In essence, vacuum carburizing is a case-hardening process that uses a sub-atmospheric pressure environment to introduce carbon into the surface of steel. The component is heated in a vacuum furnace, a hydrocarbon gas like propane is introduced, and the heat causes the gas to break down, allowing carbon atoms to diffuse into the steel's surface. This is followed by a rapid cooling (quenching) phase that locks the carbon in place, creating an extremely hard and wear-resistant outer layer.
The core advantage of vacuum carburizing is not simply hardening steel, but doing so with unparalleled precision. By removing atmospheric interference, the process provides superior control over case depth and uniformity, especially on complex parts, resulting in higher-quality components with fewer defects.

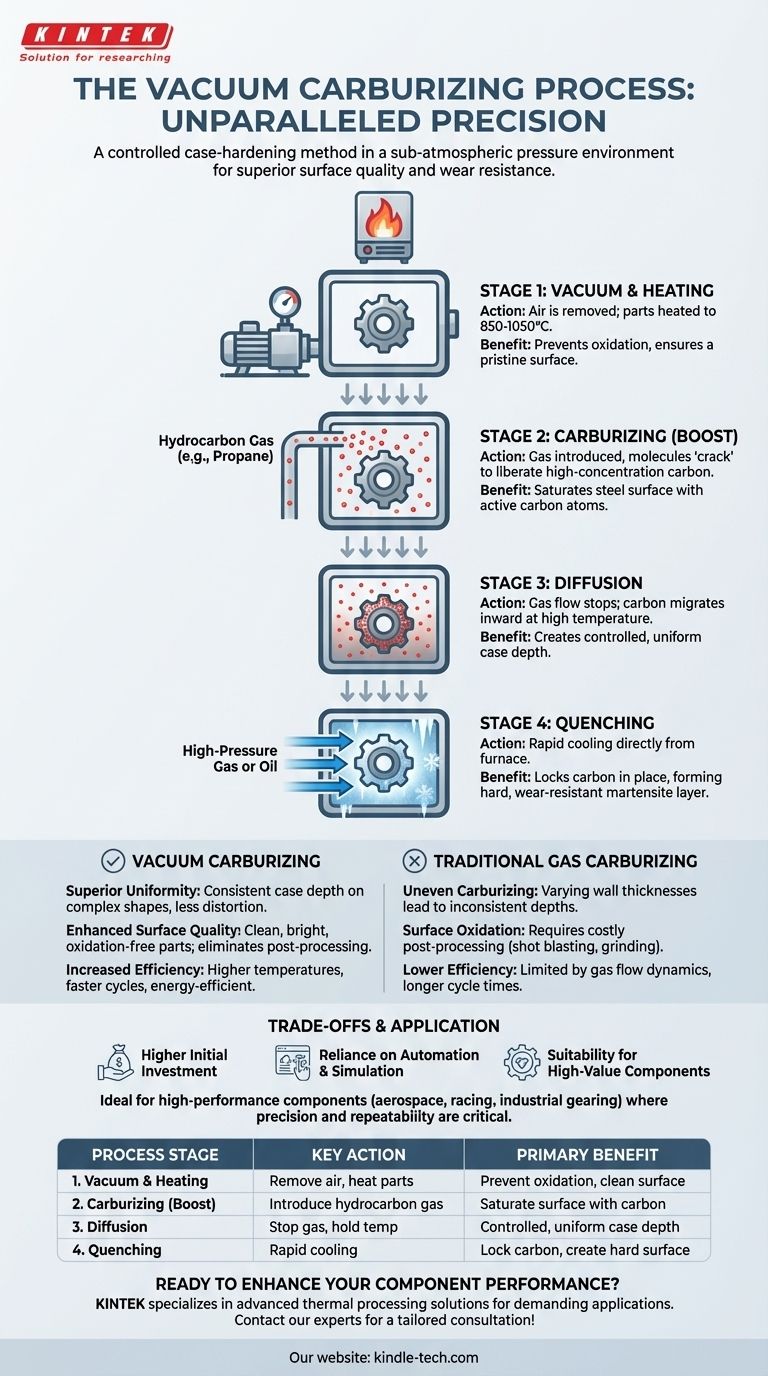
How Vacuum Carburizing Works: A Step-by-Step Analysis
The process is a carefully controlled sequence of distinct thermal and chemical stages, each serving a critical function. It is best understood as a "boost and diffuse" method performed in a pristine environment.
Stage 1: The Vacuum and Heating Cycle
First, the steel components are loaded into a sealed furnace, and the air is pumped out to create a vacuum.
This vacuum is critical because it removes oxygen and other atmospheric contaminants. This prevents surface oxidation and ensures that the carbon introduction in the next stage is pure and uninhibited. The parts are then heated to a specific carburizing temperature, typically between 850°C and 1050°C.
Stage 2: The Carburizing (Boost) Cycle
Once at temperature, a precise amount of a hydrocarbon gas, most commonly propane (C3H8), is introduced into the furnace.
The high heat causes these gas molecules to break down, or "crack," liberating a high concentration of active carbon atoms directly onto the steel's surface. This is the "boost" phase, where the surface rapidly becomes saturated with carbon.
Stage 3: The Diffusion Cycle
After a predetermined time, the flow of hydrocarbon gas is stopped. The parts are held at the high temperature in the vacuum.
During this "diffusion" phase, no new carbon is added. Instead, the high concentration of carbon at the surface naturally migrates deeper into the material, creating the desired case depth. Alternating between boost and diffuse cycles allows for extremely precise control over the final carbon profile.
Stage 4: Quenching for Hardness
The carburizing process itself only adds carbon; it does not make the part hard. The final hardness is achieved by quenching.
Directly from the furnace, the component is rapidly cooled, typically using high-pressure gas (like nitrogen) or by transferring it to an oil bath. This rapid cooling locks the carbon atoms into the steel's crystalline structure, transforming the surface into a hard, wear-resistant layer known as martensite.
Why Choose Vacuum Over Traditional Gas Carburizing?
While traditional atmosphere-based gas carburizing is effective, vacuum carburizing offers distinct metallurgical and operational advantages for demanding applications.
Superior Uniformity and Precision
The primary benefit is the elimination of uneven carburizing on parts with complex shapes or varying thicknesses.
In traditional gas carburizing, differing wall thicknesses can lead to inconsistent case depths. Vacuum carburizing heats the part uniformly, and the carbon availability is not limited by gas flow dynamics, ensuring a consistent carburized layer across all surfaces.
For example, a large bevel gear processed via vacuum carburizing can achieve a uniform case depth in half the time it would take with gas carburizing, with significantly less distortion.
Enhanced Surface Quality
Parts that undergo vacuum carburizing emerge from the furnace with a clean, bright, metallic luster.
Because the process occurs in the absence of oxygen, there is no surface oxidation or "scale" to remove. This often eliminates the need for costly and time-consuming post-processing steps like shot blasting or grinding.
Increased Efficiency and Process Speed
Vacuum furnaces can often operate at higher temperatures than traditional atmosphere furnaces.
This, combined with more efficient carbon transfer, can significantly reduce total cycle times. Furthermore, the furnaces only consume significant energy during the heating and processing cycles, making them more energy-efficient.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Despite its benefits, vacuum carburizing is not a universal solution. It involves specific considerations that make it ideal for some applications but less suitable for others.
Higher Initial Investment
Vacuum furnace technology is inherently more complex and expensive than traditional atmosphere furnace setups. The initial capital outlay for equipment is a significant factor.
Reliance on Automation and Simulation
The process relies heavily on precise computer control to manage vacuum levels, gas flow, and temperature cycles. Achieving optimal results requires sophisticated process modeling and simulation, demanding a higher level of technical expertise to operate.
Suitability for High-Value Components
The precision, repeatability, and superior quality offered by vacuum carburizing provide the most significant return on investment when applied to high-performance, high-value components where failure is not an option. It is the preferred choice for critical applications in aerospace, high-performance racing, and specialized industrial gearing.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right carburizing method depends entirely on your component's performance requirements, geometric complexity, and production value.
- If your primary focus is high-performance components with complex geometries: Vacuum carburizing is the superior choice for achieving a uniform, highly controlled case on parts like gears, injectors, and bearings.
- If your primary focus is minimizing post-processing and distortion: The clean, oxidation-free surface and uniform heating of the vacuum process will reduce or eliminate subsequent machining and straightening operations.
- If your primary focus is process speed and repeatability for critical parts: The automated, computer-controlled nature of modern vacuum systems delivers faster cycles and unparalleled batch-to-batch consistency.
Ultimately, choosing vacuum carburizing is an investment in precision engineering to achieve metallurgical properties that are simply not possible with conventional methods.
Summary Table:
| Process Stage | Key Action | Primary Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Vacuum & Heating | Air is removed; parts are heated to 850-1050°C. | Prevents oxidation; ensures a clean surface. |
| 2. Carburizing (Boost) | Hydrocarbon gas (e.g., propane) is introduced. | Saturates the steel surface with active carbon atoms. |
| 3. Diffusion | Gas flow stops; parts are held at temperature. | Carbon migrates inward for a controlled, uniform case depth. |
| 4. Quenching | Parts are rapidly cooled with gas or oil. | Locks carbon in place, creating a hard, wear-resistant surface. |
Ready to enhance your component performance with precision vacuum carburizing?
At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced lab equipment and thermal processing solutions for demanding applications. Our expertise ensures you achieve uniform case depths, superior surface quality, and minimal distortion for your most critical components.
Let's discuss how our solutions can bring precision and reliability to your laboratory or production line. Contact our experts today for a tailored consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is a braze repair process? A Low-Heat Solution for Strong, Seamless Metal Joining
- What is the cost of a vacuum brazing furnace? A guide to key factors and investment strategy
- What metals can be joined by brazing? Discover the Versatility of Modern Brazing Techniques
- Can dissimilar metals be brazed or braze welded? A Guide to Strong, Reliable Joints
- What is vacuum brazing? The Ultimate Guide to High-Purity, Flux-Free Metal Joining



















