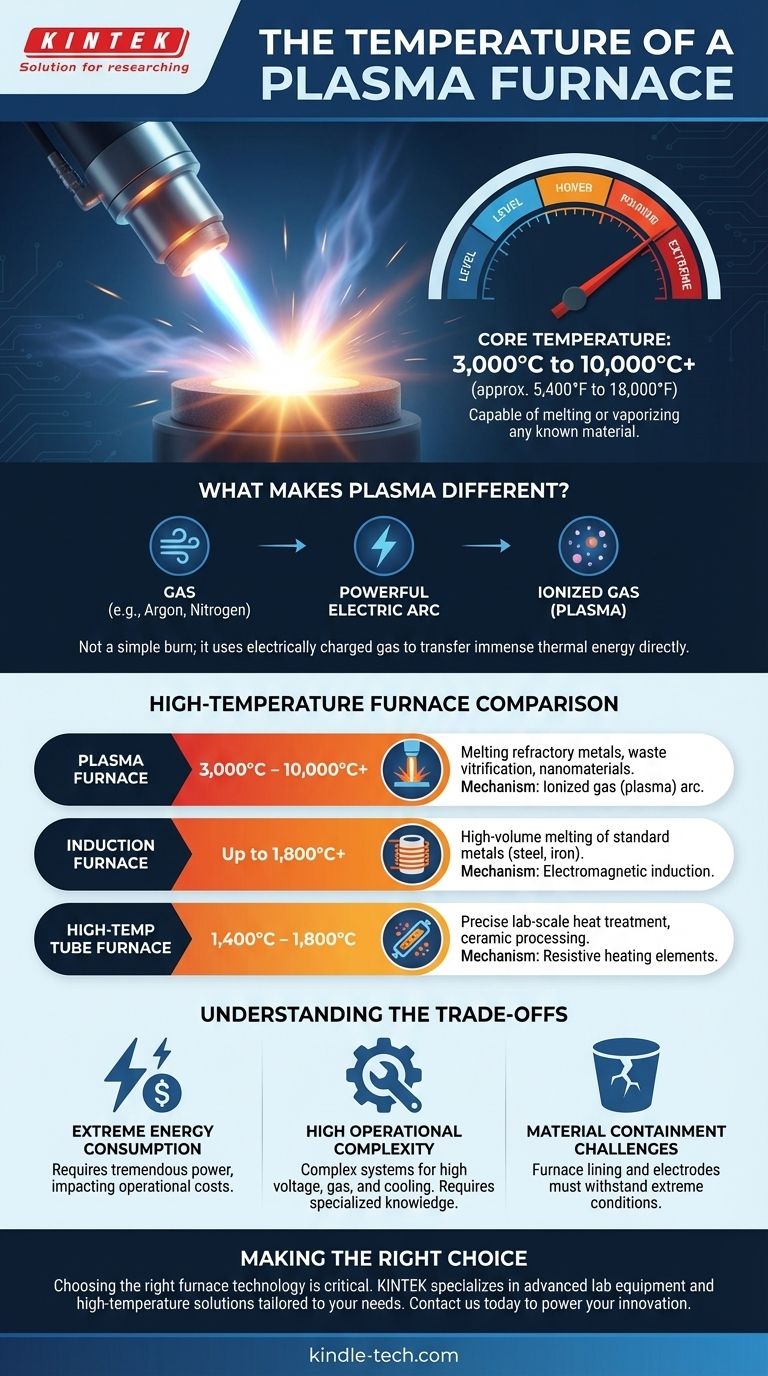
In short, a plasma furnace operates at exceptionally high temperatures, with the core of the plasma arc typically reaching between 3,000°C and 10,000°C (approximately 5,400°F to 18,000°F). In some specialized applications, these temperatures can climb even higher, far exceeding the capabilities of conventional heating technologies.
The critical takeaway is that a plasma furnace's temperature isn't just a higher number; it represents a fundamentally different state of matter. It uses electrically charged gas (plasma) to transfer energy, unlocking temperatures capable of melting or vaporizing any known material.
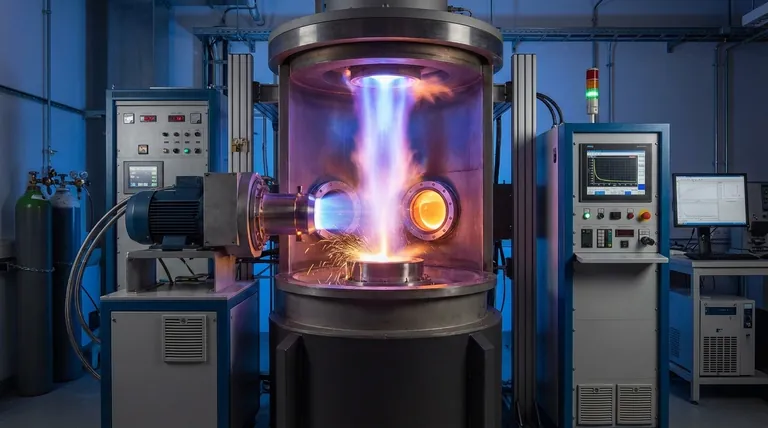

What Makes Plasma Furnaces Different?
To understand the extreme temperatures, we must first understand the technology's core principle. A plasma furnace doesn't "burn" a fuel or use a simple heating element in the traditional sense.
From Gas to Plasma
A plasma furnace works by passing a gas, such as argon or nitrogen, through a powerful electric arc. This arc strips electrons from the gas atoms, creating an ionized gas, which is the state of matter known as plasma.
Direct and Intense Energy Transfer
This plasma stream, often directed by a plasma torch, contains immense thermal energy. When this stream strikes the target material (the "charge"), it transfers its energy with incredible efficiency and speed, leading to rapid heating and melting.
How Plasma Compares to Other High-Temp Furnaces
The temperatures achieved by plasma are in a class of their own. Placing them in context with other common industrial furnaces highlights the significant difference in capability.
Plasma Furnaces (3,000°C to 10,000°C)
These furnaces are used for the most demanding applications, such as waste vitrification (turning hazardous waste into inert glass), melting highly refractory metals like tungsten, or producing specialized nanomaterials.
Induction Furnaces (Up to 1,800°C+)
As noted, an induction furnace can reach temperatures of 1800ºC or more. It works by using powerful magnetic fields to induce an electric current within the conductive material itself, causing it to heat from the inside out. This is highly efficient for melting metals like steel and iron but operates well below plasma's potential.
High-Temperature Tube Furnaces (1,400°C to 1,800°C)
These furnaces rely on resistive heating elements to heat a chamber. They can achieve temperatures between 1400°C and 1800°C and are excellent for processes requiring precise temperature control in a controlled atmosphere, like in laboratory settings or for treating high-performance ceramics.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The immense power of a plasma furnace comes with significant operational considerations that make it unsuitable for every application.
Extreme Energy Consumption
Creating and sustaining a plasma arc requires a tremendous amount of electrical energy. The power consumption is a primary factor in its operational cost and limits its use to applications where such heat is absolutely necessary.
High Operational Complexity
These are not simple devices. They involve complex systems for managing high-voltage electricity, gas flow, and cooling. Operating and maintaining them requires highly specialized knowledge and stringent safety protocols.
Material Containment Challenges
The furnace lining and electrodes themselves must be made of materials capable of withstanding the extreme temperatures and harsh conditions inside the furnace. This adds to the cost and maintenance complexity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The right heating technology is entirely dependent on the material and the desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is melting refractory materials or vitrifying hazardous waste: A plasma furnace is the only viable option due to its unparalleled temperature capabilities.
- If your primary focus is efficient, high-volume melting of standard metals like steel or aluminum: An induction furnace provides excellent control, speed, and energy efficiency for this temperature range.
- If your primary focus is precise, controlled heat treatment or laboratory-scale material synthesis: A high-temperature tube furnace offers the stability and controlled atmosphere required for these sensitive tasks.
Ultimately, understanding the core heating mechanism is the key to selecting the right tool for your high-temperature application.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Type | Typical Temperature Range | Core Heating Mechanism | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Plasma Furnace | 3,000°C to 10,000°C+ | Ionized gas (plasma) arc | Melting refractory metals, waste vitrification, nanomaterials |
| Induction Furnace | Up to 1,800°C+ | Electromagnetic induction | High-volume melting of standard metals (steel, iron) |
| High-Temp Tube Furnace | 1,400°C to 1,800°C | Resistive heating elements | Precise lab-scale heat treatment, ceramic processing |
Ready to harness extreme heat for your most challenging projects?
Choosing the right furnace technology is critical to your success. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing advanced lab equipment, including high-temperature solutions tailored to your specific material and process requirements.
Our experts can help you determine if a plasma, induction, or tube furnace is the right choice for your application—ensuring you achieve the precise results you need with optimal efficiency.
Contact us today to discuss your high-temperature challenges and discover how KINTEK's solutions can power your innovation. ➡️ Get in touch via our contact form
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the temperature of a tube furnace? A Guide to High-Temp Heating Elements & Control
- What is the technical value of using a quartz tube reaction chamber for static corrosion testing? Achieve Precision.
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace facilitate the phase transformation of alumina products? Master Thermal Control
- What is a tubular furnace used for? Precision Heating for Material Synthesis & Analysis
- How do a quartz tube reactor and atmosphere furnace collaborate in Co@NC pyrolysis? Master Precision Synthesis



















