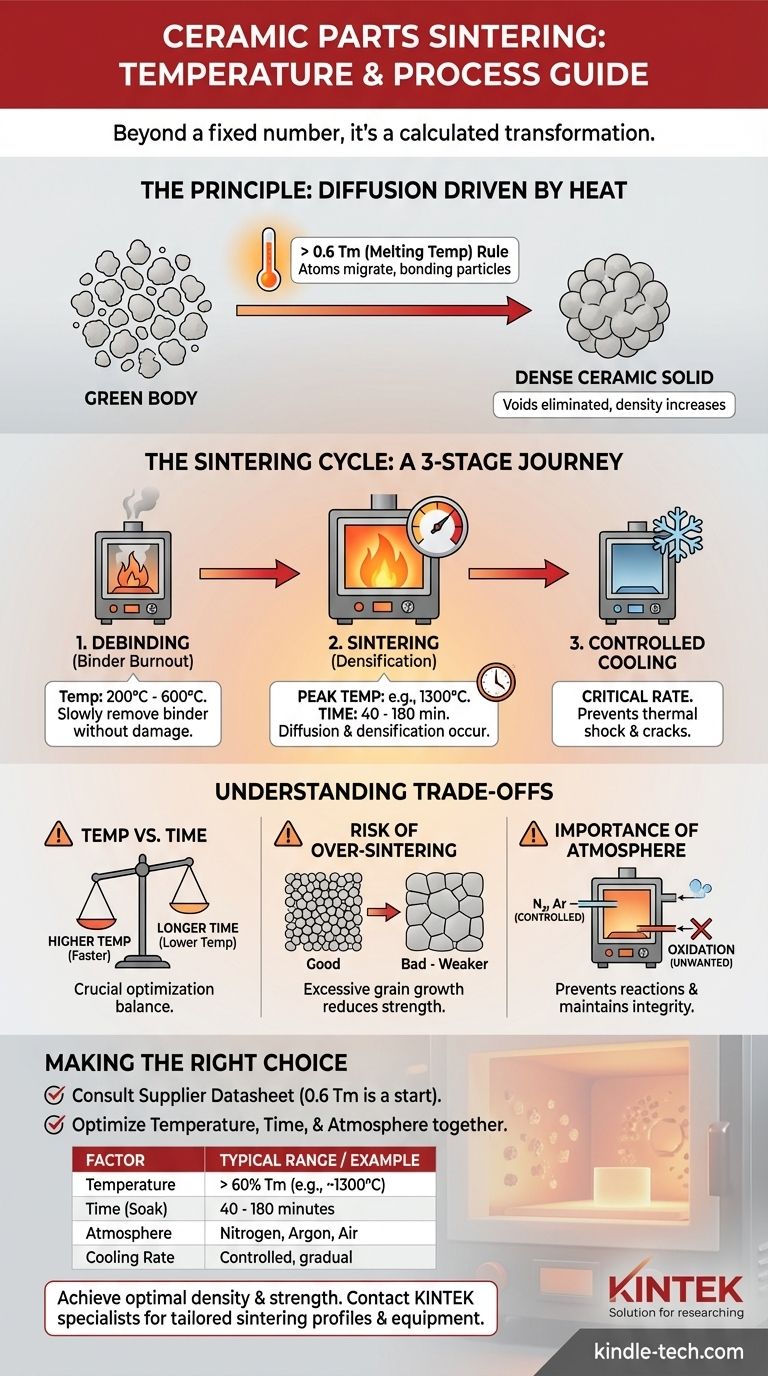
For ceramic parts, there is no single universal sintering temperature. While a typical peak temperature for some common ceramics is around 1,300°C, the precise value is fundamentally dependent on the specific material being used. The process involves a carefully controlled heating and cooling cycle, not just a single setpoint.
The critical takeaway is that sintering temperature is not a fixed number but a calculated parameter, generally set to be greater than 60% of the material's absolute melting temperature (Tm). This ensures sufficient thermal energy is available to bond the ceramic particles into a dense, solid part.

The Principle of Sintering: More Than Just Heat
Sintering is the process that transforms a compacted powder, known as a "green body," into a dense, coherent solid. This transformation relies on atomic-level mechanics driven by high temperatures.
From Powder to Solid
The goal of sintering is to reduce the empty space (porosity) between the initial powder particles. By heating the material, these particles fuse together, gradually eliminating the voids and increasing the part's overall density and strength.
The Role of Temperature in Diffusion
High temperature provides the necessary energy for atoms to move and migrate across the boundaries of adjacent particles. This process, called diffusion, is the core mechanism of sintering. It allows the particles to bond, reduces surface area, and consolidates the material into a strong ceramic body.
The "0.6 Tm" Rule of Thumb
As a guiding principle, the sintering temperature must be high enough to enable significant diffusion. This typically requires a temperature greater than approximately 0.6 times the material's melting temperature (Tm). Below this threshold, the atomic movement is too slow for effective densification to occur in a reasonable timeframe.
A Sintering Cycle Is a Multi-Stage Process
Achieving a successful outcome involves more than just reaching a peak temperature. Sintering is a complete thermal cycle with distinct stages, each serving a critical purpose.
Stage 1: Debinding (Binder Burnout)
Before sintering, ceramic powders are often mixed with a binder to form the initial shape. The first phase of the heating cycle, often at lower temperatures (e.g., 200°C - 600°C), is designed to slowly burn out this binder material without damaging the part.
Stage 2: Sintering (Densification)
This is the high-temperature phase where the actual consolidation occurs. The furnace ramps up to the target sintering temperature (e.g., 1,300°C) and is held there for a specific duration, often between 40 to 180 minutes. During this "soak time," diffusion works to densify the part.
Stage 3: Controlled Cooling
After the high-temperature hold, the part must be cooled in a controlled manner. Cooling too quickly can induce thermal shock, leading to cracks and component failure. The cooling rate is an essential part of the overall process profile.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Optimizing a sintering cycle requires balancing competing factors. The choices you make directly impact the final properties of the ceramic component.
Temperature vs. Time
A higher sintering temperature can achieve densification more quickly. However, a similar level of density can often be reached by holding the part at a slightly lower temperature for a longer period. This trade-off is crucial for process optimization.
The Risk of Over-sintering
Using a temperature that is too high or holding it for too long can be detrimental. This can lead to excessive grain growth, where smaller grains merge into larger ones. While the part may be dense, large grains can often reduce the material's mechanical strength and fracture toughness.
The Importance of Atmosphere
Sintering does not happen in a vacuum unless specified. The gas inside the furnace (the atmosphere) is critical. A controlled atmosphere (like nitrogen or argon) can prevent unwanted chemical reactions, such as oxidation, ensuring the material's chemical integrity is maintained.
Making the Right Choice for Your Material
The ideal sintering cycle is a tailored solution based on the material and the desired final properties.
- If your primary focus is a specific ceramic (e.g., Alumina, Zirconia): Always begin by consulting the material supplier's datasheet. The "0.6 Tm" rule provides an excellent starting point, but precise, validated cycles are always material-specific.
- If your primary focus is process optimization: Remember that temperature, time, and atmosphere are interconnected variables. Adjusting one will affect the others, influencing final density, grain size, and mechanical strength.
Ultimately, successful sintering is a process of controlled transformation, not just an application of heat.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Key Consideration | Typical Range/Example |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | Based on material's melting point (Tm) | > 60% of Tm (e.g., ~1300°C for many ceramics) |
| Time (Soak) | Duration at peak temperature | 40 - 180 minutes |
| Atmosphere | Prevents unwanted reactions | Nitrogen, Argon, Air |
| Cooling Rate | Prevents thermal shock | Controlled, gradual |
Achieve optimal density and strength for your ceramic components. The precise sintering temperature and cycle are critical to your product's performance. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs. Our experts can help you select the right furnace and develop a tailored sintering profile for your specific material—whether it's Alumina, Zirconia, or a specialized technical ceramic. Contact our sintering specialists today to discuss your application and ensure your process is a success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum hot pressing furnace? Achieve 98.9% Density in Al2O3-TiC Laminated Ceramics
- How does a vacuum environment system contribute to the hot pressing sintering of B4C-CeB6? Unlock Peak Ceramic Density
- What technical advantages does a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace provide? Enhance Fe-Ni/Zr2P2WO12 Composite Density
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace? Superior Density for Nanocrystalline Fe3Al
- What are the primary advantages of using a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace? Maximize Density in B4C-CeB6 Ceramics



















