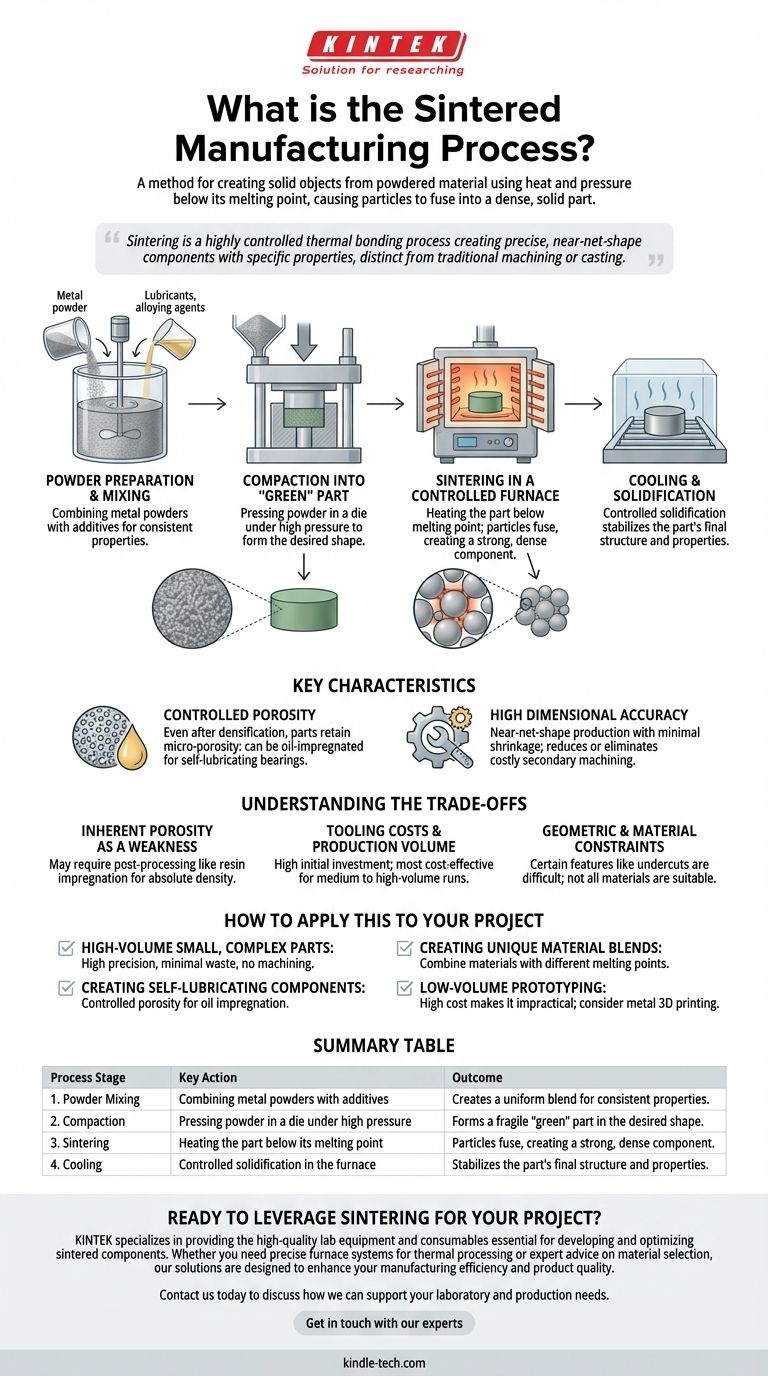
At its core, the sintered manufacturing process is a method for creating solid objects from powdered material using heat and pressure. Unlike casting, this process heats the material to a temperature below its melting point, causing the individual particles to fuse together and form a dense, solid part. This technique is fundamental to powder metallurgy.
Sintering is not simply about melting powder into a shape. It is a highly controlled thermal bonding process that creates precise, near-net-shape components with specific properties like controlled porosity, making it a distinct and powerful alternative to traditional machining or casting.

The Sintering Process: A Step-by-Step Breakdown
The production of a sintered part is a precise, multi-stage operation. While variations exist, the process consistently follows three primary phases: mixing, compacting, and the final sintering (heating).
Step 1: Powder Preparation and Mixing
Before any shaping can occur, the raw material must be prepared. This involves selecting a primary metal powder and often mixing it with other elements.
These additives can include alloying agents like copper or cemented carbides to enhance final properties, or processing aids like lubricants and binders that help during the compaction phase.
Step 2: Compaction into the "Green" Part
The carefully prepared powder mix is then loaded into a die or mold. Here, it is subjected to extremely high pressure.
This pressure forces the powder particles into close contact, forming a solid but fragile part known as a "green compact." This component has the desired shape but lacks the final strength and density.
Step 3: Sintering in a Controlled Furnace
The green compact is carefully removed from the die and placed into a specialized furnace with a controlled atmosphere. This is the critical step where the part gains its final properties.
The part is heated to a precise temperature below the material's melting point. This heat burns off any binders or lubricants and, more importantly, activates atomic diffusion between the powder particles. The particles bond and merge, significantly reducing the porous spaces between them and densifying the component into a unified mass.
Step 4: Cooling and Solidification
After holding at the sintering temperature for a set time, the component is cooled in a controlled manner. This allows the newly formed metallic bonds and crystalline structures to stabilize, resulting in a solid, functional part.
Key Characteristics of a Sintered Part
The sintering process imparts unique characteristics that define its advantages in manufacturing.
Controlled Porosity
Even after densification, sintered parts retain a certain level of micro-porosity. While this can be a mechanical consideration, it can also be a key design feature. This porosity allows parts to be impregnated with oil, creating self-lubricating bearings.
High Dimensional Accuracy
Sintering is known for producing parts with high dimensional precision, often referred to as "near-net-shape." A slight, predictable amount of shrinkage occurs during heating, which is accounted for in the initial tool design. This accuracy minimizes or even eliminates the need for costly secondary machining operations.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, sintering is not universally applicable. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Inherent Porosity as a Weakness
If a component requires absolute density for maximum strength or pressure-tightness, the natural micro-porosity of a standard sintered part can be a disadvantage. In these cases, post-processing steps like resin impregnation are required to seal the pores.
Tooling Costs and Production Volume
The dies used for compaction are made from hardened tool steel and are expensive to produce. This high initial investment means that sintering is most cost-effective for medium to high-volume production runs, where the cost of the tooling can be amortized over many thousands of parts.
Geometric and Material Constraints
The need to press powder in a die and eject the green compact places some constraints on part geometry; features like undercuts or holes perpendicular to the pressing direction can be difficult or impossible to form. Furthermore, not all materials are suitable for sintering.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Once the main sintering process is complete, parts can undergo a variety of finishing operations to meet final specifications.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production of small, complex parts: Sintering is an excellent choice because it delivers high precision with minimal material waste and no need for subsequent machining.
- If your primary focus is creating self-lubricating components: Sintering is the definitive process, as its controlled porosity is perfectly suited for oil impregnation.
- If your primary focus is creating unique material blends: Sintering allows you to combine materials with very different melting points (like metals and ceramics) that cannot be alloyed through traditional casting.
- If your primary focus is low-volume prototyping: The high cost of tooling makes traditional sintering impractical; consider related technologies like metal 3D printing (Direct Metal Laser Sintering) instead.
By understanding its principles and trade-offs, you can leverage sintering to manufacture highly precise and functional components with remarkable efficiency.
Summary Table:
| Process Stage | Key Action | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Powder Mixing | Combining metal powders with additives. | Creates a uniform blend for consistent properties. |
| 2. Compaction | Pressing powder in a die under high pressure. | Forms a fragile "green" part in the desired shape. |
| 3. Sintering | Heating the part below its melting point. | Particles fuse, creating a strong, dense component. |
| 4. Cooling | Controlled solidification in the furnace. | Stabilizes the part's final structure and properties. |
Ready to leverage sintering for your project?
KINTEK specializes in providing the high-quality lab equipment and consumables essential for developing and optimizing sintered components. Whether you need precise furnace systems for thermal processing or expert advice on material selection, our solutions are designed to enhance your manufacturing efficiency and product quality.
Contact us today to discuss how we can support your laboratory and production needs. Get in touch with our experts
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Automatic High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- 24T 30T 60T Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
- Double Plate Heating Press Mold for Lab
- Warm Isostatic Press for Solid State Battery Research
People Also Ask
- Does a hydraulic press have heat? How Heated Platens Unlock Advanced Molding and Curing
- What are heated hydraulic presses used for? Molding Composites, Vulcanizing Rubber, and More
- What is a hot hydraulic press? Harness Heat and Pressure for Advanced Manufacturing
- How much force can a hydraulic press exert? Understanding its immense power and design limits.
- Why do you need to follow the safety procedure in using hydraulic tools? Prevent Catastrophic Failure and Injury



















