The primary purpose of an induction furnace is to melt or heat electrically conductive metals like iron, steel, copper, and aluminum using electromagnetic induction. Unlike traditional furnaces that burn fuel, an induction furnace uses a clean, controlled, and efficient process where heat is generated directly within the material itself, preventing contamination and allowing for precise temperature control.
An induction furnace's true value lies in its unique heating method. By using electromagnetic induction to generate heat directly within the material, it provides a level of cleanliness, temperature control, and energy efficiency that combustion-based furnaces cannot match.
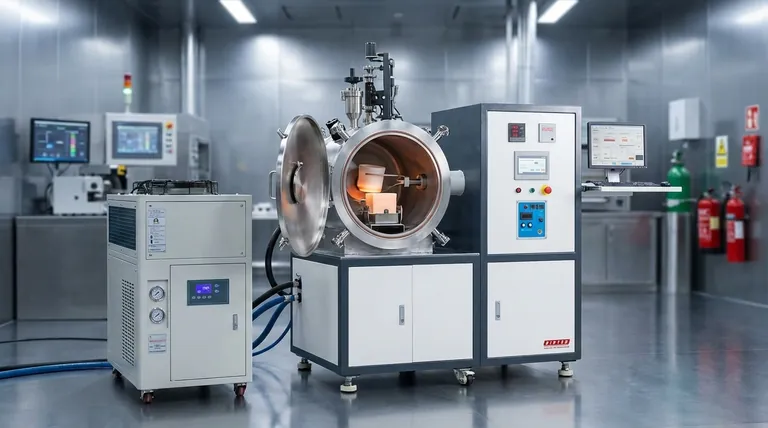

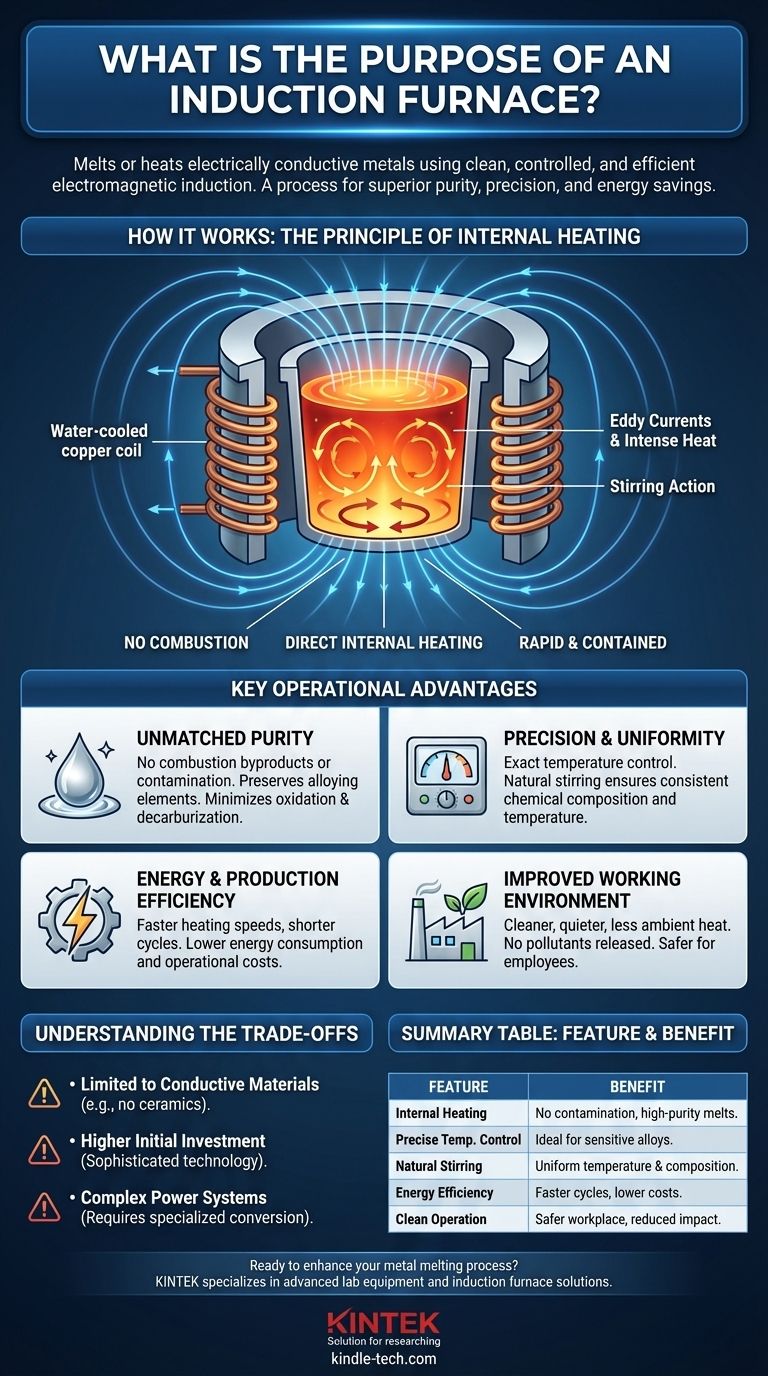
How Induction Heating Delivers Superior Results
To understand why an induction furnace is chosen for demanding applications, we must first look at its core operating principle. It is fundamentally different from any furnace that relies on an external heat source.
The Principle of Internal Heating
An induction furnace operates without any flame or arc. It uses a water-cooled copper coil that creates a powerful, alternating magnetic field when a strong alternating current is passed through it.
When a conductive metal (the "charge") is placed inside this field, the magnetic field induces powerful electrical currents, known as eddy currents, within the metal. The metal's natural resistance to these currents generates intense heat, causing it to heat up and eventually melt from the inside out.
Unmatched Purity and Material Integrity
Because there is no combustion, there are no byproducts like carbon that can contaminate the molten metal. This is critical when producing high-purity alloys or specialty steels where even trace impurities can alter the final properties.
This process also minimizes oxidation and decarburization (the loss of carbon from steel), as the heating is rapid and contained. This preserves valuable alloying elements that might otherwise burn off in a hotter, less-controlled environment.
Precision and Temperature Uniformity
The amount of heat generated is directly proportional to the power supplied to the coil. This allows for extremely precise and responsive temperature control, which is vital for hitting the narrow processing windows of sensitive alloys.
Furthermore, the alternating magnetic field creates a natural stirring action within the molten metal. This ensures the entire batch has a uniform temperature and chemical composition, preventing inconsistencies in the final product.
Key Operational Advantages
The technical benefits of induction heating translate directly into tangible operational advantages in a foundry or manufacturing setting.
Energy and Production Efficiency
Generating heat directly within the charge is far more energy-efficient than heating an entire chamber and waiting for that heat to transfer to the metal. This results in faster heating speeds, shorter melting cycles, and higher overall production efficiency.
This efficiency not only saves material and time but also significantly reduces energy consumption and operational costs.
Improved Working Environment
Induction furnaces are significantly cleaner, quieter, and produce far less ambient heat than fossil fuel furnaces. They do not release pollutants into the atmosphere.
This creates a safer and more pleasant working environment for employees, reduces the facility's environmental footprint, and simplifies compliance with environmental regulations.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly advantageous, the induction furnace is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to making an informed decision.
Limitation to Conductive Materials
The very principle of induction heating means the furnace can only be used for materials that conduct electricity. It is not suitable for heating or melting non-conductive materials like ceramics or certain types of glasses.
High Initial Investment
The technology behind an induction furnace—including the high-power supply, capacitors, and water-cooled coils—is sophisticated. This typically results in a higher initial capital cost compared to simpler, traditional furnace designs.
Complexity of Power Systems
An induction furnace requires a specialized power system to convert line-frequency AC power into the high-frequency power needed for the coil. These systems are more complex to install, maintain, and troubleshoot than the fuel lines or arc systems of other furnaces.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right furnace technology depends entirely on your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is producing high-purity alloys: The contamination-free melting process of an induction furnace makes it the ideal choice.
- If your primary focus is operational efficiency and speed: Its rapid heating cycles and low energy consumption offer significant advantages for high-throughput production.
- If your primary focus is workplace safety and environmental impact: The clean, emission-free operation drastically improves the working environment and reduces your carbon footprint.
Ultimately, the induction furnace empowers you to achieve a higher standard of material quality and operational excellence.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Internal Heating | No combustion, prevents contamination & ensures high-purity melts |
| Precise Temperature Control | Ideal for sensitive alloys with narrow processing windows |
| Natural Stirring Action | Ensures uniform temperature and chemical composition |
| Energy Efficiency | Faster heating, shorter cycles, and lower operational costs |
| Clean Operation | No emissions, safer workplace, and reduced environmental impact |
Ready to enhance your metal melting process with superior purity and efficiency?
KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables, serving the precise needs of laboratories and foundries. Our induction furnace solutions are designed to deliver the cleanliness, control, and cost savings your operations demand.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect induction furnace for your specific metals and production goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the vacuum induction method? Master High-Purity Metal Melting for Advanced Alloys
- What are the advantages of induction melting? Achieve Faster, Cleaner, and More Controlled Metal Melting
- What is the primary function of a vacuum induction melting furnace? Melt High-Purity Metals with Precision
- What types of metals are typically processed in a vacuum induction melting furnace? High-Purity Alloys for Critical Applications
- What is the principle of vacuum induction melting? Achieve Ultra-High Purity Metals



















