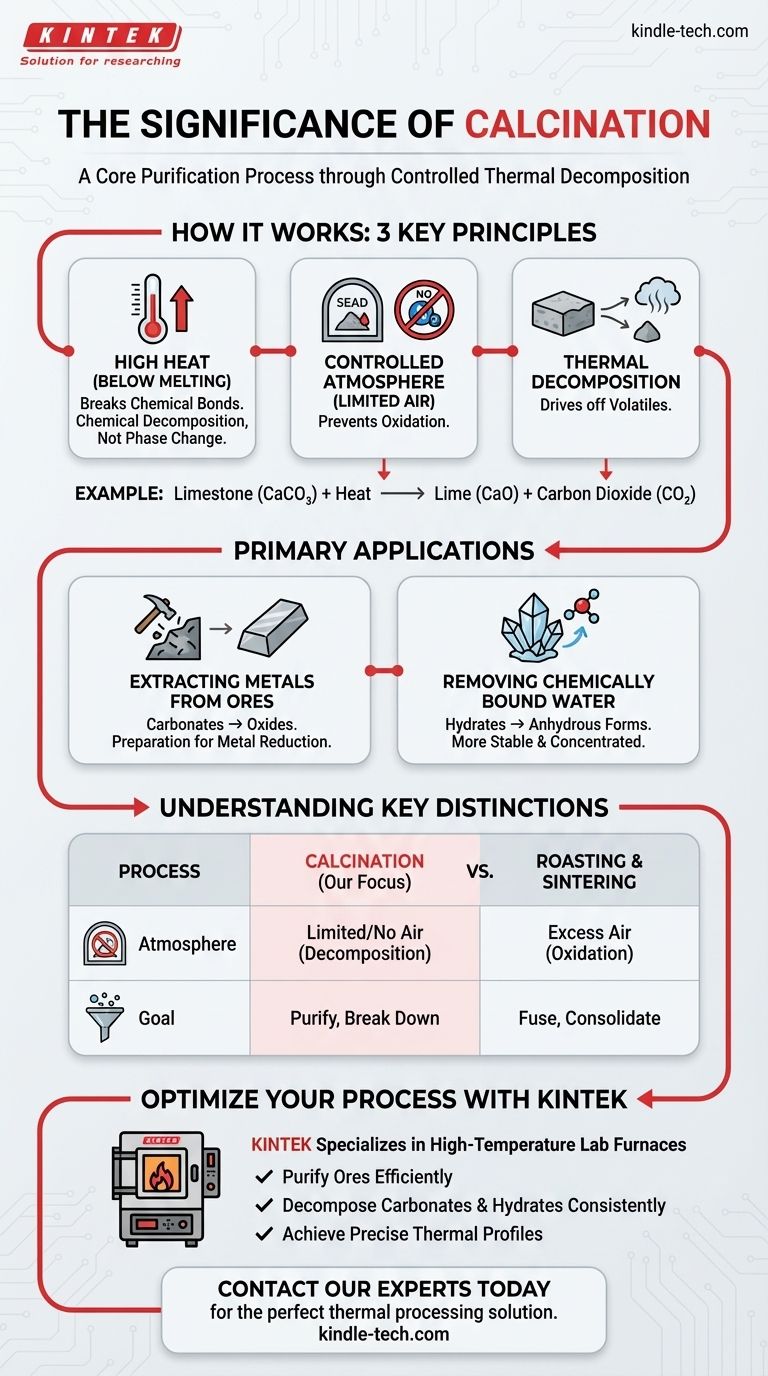
At its core, calcination is a purification process. It uses high heat—carefully controlled to stay below the material's melting point—to induce chemical changes. In an environment with little to no air, this process drives out volatile substances like carbon dioxide or water, transforming a raw material into a more concentrated and stable form.
The true significance of calcination is not just heating, but controlled chemical transformation. It serves as a critical preparatory step to break down compounds and remove impurities, making a raw material suitable for subsequent processes like metal extraction.
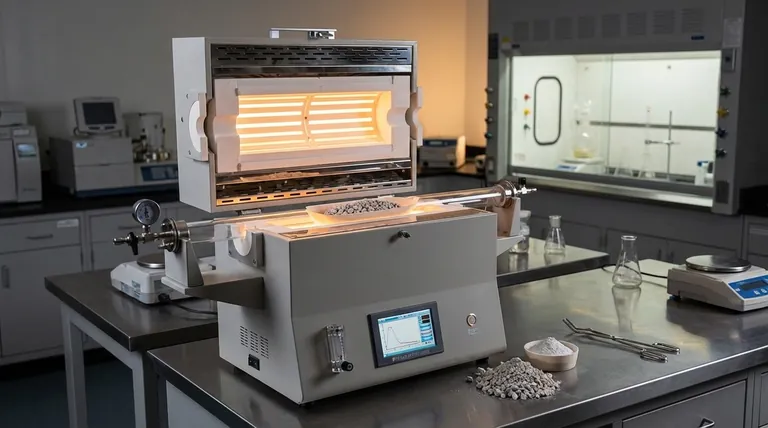

How Calcination Fundamentally Works
Calcination is a precise thermal treatment designed to change a material's chemical composition, not its physical state from solid to liquid. This is achieved through three key principles working in concert.
The Role of High Heat (Below Melting)
The process relies on applying enough thermal energy to break specific chemical bonds within a compound.
By keeping the temperature below the melting point, the material remains a solid. This ensures the goal is chemical decomposition, not a phase change.
The Controlled Atmosphere (Limited Air)
Calcination is typically performed in the absence or a very limited supply of air.
This is critical because it prevents oxidation or combustion. The goal is to break down the existing material, not to have it react with oxygen in the air.
The Result: Thermal Decomposition
The heat provides the energy needed to decompose the material into two parts: the desired solid and a volatile gas that is driven off.
A classic example is the calcination of limestone (calcium carbonate, CaCO₃), which decomposes into lime (calcium oxide, CaO) and carbon dioxide (CO₂) gas. The solid lime is the valuable product.
The Primary Applications of Calcination
This process is a cornerstone of materials processing, particularly in metallurgy and chemical manufacturing. Its primary purpose is purification and preparation.
Extracting Metals from Ores
Calcination is a crucial first step for processing many mineral ores, especially carbonates and hydrates.
Heating a metal carbonate ore removes the carbon dioxide, leaving behind a more concentrated metal oxide. This metal oxide is then much easier to reduce to the final, pure metal in a later step.
Removing Chemically Bound Water
Many minerals exist as hydrates, meaning water molecules are incorporated into their crystal structure.
Calcination provides the energy to drive off this bound water, converting the material into its anhydrous (water-free) form, which is often more stable and concentrated.
Understanding Key Distinctions
To fully grasp the significance of calcination, it is essential to distinguish it from other common thermal processes. Mistaking these processes can lead to incorrect outcomes.
Calcination vs. Roasting
The key difference is the presence of air. Calcination occurs with little to no air to cause decomposition.
Roasting, by contrast, is done with an excess of air specifically to induce an oxidation reaction, such as converting a metal sulfide into a metal oxide.
Calcination vs. Sintering
These processes have opposite goals. Calcination breaks down compounds and drives off impurities.
Sintering uses heat to fuse small particles together into a single, solid piece without melting them. It is a process of consolidation, not purification.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Applying the correct thermal process is critical for achieving the desired material properties. Your objective will determine whether calcination is the right approach.
- If your primary focus is purification of an ore: Calcination is the ideal method for removing volatile components like CO₂ or H₂O from mineral carbonates and hydrates.
- If your primary focus is chemical conversion: Use calcination to thermally decompose a raw material into a more reactive or useful intermediate, such as converting limestone to lime for cement production.
- If your goal is to fuse particles or react a material with air: You need a different process entirely, such as sintering for fusion or roasting for oxidation.
Ultimately, calcination is a foundational tool for controlling the chemical purity and reactivity of inorganic materials.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Chemical decomposition and purification, not melting. |
| Atmosphere | Limited or no air to prevent oxidation. |
| Key Inputs | Raw materials like metal carbonates or hydrates. |
| Key Outputs | Purified solids (e.g., metal oxides) and driven-off volatile gases. |
| Main Applications | Metal extraction from ores, cement production, removing chemically bound water. |
Ready to optimize your material purification process?
Calcination is a critical step for achieving high-purity materials in metallurgy and chemical manufacturing. The right equipment is essential for precise temperature control and a controlled atmosphere to ensure successful decomposition without oxidation.
KINTEK specializes in high-temperature lab furnaces ideal for calcination processes. Our robust and reliable equipment helps you:
- Purify ores efficiently for metal extraction.
- Decompose carbonates and hydrates with consistent results.
- Achieve precise thermal profiles for controlled chemical transformation.
Let's discuss your specific application. Contact our experts today to find the perfect thermal processing solution for your laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the process of a plastic pyrolysis plant? A Complete Guide to Converting Waste Plastic into Fuel
- What are the byproducts of biochar? Valuable Co-Products from Pyrolysis
- What are the end products of biomass gasification? A Guide to Syngas, Biochar, and More
- What is the difference between incineration pyrolysis and gasification? Mastering Thermal Conversion Technologies
- What is different between calcination? Unlocking Thermal Processing for Material Science
- What are the uses of calcination process? A Guide to Material Transformation
- What is the purpose of a pyrolysis reactor? To Transform Waste into Valuable Bio-Oil, Biochar, and Syngas
- What are the different types of pyrolysis reactions? A Guide to Optimizing Biochar, Bio-Oil, and Syngas



















