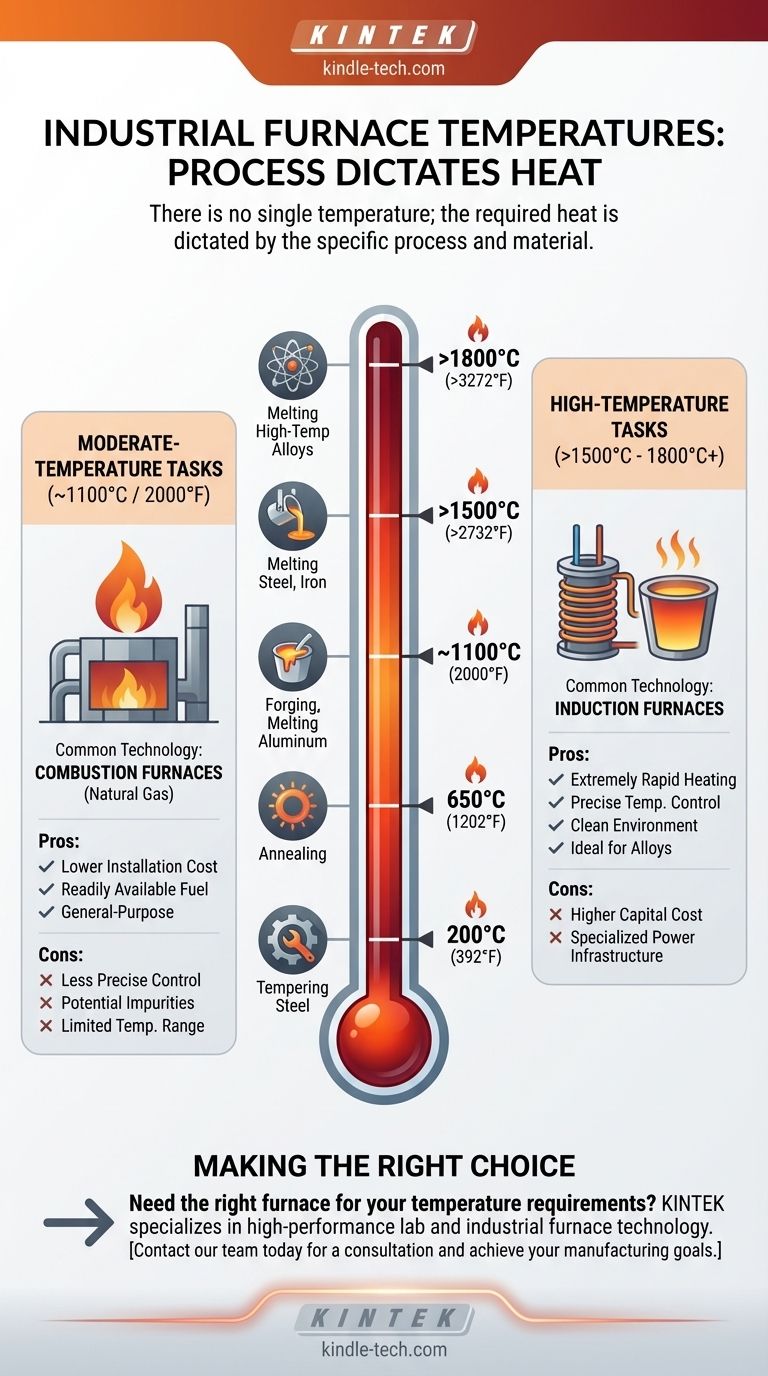
There is no single temperature for an industrial furnace; the required heat is dictated entirely by the furnace's specific application and the materials being processed. Temperatures can range from a few hundred degrees for tempering to well over 1800°C (3272°F) for melting high-temperature alloys, with different furnace technologies designed to meet these distinct needs.
The temperature of an industrial furnace is not a fixed property of the furnace itself, but a function of the industrial process it serves. The specific material and desired transformation—such as melting, forging, or heat treating—determine the required temperature, which in turn dictates the appropriate furnace technology.

Why Temperature Varies: Process Dictates Technology
The vast range in furnace temperatures stems from the diverse needs of industrial manufacturing. The goal is always to match the heating technology to the specific requirements of the material and the process.
The Role of the Industrial Process
Different metallurgical or chemical processes require vastly different thermal energy. For example, melting steel requires reaching temperatures above its melting point of ~1500°C.
In contrast, tempering steel to increase its toughness may only require temperatures between 200°C and 650°C. Each process has a specific, and often narrow, optimal temperature window.
Matching Technology to High-Temperature Tasks
For the most demanding applications, such as melting steel, iron, or specialty alloys, specific technologies are required to generate extreme heat efficiently and cleanly.
Induction furnaces are a prime example. By using powerful electromagnetic fields to heat the material directly, they can achieve temperatures exceeding 1800°C. This method is fast, precise, and clean, as the material never comes into contact with fuel or combustion byproducts.
Matching Technology to Moderate-Temperature Tasks
Many common industrial processes do not require the extreme heat needed for melting steel. These include forging, annealing, and melting lower-temperature metals like aluminum or zinc.
For these applications, combustion furnaces, often powered by natural gas, are a common and effective solution. These furnaces can reliably reach temperatures up to approximately 1100°C (2000°F), which is more than sufficient for a wide range of heat treating and non-ferrous metal applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The choice between furnace types is a critical engineering decision based on a balance of performance, cost, and operational complexity. The required temperature is the primary factor, but it is not the only consideration.
Combustion Furnaces
Combustion furnaces, like those using natural gas, are often less expensive to install and can be powered by readily available fuel sources. They are workhorses for general-purpose heating.
However, they offer less precise temperature control and can introduce impurities into the material from the combustion process. Their operational temperature is also limited compared to specialized electric furnaces.
Induction Furnaces
Induction furnaces offer superior performance, including extremely rapid heating, highly precise temperature control, and a cleaner operating environment that protects material purity. This is why they are essential for high-performance alloys.
The primary trade-off is cost. Induction furnaces have a significantly higher initial capital cost and require specialized electrical infrastructure to support their high power consumption.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct furnace technology begins with a clear understanding of your process requirements, especially the target temperature.
- If your primary focus is melting steel, iron, or high-performance alloys: An induction furnace is necessary to achieve the required temperatures (often over 1500°C) with the necessary process purity.
- If your primary focus is heat treating, forging, or melting non-ferrous metals like aluminum: A natural gas combustion furnace is often the more practical and cost-effective choice, providing sufficient heat up to ~1100°C.
Ultimately, understanding your material's transformation requirements is the first and most critical step in determining the necessary furnace technology.
Summary Table:
| Process / Material | Typical Temperature Range | Common Furnace Technology |
|---|---|---|
| Tempering Steel | 200°C - 650°C (392°F - 1202°F) | Combustion Furnace |
| Forging, Annealing, Melting Aluminum | Up to ~1100°C (~2000°F) | Combustion Furnace |
| Melting Steel | >1500°C (>2732°F) | Induction Furnace |
| Melting High-Temperature Alloys | >1800°C (>3272°F) | Induction Furnace |
Ready to find the right furnace for your specific temperature requirements?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab and industrial furnace technology. Whether your process demands the extreme heat of an induction furnace for melting alloys or the reliable performance of a combustion system for heat treating, our experts will help you select the perfect equipment to ensure efficiency, purity, and precise temperature control.
Contact our team today for a personalized consultation and let us help you achieve your manufacturing goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Why is a vacuum oven necessary for drying NVOPF electrode sheets? Ensure Battery Stability and Purity
- Are steel containing carbon used for carburizing? The Right Steel for a Hard Surface & Tough Core
- What is the role of an industrial-grade high-temperature furnace in processing TP316H? Precision Thermal Control
- What is the length of time which heat is applied during the annealing heat treatment process? The Critical Soaking Time Explained
- What role does a two-stage rotary vane vacuum pump play in a radio frequency (rf) plasma carbonitriding system?
- What is vacuum carburizing? Achieve Superior Hardening with Precision & Speed
- How does vacuum brazing work? Achieve Superior, Flux-Free Metal Joining
- What are the three steps in sintering cycle in powder metallurgy? Master the Heat Treatment Process



















