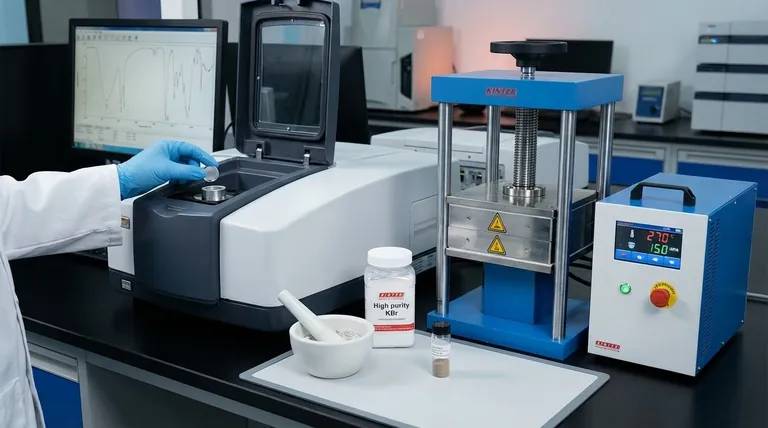
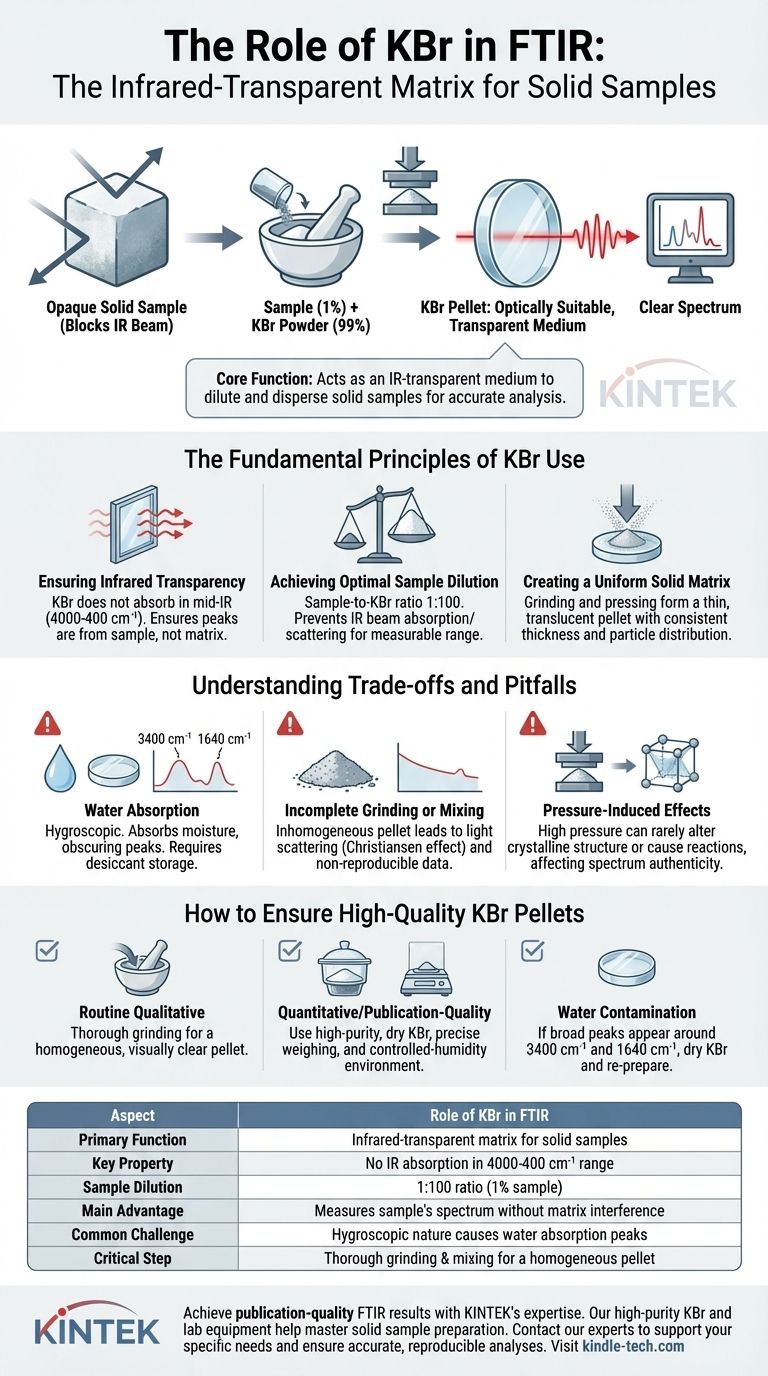
In FTIR spectroscopy, potassium bromide (KBr) serves as an ideal matrix for analyzing solid samples. Its primary role is to act as an infrared-transparent medium that holds a finely diluted sample, allowing the instrument's IR beam to pass through and measure the sample's unique absorption spectrum without interference from the matrix itself.
The core function of KBr is to solve the problem of analyzing opaque, solid materials. By dispersing a tiny amount of sample within a transparent KBr pellet, you create an optically suitable medium that allows for clear, reproducible FTIR measurements.

The Fundamental Principles of KBr Use
The use of KBr is based on a few key properties that make it uniquely suited for preparing solid samples for transmission FTIR analysis. Understanding these principles is crucial for obtaining high-quality data.
Ensuring Infrared Transparency
KBr is chosen because it does not absorb light in the mid-infrared region (typically 4000-400 cm⁻¹), which is the area of interest for most organic and inorganic analyses. This optical transparency ensures that any absorption peaks detected by the instrument originate from your sample, not the KBr matrix. It effectively creates a clear "window" to view the sample's spectral fingerprint.
Achieving Optimal Sample Dilution
Most solid samples, even as fine powders, are too concentrated and will absorb or scatter the entire IR beam, resulting in a useless spectrum with no discernible peaks. The KBr method overcomes this by requiring extreme dilution. Typically, the sample constitutes only 1% of the total mixture, with a sample-to-KBr ratio of 1:100. This dilution brings the sample's absorbance into a linear, measurable range for the detector.
Creating a Uniform Solid Matrix
The process involves grinding the sample with KBr powder to disperse the analyte particles uniformly. This mixture is then pressed under high pressure in a die to form a thin, glass-like, translucent pellet. This creates a solid sample with a consistent thickness and particle distribution, which is essential for obtaining reproducible and high-quality spectra.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Pitfalls
While the KBr pellet technique is a standard method, it is not without challenges. Awareness of these potential issues is key to troubleshooting poor results.
The Problem of Water Absorption
The most common pitfall is KBr's hygroscopic nature; it readily absorbs moisture from the atmosphere. Water has very strong and broad IR absorption bands (around 3400 cm⁻¹ and 1640 cm⁻¹) that can easily obscure important peaks from your sample. For this reason, KBr must be stored in a desiccator and handled quickly. For sensitive measurements, pellets are often prepared in a dry glovebox.
Incomplete Grinding or Mixing
If the sample is not ground into a fine powder and mixed thoroughly with the KBr, the resulting pellet will be inhomogeneous. This causes two primary problems: a sloping baseline in the spectrum due to light scattering (the Christiansen effect) and non-reproducible peak intensities. The goal is to reduce sample particle size to be smaller than the wavelength of the IR light.
Pressure-Induced Effects
The high pressure used to form the pellet can occasionally alter the crystalline structure of a sample (polymorphism) or cause a reaction between the sample and the KBr itself. While rare, this can lead to a spectrum that does not represent the sample in its original state.
How to Ensure High-Quality KBr Pellets
Applying these principles correctly will determine the quality of your spectral data. Your approach should depend on the goal of your analysis.
- If your primary focus is routine qualitative identification: Ensure the sample and KBr are ground together thoroughly until the mixture is a homogenous, fine powder to produce a visually clear pellet.
- If your primary focus is quantitative analysis or publication-quality data: Use high-purity, dry KBr stored in a desiccator, weigh the components precisely, and consider preparing the pellet in a controlled-humidity environment to eliminate water contamination.
- If your spectrum shows broad, unexpected peaks around 3400 cm⁻¹ and 1640 cm⁻¹: This is almost certainly from water contamination; you must dry your KBr and prepare a new pellet.
Mastering this sample preparation technique is a fundamental step toward achieving reliable and accurate solid-state FTIR analysis.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Role of KBr in FTIR |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Acts as an infrared-transparent matrix for solid samples |
| Key Property | Does not absorb IR light in the 4000-400 cm⁻¹ range |
| Sample Dilution | Typical sample-to-KBr ratio is 1:100 (1% sample) |
| Main Advantage | Allows measurement of sample's absorption spectrum without matrix interference |
| Common Challenge | Hygroscopic nature can lead to water absorption peaks |
| Critical Step | Thorough grinding and mixing for a homogeneous pellet |
Achieve publication-quality FTIR results with KINTEK's expertise.
Struggling with water contamination or inconsistent pellets? Our high-purity KBr and lab equipment are designed to help you master solid sample preparation. KINTEK specializes in providing reliable laboratory consumables and equipment tailored for analytical techniques like FTIR.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific needs and ensure your analyses are both accurate and reproducible.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press Machine for Glove Box
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press for Button Battery
- Laboratory Manual Hydraulic Pellet Press for Lab Use
- Automatic Laboratory Hydraulic Press for XRF & KBR Pellet Press
People Also Ask
- Is induction more efficient than resistance? Unlock Faster Cooking with Up to 90% Energy Efficiency
- What is the minimum temperature for sintering? It Depends on Your Material's Melting Point
- What is the lifetime of a sputtering target? Maximize Material Usage and Efficiency
- What is hot forging used for? Manufacturing Critical, High-Strength Metal Components
- What is batch pyrolysis? A Start-Stop Process for Flexible Waste Conversion
- What are the pros and cons of laser sintering? Unlock Complex, Functional Parts
- What role does drying or curing equipment play in NSHPC synthesis? Ensuring Structural Precision in Porous Carbons
- What is the thickness of coating? A Guide from Nanoscale to Macroscale Applications



















