum, a high mechanical pressure is applied to the material. This physically forces the particles together, achieving maximum density.
Step 3: Heating and Soaking
The furnace temperature is ramped up according to a precise schedule. It is then held at the target sintering temperature for a set period, known as "soaking." This allows time for the atomic diffusion process to complete.
Step 4: Controlled Cooling
The component is cooled down slowly and carefully. Rapid cooling can induce thermal shock and create cracks or internal stresses, compromising the final product's integrity.
The Special Case: Sintering a Furnace Lining
Preparing the furnace lining is a distinct, one-time procedure with a clear goal: to create a durable, three-layer structure. This consists of a fully sintered inner layer, a semi-sintered middle layer, and an unsintered powder layer against the furnace wall for insulation.
Stage 1: The Baking Stage (Low Temperature)
The furnace is heated slowly to around 600°C and held at that temperature. The sole purpose of this stage is to drive out any residual moisture from the refractory material, preventing steam pressure from cracking the lining later.
Stage 2: The Semi-Sintering Stage (Medium Temperature)
The temperature is increased to approximately 900°C, held, and then raised again to about 1200°C. This begins the fusion process, solidifying the innermost layers of the lining without fully hardening the entire depth.
Stage 3: The Complete Sintering Stage (High Temperature)
Finally, the temperature is raised to the material's full sintering temperature. This completely vitrifies the inner surface that will be in contact with molten metal, creating a hard, non-reactive crucible. The quality of this final stage directly dictates the service life of the furnace lining.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The choice of sintering environment for processing materials is a trade-off between purity, density, and cost. Each method is suited for different outcomes.
Vacuum Sintering: For Ultimate Purity
This is the ideal choice when preventing any form of oxidation or contamination is the top priority. It is essential for materials that react readily with oxygen or nitrogen, even at trace levels.
Atmosphere Sintering: For Controlled Reactions
This method provides excellent protection from oxidation at a lower operational cost than a high-vacuum system. It allows for the use of specific gases that can interact beneficially with the material being processed.
Hot Press Sintering: For Maximum Density
For extremely hard-to-sinter materials or when achieving near-total density is a requirement, applying external pressure is the only solution. This process is more complex and uses more expensive equipment but delivers superior mechanical properties.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your application dictates the correct sintering process.
- If your primary focus is commissioning a new furnace: The multi-stage lining sintering process is a mandatory first step to ensure operational safety and longevity.
- If your primary focus is producing high-purity medical implants or reactive metal parts: Vacuum sintering is the industry standard to prevent contamination.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest possible material strength and density: Hot press sintering is necessary for advanced ceramics and composites.
- If your primary focus is the bulk production of standard ceramic components: Atmosphere sintering offers a reliable and cost-effective method for creating a controlled environment.
Ultimately, selecting and executing the correct sintering process is fundamental to achieving the desired physical properties and performance of your final material.
Summary Table:
| Sintering Method | Primary Goal | Key Feature | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vacuum Sintering | Ultimate Purity | Prevents oxidation/contamination | Medical implants, reactive metals |
| Atmosphere Sintering | Controlled Reactions | Cost-effective inert environment | Bulk ceramic production |
| Hot Press Sintering | Maximum Density | Applies external pressure | Advanced ceramics, composites |
| Furnace Lining Sintering | Lining Durability | Multi-stage heating process | New furnace commissioning |
Ready to optimize your sintering process? KINTEK specializes in precision lab furnaces and equipment for sintering ceramics, metals, and composites. Whether you need a vacuum furnace for high-purity applications or a robust system for furnace lining preparation, our solutions ensure superior results and operational longevity. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific sintering requirements and discover how KINTEK can enhance your laboratory's capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
People Also Ask
- What is partial pressure in vacuum heat treatment? Prevent Alloy Depletion & Ensure Metallurgical Control
- What is the hottest temperature in the industrial furnace? Find the Right Heat for Your Process
- Why is my brazing rod not sticking to copper? Master the 3 pillars for perfect brazing joints
- What is the difference between induction brazing and furnace brazing? Choose the Right Method for Your Production
- What are the different methods of annealing? Choose the Right Heat Treatment for Your Material's Needs
- What is the process of quenching? A Guide to Controlled Metal Hardening
- What role does a vacuum diffusion welding furnace play in the fabrication of multi-layer titanium alloy laminates?
- What is vacuum hardness? Unlock Superior Material Performance with Vacuum Processing



















