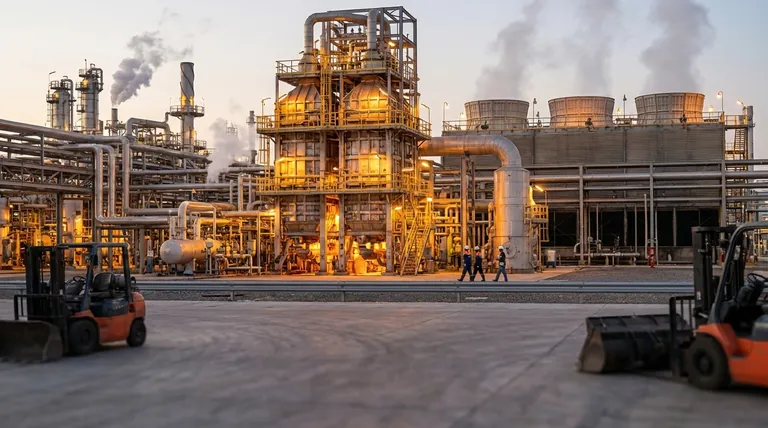
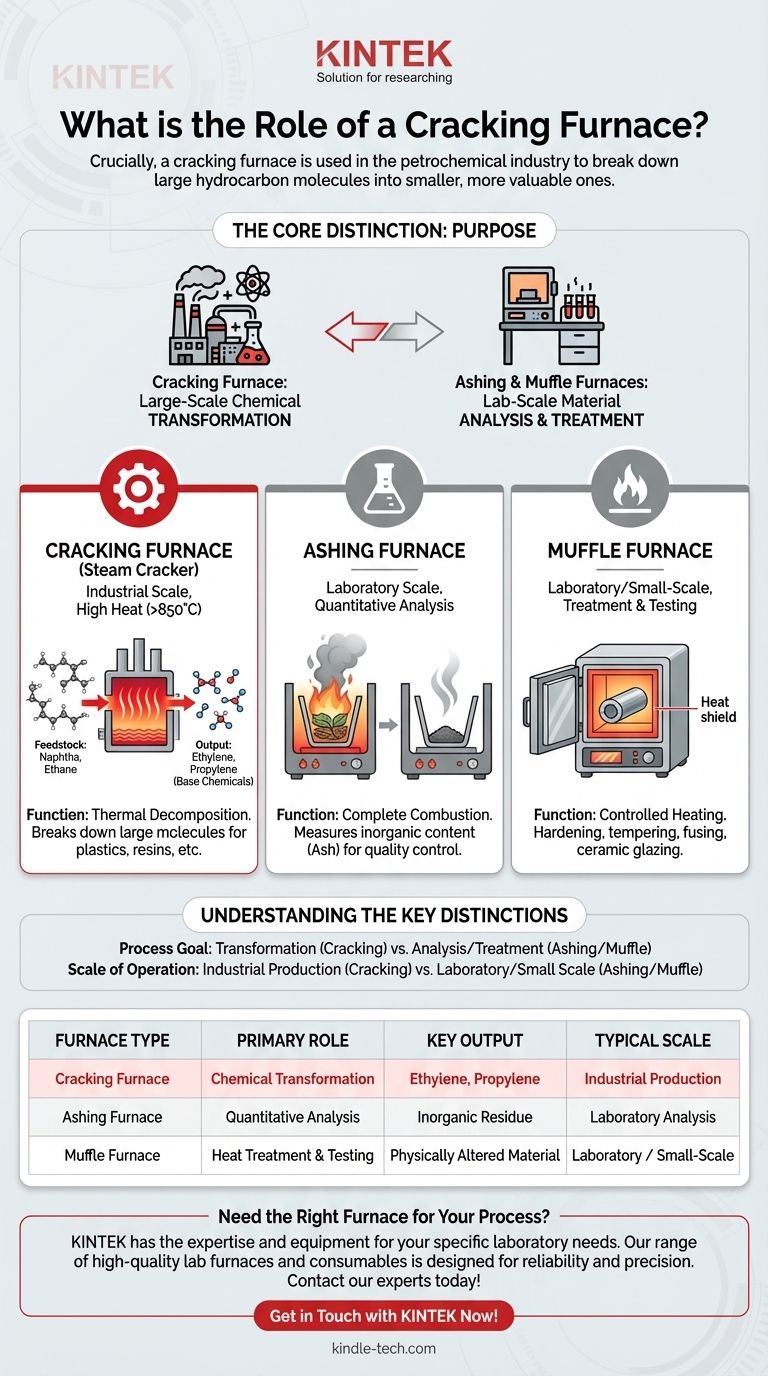
Crucially, a cracking furnace is used in the petrochemical industry to break down large hydrocarbon molecules into smaller, more valuable ones. This process, known as thermal cracking, is fundamentally different from the roles of the ashing and muffle furnaces described in the provided references, which are primarily used for material analysis and heat treatment.
The core distinction is one of purpose: a cracking furnace is designed for large-scale chemical transformation to create new products, whereas ashing and muffle furnaces are typically used for smaller-scale material analysis or physical treatment.

The Purpose of a Cracking Furnace
A cracking furnace, often called a steam cracker, is the heart of a modern petrochemical plant. Its function is not to analyze a sample but to fundamentally alter its chemical structure on a massive industrial scale.
Thermal Decomposition of Hydrocarbons
The primary role is to subject a feedstock, such as naphtha or ethane, to extremely high temperatures (typically 850°C or higher).
This intense heat "cracks" the long-chain hydrocarbon molecules, breaking them apart into smaller, unsaturated hydrocarbons.
Producing Valuable Chemical Building Blocks
The output of this process isn't ash or a treated metal; it's a mixture of valuable base chemicals.
The most important products are light olefins like ethylene and propylene, which are the foundational ingredients for producing a vast range of plastics, resins, and industrial chemicals.
Understanding Furnaces for Analysis and Treatment
The provided references describe furnaces with entirely different goals. They are used to understand or physically modify a material, not to create new base chemicals from it.
The Role of an Ashing Furnace
An ashing furnace is a tool for quantitative analysis. Its purpose is to completely burn off all organic material in a sample.
By measuring the sample's weight before and after this combustion, analysts can accurately determine the percentage of inorganic, non-combustible material (ash) it contains. This is critical for quality control in materials like coal, plastics, and rubber.
The Role of a Muffle Furnace
A muffle furnace is a versatile, high-temperature oven used for material treatment and testing. Its insulated chamber separates the material from direct contact with the heating elements.
This makes it ideal for processes like hardening or tempering steel, fusing glass, creating ceramic glazes, and performing various scientific analyses that require controlled, high-temperature environments.
Understanding the Key Distinctions
Choosing the right furnace depends entirely on the intended outcome. The confusion between these types often stems from the general use of high heat, but their applications are worlds apart.
Process Goal: Transformation vs. Analysis
A cracking furnace causes a fundamental chemical transformation, creating new, smaller molecules from larger ones.
Ashing and muffle furnaces are used to either analyze a material's composition by removing a component (ashing) or to alter a material's physical properties through heat (muffle).
Scale of Operation: Industrial Production vs. Laboratory
Cracking furnaces are massive industrial units, central to large-scale chemical manufacturing plants.
Ashing and muffle furnaces are typically much smaller, often found in laboratory or small-scale production settings for research, quality control, and specialized heat-treatment tasks.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
Your objective dictates the necessary equipment. The name of the furnace is secondary to the process it is designed to execute.
- If your primary focus is producing base chemicals like ethylene: You require a cracking furnace for large-scale thermal decomposition of hydrocarbons.
- If your primary focus is determining the inorganic content of a sample: You need an ashing furnace for complete combustion and residue analysis.
- If your primary focus is heat-treating metals, creating ceramics, or conducting high-temperature lab tests: A muffle furnace provides the necessary controlled heating environment.
Ultimately, selecting the correct furnace is about matching its unique engineering design to your specific chemical or physical goal.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Type | Primary Role | Key Output | Typical Scale |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cracking Furnace | Chemical Transformation (Cracking) | Ethylene, Propylene | Industrial Production |
| Ashing Furnace | Quantitative Analysis (Ash Content) | Inorganic Residue | Laboratory Analysis |
| Muffle Furnace | Heat Treatment & Testing | Physically Altered Material | Laboratory / Small-Scale |
Need the Right Furnace for Your Process?
Understanding the distinction between furnace types is critical for your operation's success. Whether your goal is large-scale chemical production, precise material analysis, or controlled heat treatment, KINTEK has the expertise and equipment to meet your specific laboratory needs.
Our range of high-quality lab furnaces and consumables is designed for reliability and precision. Contact our experts today to discuss your application and find the perfect solution for your project.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the objective of a muffle furnace? Achieve Pure, High-Temperature Processing
- What is a muffle furnace in the environment? Achieve Clean, Contaminant-Free Heating
- What is the tolerance of a muffle furnace? A Guide to Temperature Accuracy & Uniformity
- What precautions should you take while using a muffle furnace? Ensure Safe High-Temperature Processing in Your Lab
- How do you calibrate a muffle furnace? Achieve Precise Temperature Control for Your Lab



















