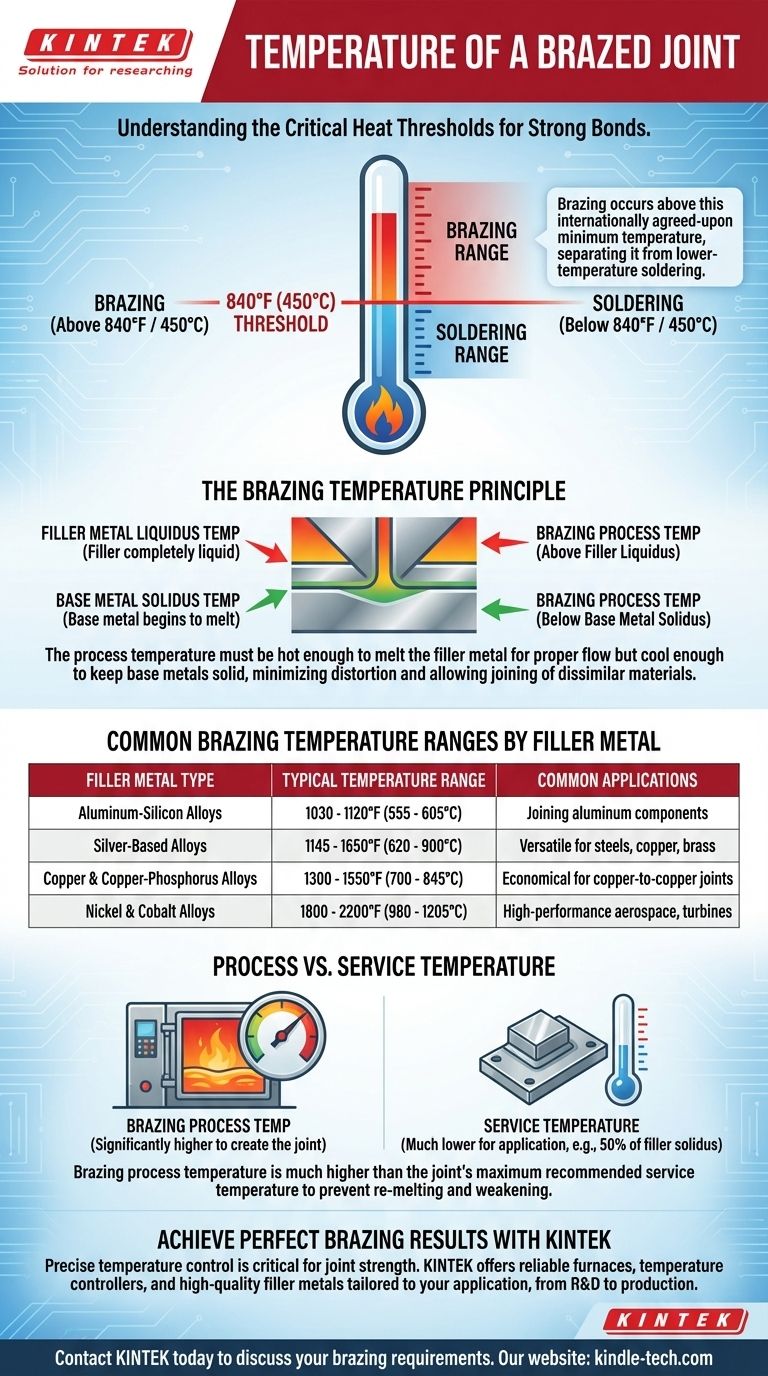
The temperature of a brazed joint is defined by the specific filler metal being used, but the process always occurs at temperatures above 840°F (450°C). This minimum temperature is the internationally agreed-upon threshold that separates brazing from the lower-temperature process of soldering. The actual brazing temperature will be slightly above the melting point of the filler alloy but always below the melting point of the parts being joined.
The critical temperature in brazing is not a single value but a specific range dictated by the chosen filler metal. The process must be hot enough to melt the filler but cool enough to keep the base metals solid, a principle that fundamentally distinguishes it from welding.

The Defining Role of Temperature in Brazing
Understanding the temperatures involved is core to understanding the entire brazing process. It governs everything from material selection to the final strength of the joint.
The 840°F (450°C) Threshold
This temperature is the official line between soldering and brazing. Any process using a filler metal that melts below this point is soldering; any process above it is brazing.
Filler Metal's Liquidus Temperature
Every brazing filler alloy has a liquidus temperature, which is the point at which it becomes completely liquid. To ensure the filler flows properly into the joint via capillary action, the brazing process temperature must be set slightly above the filler's liquidus.
Staying Below the Solidus of Base Metals
Conversely, every material has a solidus temperature, where it begins to melt. A core principle of brazing is that the process temperature must remain safely below the solidus of the metals being joined. This prevents the base parts from melting, which minimizes thermal distortion and makes it possible to join dissimilar metals.
Common Brazing Temperature Ranges by Filler Metal
The required temperature is a direct function of the filler metal's composition. Different alloys are used for different base metals and applications, each with its own working range.
Aluminum-Silicon Alloys
These fillers are used to join aluminum components. Their low melting point is essential to avoid melting the aluminum base metal, which itself has a relatively low melting point.
- Typical Range: 1030 - 1120°F (555 - 605°C)
Silver-Based Alloys
Often called "silver solders" (a technical misnomer), these are some of the most versatile and widely used filler metals for joining steels, copper, and brass.
- Typical Range: 1145 - 1650°F (620 - 900°C)
Copper and Copper-Phosphorus Alloys
These are economical choices used primarily for joining copper to copper (often without flux) or other copper-based alloys like brass and bronze.
- Typical Range: 1300 - 1550°F (700 - 845°C)
Nickel and Cobalt Alloys
Used in high-performance applications like aerospace engines and industrial turbines, these fillers provide exceptional strength and corrosion resistance at high service temperatures.
- Typical Range: 1800 - 2200°F (980 - 1205°C)
Understanding the Trade-offs: Process vs. Service Temperature
A common point of confusion is the difference between the temperature required to create the joint and the temperature the joint can withstand in its final application.
Process Temperature vs. Operating Temperature
The brazing process temperature is always significantly higher than the joint's maximum recommended service temperature. The filler metal re-solidifies as it cools, but it will lose strength and begin to soften long before it reaches its original melting point.
The Rule of Thumb
As a general guideline, a brazed joint should not be used in applications where the service temperature exceeds 50% of the filler metal's solidus temperature. For critical applications, this must be verified by the filler metal manufacturer's specifications.
The Risk of Overheating
Exceeding the proper brazing temperature or getting too close to the base metal's melting point can cause significant problems. These include distortion of the parts, undesirable grain growth in the metal, or even complete failure of the component. Precise temperature control is essential.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct brazing temperature is about matching the filler metal to the base materials and the demands of the final product.
- If your primary focus is joining common metals like copper or steel: Start with silver-based filler alloys, which offer a versatile temperature range of 1145-1650°F (620-900°C) suitable for most general-purpose work.
- If your primary focus is joining heat-sensitive or dissimilar materials: Choose a filler metal with the lowest possible liquidus temperature that still meets your strength requirements to minimize thermal stress on the components.
- If your primary focus is high-performance aerospace or turbine applications: You must work with nickel or cobalt-based alloys in a controlled atmosphere, requiring process temperatures exceeding 1800°F (980°C) to achieve the necessary strength.
Mastering brazing begins with understanding that temperature is not just a setting, but the key to controlling the metallurgical bond itself.
Summary Table:
| Filler Metal Type | Typical Brazing Temperature Range | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Aluminum-Silicon Alloys | 1030 - 1120°F (555 - 605°C) | Joining aluminum components |
| Silver-Based Alloys | 1145 - 1650°F (620 - 900°C) | Versatile for steels, copper, brass |
| Copper & Copper-Phosphorus | 1300 - 1550°F (700 - 845°C) | Economical for copper-to-copper joints |
| Nickel & Cobalt Alloys | 1800 - 2200°F (980 - 1205°C) | High-performance aerospace, turbines |
Achieve Perfect Brazing Results with KINTEK
Selecting the right brazing temperature is critical for joint strength and integrity. Whether you're working with sensitive aluminum components or high-temperature nickel alloys, KINTEK's expertise in lab equipment and consumables ensures you have the precise tools and materials needed for success.
We provide reliable furnaces, temperature controllers, and high-quality filler metals tailored to your specific application—from R&D to production. Let our team help you optimize your brazing process for superior, repeatable results.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your brazing requirements and discover how our solutions can enhance your laboratory's capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- Where are vacuum furnaces used? Essential for High-Purity Heat Treatment in Critical Industries
- What are the factors that affect the strength of a brazed joint? Master the 4 Keys to a Perfect Bond
- What is a braze repair process? A Low-Heat Solution for Strong, Seamless Metal Joining
- What is the major advantage that brazing has over welding? Joining Dissimilar Metals with Ease
- What is the most important factor influencing the strength of the brazed joint? Master Joint Clearance for Maximum Strength



















