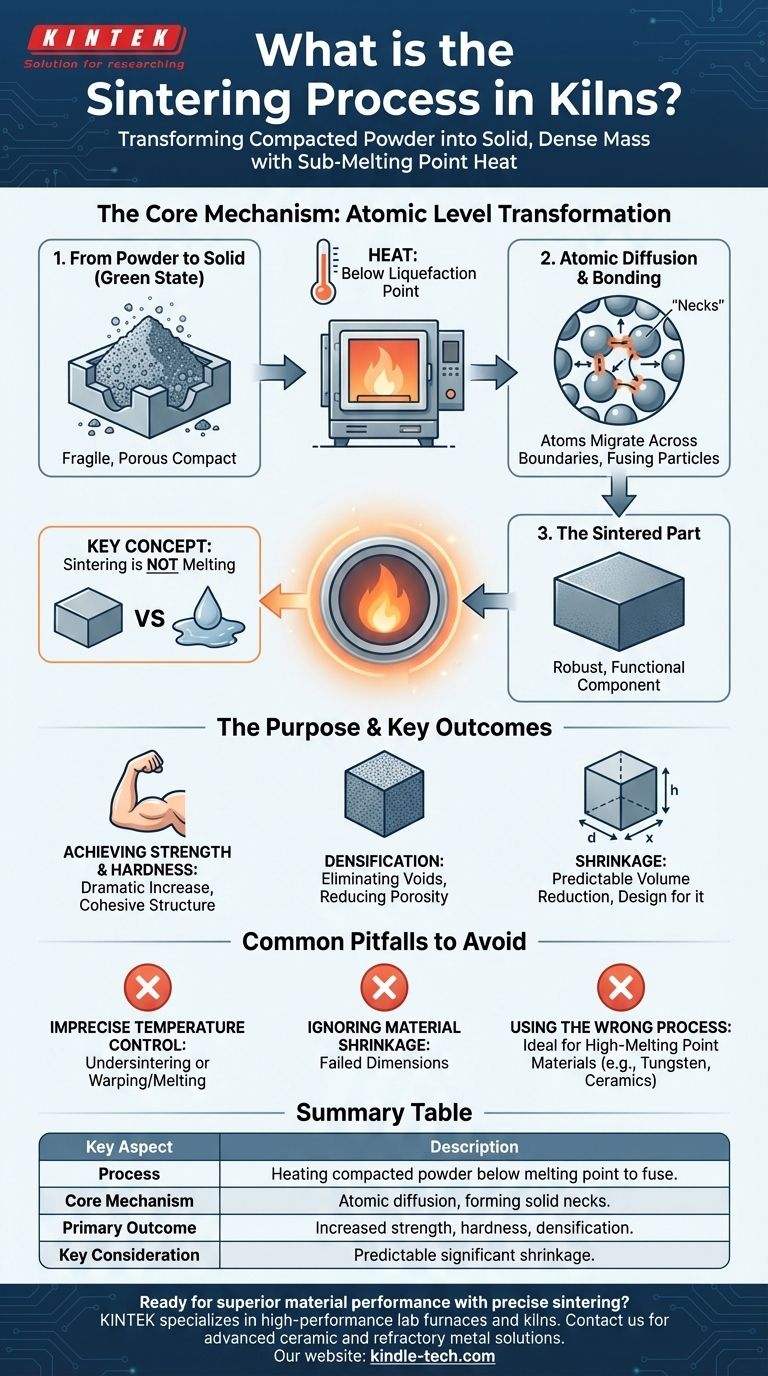
In essence, sintering is a high-temperature process used in a kiln to transform a compacted powder into a solid, dense mass. It achieves this by heating the material to a point just below its melting temperature, causing the individual particles to fuse together at an atomic level. This results in a significantly stronger and more durable final product.
The critical concept to understand is that sintering is not melting. It is a solid-state process where heat encourages atoms to migrate across particle boundaries, effectively welding them into a single, densified piece without ever becoming a liquid.
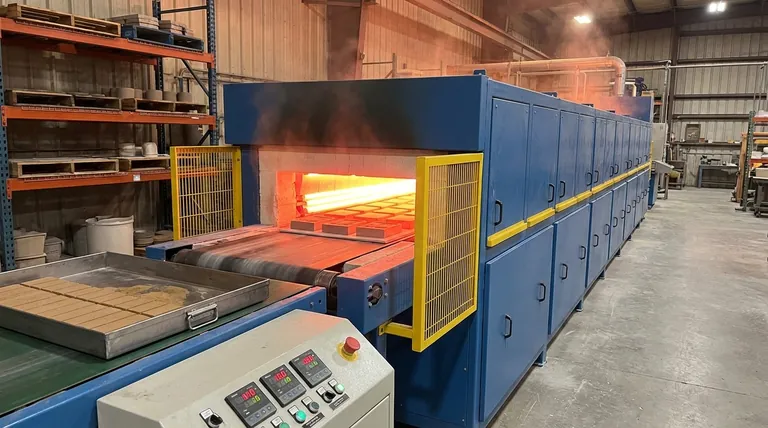

The Core Mechanism: How Sintering Works at an Atomic Level
Sintering is a fascinating process that fundamentally alters a material's structure. It transforms a fragile, porous object into a robust, functional component.
From Powder to Solid
The process begins with a material in a powdered form, which is first compacted into a desired shape, often called a "green state" compact. This initial form is weak and chalky. The goal of sintering is to convert this fragile compact into a fully solid object.
The Role of Sub-Melting Point Heat
A kiln or furnace applies extreme heat, but crucially, it keeps the temperature below the material's liquefaction point. This high thermal energy gives the atoms within the material the mobility they need to move.
Atomic Diffusion and Particle Bonding
With this increased energy, atoms from adjacent particles begin to diffuse across the boundaries that separate them. This migration of atoms effectively builds "necks" or bridges between the particles, fusing them together and gradually eliminating the voids or pores between them.
The Purpose and Key Outcomes of Sintering
Engineers and manufacturers use sintering to achieve specific material properties that would be difficult or impossible to obtain through other methods like melting and casting.
Achieving Strength and Hardness
The primary outcome of atomic bonding is a dramatic increase in strength and hardness. The once-separate particles are now part of a unified, cohesive structure, making the final piece incredibly robust.
The Process of Densification
As particles fuse and the pores between them are eliminated, the material becomes much denser. This densification is critical for the performance of many technical materials, as it reduces porosity and improves mechanical properties.
The Inevitable Consequence: Shrinkage
A direct and predictable result of densification is shrinkage. As the empty space between particles is removed, the entire component shrinks in volume. Materials like zirconia, for example, can undergo a significant amount of shrinkage that must be accounted for in the initial design.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
While powerful, the sintering process requires precise control. Misunderstanding its principles can lead to failed parts and wasted resources.
Imprecise Temperature Control
The entire process hinges on maintaining a temperature high enough for atomic diffusion but low enough to prevent melting. If the temperature is too low, the part won't be fully densified. If it's too high, the part will warp or melt, losing its shape and integrity.
Ignoring Material Shrinkage
Failing to accurately calculate and compensate for shrinkage is one of the most common mistakes. Parts must be designed in an oversized "green state" so that they shrink to the exact final dimensions required after sintering.
Using the Wrong Process for the Material
Sintering is particularly effective for materials with extremely high melting points, such as tungsten, molybdenum, and technical ceramics. Trying to melt and cast these materials is often impractical, making sintering the ideal manufacturing path.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the core principles of sintering allows you to leverage it effectively for different objectives.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum strength: Sintering is the essential step that transforms a fragile powder compact into a durable, load-bearing component.
- If your primary focus is creating a non-porous part: The process is fundamentally about densification, systematically eliminating voids to create a solid mass.
- If your primary focus is manufacturing complex shapes: You must master the art of predicting and accounting for material shrinkage to ensure your final parts meet dimensional specifications.
Mastering this thermal process is fundamental to producing high-performance materials and components.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Process | Heating compacted powder below its melting point to fuse particles. |
| Core Mechanism | Atomic diffusion across particle boundaries, forming solid necks. |
| Primary Outcome | Increased strength, hardness, and density (densification). |
| Key Consideration | Predictable and significant material shrinkage occurs. |
Ready to achieve superior material performance with precise sintering?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab furnaces and kilns designed for exacting sintering processes. Whether you're working with advanced ceramics, refractory metals, or other powdered materials, our equipment delivers the precise temperature control and uniform heating essential for successful densification and strength development.
Contact us today to discuss your specific sintering requirements and discover how KINTEK's solutions can enhance your research and manufacturing outcomes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Disc Rotary Mixer for Efficient Sample Mixing and Homogenization
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between calcining and roasting? A Guide to High-Temperature Processing
- What is the purpose of a calciner? Boost Efficiency in High-Temperature Processing
- What are the types of pyrolysis reactors used in industry? Choose the Right Technology for Your Product
- What is the principle of rotary kiln? Mastering Continuous Thermal Processing
- What biomass is used in pyrolysis? Selecting the Optimal Feedstock for Your Goals



















