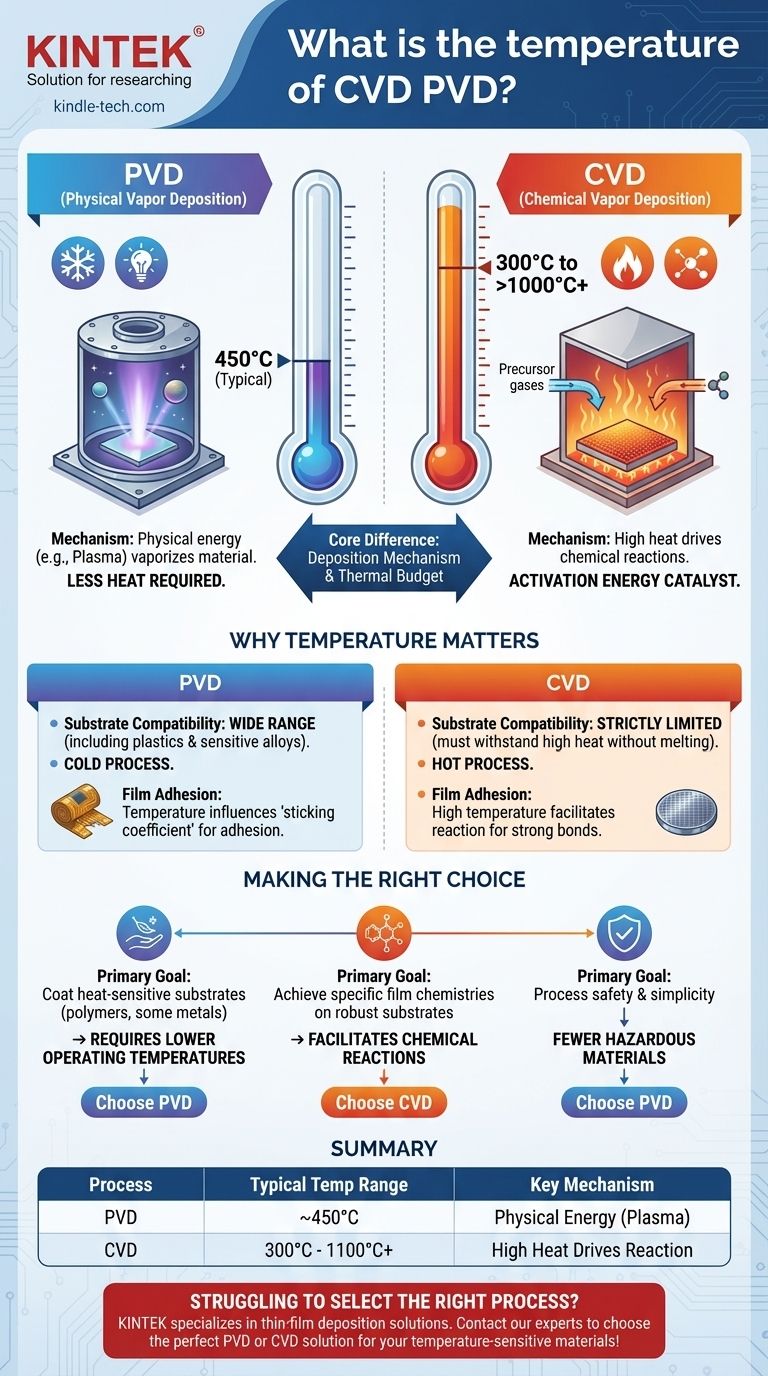
At a fundamental level, Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is a lower-temperature process, typically operating around 450°C. In contrast, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) requires significantly higher temperatures, often ranging from 300°C to over 1000°C, to facilitate the necessary chemical reactions on the substrate's surface.
The core difference is not arbitrary; it stems from the mechanism of deposition. PVD uses physical energy like plasma to vaporize material, requiring less overall heat. CVD relies on high thermal energy to drive chemical reactions, making temperature a critical and defining process parameter.

Why Temperature Is the Deciding Factor
The choice between PVD and CVD often comes down to the thermal budget of your substrate and the desired film properties. Understanding why their temperature profiles differ is key to making an informed decision.
The Role of Heat in CVD
In Chemical Vapor Deposition, precursor gases are introduced into a reaction chamber. High temperature is the catalyst.
The heat, often supplied by a furnace or laser, provides the activation energy needed for these gases to react with each other and with the substrate.
This chemical reaction results in the formation of a solid thin film on the substrate's surface. Without this intense heat, the required chemical bonds would not form.
The Role of Plasma in PVD
Physical Vapor Deposition operates on a different principle. It is a line-of-sight, physical process.
Instead of a chemical reaction, PVD uses methods like sputtering to physically dislodge atoms from a solid target material inside a vacuum chamber.
While the process generates some heat, the plasma provides most of the energy. The substrate does not need to be heated to the extreme temperatures required for a chemical reaction, making PVD an inherently cooler process.
The Practical Implications of Temperature
The thermal requirements of each process have direct and significant consequences for your project, influencing everything from material selection to final film quality.
Substrate Compatibility is Crucial
The high temperatures of CVD (often 600°C to 1100°C) strictly limit the types of materials that can be coated. Only substrates that can withstand this heat without melting, deforming, or degrading are viable candidates.
PVD's lower operating temperature makes it compatible with a much wider range of materials, including plastics, temperature-sensitive alloys, and other substrates that would be destroyed by the CVD process.
Impact on Film Adhesion and Properties
Temperature is a critical variable that influences the "sticking coefficient," or how efficiently the deposited material adheres to the substrate.
The optimal temperature for efficient deposition and strong film adhesion must be considered. In both methods, controlling the substrate temperature is crucial for achieving the desired thickness, uniformity, and quality of the final thin film.
Understanding the Trade-offs Beyond Temperature
While temperature is a primary differentiator, it is not the only factor. A complete evaluation must include other process characteristics.
Process Complexity and Safety
CVD is often a more complex process and frequently involves the use of toxic, corrosive, or flammable precursor gases, which requires stringent safety protocols.
PVD is generally considered a safer process as it does not rely on hazardous chemicals. However, proper chamber ventilation is still critical to mitigate any risks associated with the vacuum environment.
Material Deposition and Versatility
Both methods are highly capable, producing thin films from a few nanometers to several microns thick.
The choice can also depend on the specific material being deposited. For some materials, the high temperatures required for CVD may exceed their boiling point, making PVD the only practical option.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct deposition method requires aligning the process capabilities with your primary goal. Use the thermal budget of your substrate as the starting point for your decision.
- If your primary focus is coating heat-sensitive substrates (like polymers or certain metals): PVD is the necessary choice due to its significantly lower operating temperatures.
- If your primary focus is achieving specific film chemistries on a robust, heat-tolerant substrate: CVD is a powerful option, as the high temperature facilitates chemical reactions that can produce highly pure or complex films.
- If your primary focus is process safety and simplicity: PVD generally involves fewer hazardous materials and a less complex setup, making it a more straightforward process to manage.
Ultimately, your decision rests on matching the process's thermal requirements to the limitations of your material.
Summary Table:
| Process | Typical Temperature Range | Key Mechanism |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) | 300°C - 1100°C+ | High heat drives chemical reactions on the substrate. |
| Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) | ~450°C | Physical energy (e.g., plasma) vaporizes material; less heat required. |
Struggling to select the right deposition process for your temperature-sensitive materials? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables for thin-film deposition. Our experts can help you choose the perfect PVD or CVD solution to ensure strong film adhesion and protect your substrates. Contact our team today to discuss your specific application needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
People Also Ask
- What are the examples of CVD method? Discover the Versatile Applications of Chemical Vapor Deposition
- What is the difference between CVD and PECVD? Choose the Right Thin-Film Deposition Method
- How plasma is generated in PECVD? A Step-by-Step Breakdown of the Process
- How are PECVD and CVD different? A Guide to Choosing the Right Thin-Film Deposition Process
- What are the advantages of PECVD over CVD? Achieve High-Quality Thin Films at Lower Temperatures



















