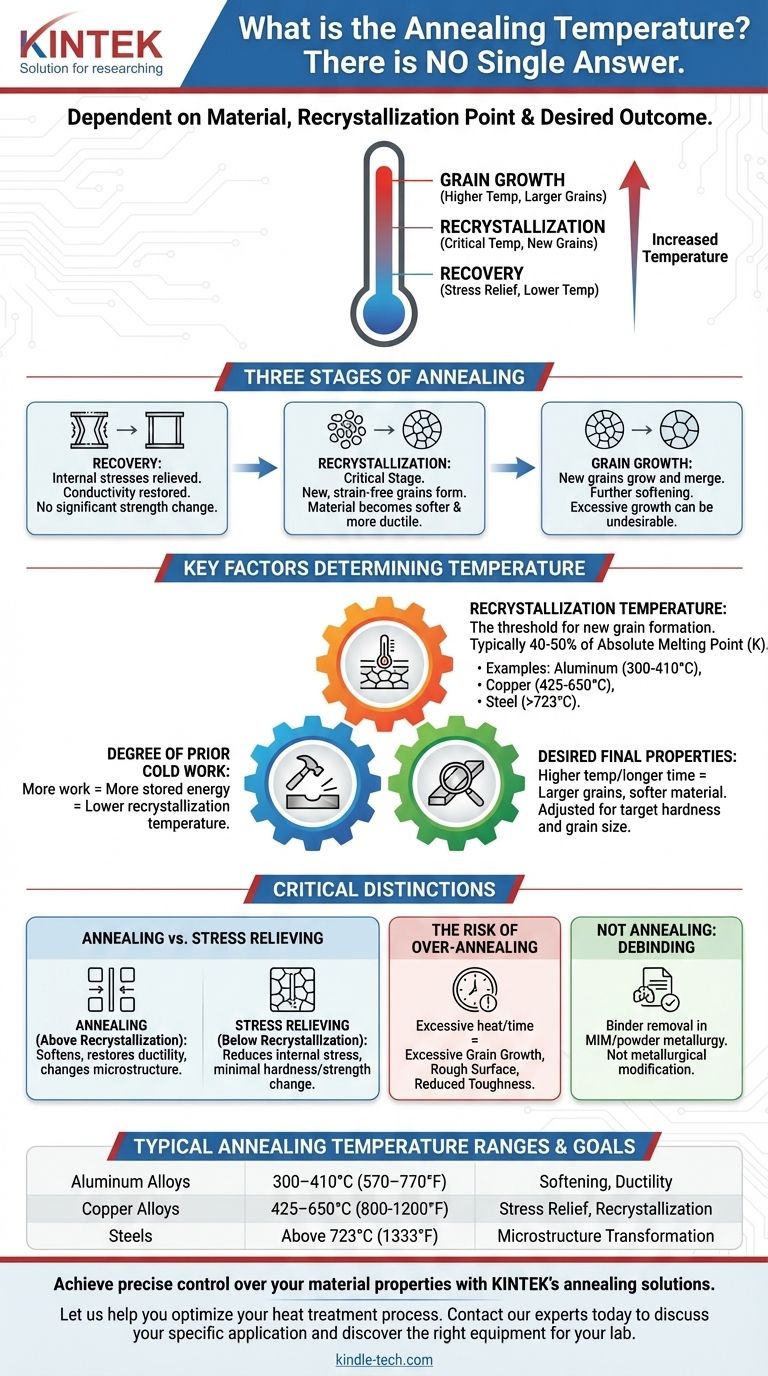
There is no single temperature for the annealing process. The correct temperature is entirely dependent on the specific material being treated and the desired outcome, as it is fundamentally tied to the material's unique recrystallization point.
Annealing is not a fixed-temperature recipe but a controlled heating and cooling cycle designed to alter a material's internal structure. The target temperature is chosen relative to the material’s specific recrystallization temperature to achieve goals like softening, stress relief, or improved ductility.

What is Annealing? The Goal of Heat Treatment
Annealing is a fundamental heat treatment process used to reverse the effects of work hardening. When a metal is bent, rolled, or drawn (a process known as cold working), its internal crystal structure becomes strained and distorted, making it harder but also more brittle.
The Purpose: Restoring Ductility
The primary goal of annealing is to soften the material and restore its ductility. This allows the material to be worked further without fracturing.
The process involves heating the material to a specific temperature, holding it there for a period, and then cooling it slowly. This controlled cycle allows the material's internal microstructure to reform into a more stable, stress-free state.
The Three Stages of Annealing
Annealing unfolds in three distinct stages as the temperature rises:
- Recovery: At lower temperatures, internal stresses from cold working are relieved. The material's electrical conductivity is restored, but there is no significant change in its strength or hardness.
- Recrystallization: This is the critical stage. When the material reaches its recrystallization temperature, new, strain-free grains begin to form and replace the old, deformed ones. This is where the material becomes significantly softer and more ductile.
- Grain Growth: If the material is held at or above the recrystallization temperature for too long, the new grains will begin to grow and merge. This can further soften the material but may sometimes be undesirable if it leads to poor surface finish or other negative properties.
Key Factors That Determine Annealing Temperature
Choosing the right annealing temperature is a precise engineering decision. The temperature is not arbitrary; it is dictated by the material's physics.
The Material's Recrystallization Temperature
The most important factor is the recrystallization temperature. This is the threshold at which new grains begin to form. As a rule of thumb, this temperature is typically 40-50% of the material's absolute melting point (measured in Kelvin).
- Low-melting-point metals like lead and tin can recrystallize at room temperature.
- Aluminum alloys anneal at approximately 300–410°C (570–770°F).
- Copper alloys anneal over a wide range, often between 425-650°C (800-1200°F).
- Steels have a more complex behavior tied to their carbon content and phase diagrams, typically requiring annealing above 723°C (1333°F) to transform their structure into austenite.
The Degree of Prior Cold Work
The more a material has been cold-worked, the more stored energy it contains. This stored energy lowers the temperature required to start recrystallization.
A heavily deformed part will anneal at a slightly lower temperature or in a shorter time than a lightly worked part of the same material.
The Desired Final Properties
The final annealing temperature and holding time are adjusted to achieve a target grain size and hardness. A higher temperature or longer time generally results in larger grains and a softer material.
Understanding the Critical Distinctions
It is easy to confuse annealing with other heat-based processes. Making the correct distinction is critical for achieving the intended engineering outcome.
Annealing vs. Stress Relieving
Stress relieving is performed at a much lower temperature, below the recrystallization point. Its only goal is to reduce internal stresses created during manufacturing (like welding or machining) without significantly changing the material's hardness or strength.
The Risk of Over-Annealing
Heating a material too high or for too long can cause excessive grain growth. While this makes the material very soft, it can also lead to a rough "orange peel" surface texture during subsequent forming operations or, in some cases, reduced toughness.
Clarifying "Debinding"
The process mentioned in the reference, debinding, is not annealing. Debinding is a step in powder metallurgy or metal injection molding (MIM) where a polymer binder is burned away from the "green" part before the final sintering step.
While debinding involves heating to temperatures that can be in the range of some annealing cycles (e.g., up to 600°C), its purpose is entirely different. It is about binder removal, not metallurgical property modification.
Selecting the Correct Annealing Parameters
To properly anneal a material, you must move beyond generic numbers and focus on the specific goal for your chosen alloy.
- If your primary focus is maximum softness for severe forming: You will need to perform a full anneal, heating the material well above its recrystallization temperature to ensure a complete transformation.
- If your primary focus is simply relieving internal stress after welding: A lower-temperature stress relief cycle, performed below the critical recrystallization point, is the correct and more efficient choice.
- If you are working with carbon steel: You must consult the iron-carbon phase diagram to select the precise temperature needed to achieve the desired microstructure (e.g., full austenitization).
Ultimately, the correct annealing temperature is a function of the material's fundamental properties and your engineering goal.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Typical Annealing Temperature Range | Key Goal |
|---|---|---|
| Aluminum Alloys | 300–410°C (570–770°F) | Softening, Ductility |
| Copper Alloys | 425-650°C (800-1200°F) | Stress Relief, Recrystallization |
| Steels | Above 723°C (1333°F) | Microstructure Transformation |
| Low-Melting Metals (e.g., Lead) | Near Room Temperature | Recrystallization |
Achieve precise control over your material properties with KINTEK's annealing solutions.
Whether you're working with aluminum, copper, steel, or other alloys, selecting the correct annealing temperature is critical for achieving the desired hardness, ductility, and stress relief. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing the reliable furnaces and expert support your laboratory needs to perform perfect annealing cycles every time.
Let us help you optimize your heat treatment process. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and discover the right equipment for your lab.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the five basic heat treatment processes of metals? Master Annealing, Hardening & More
- What is a vacuum heat treatment furnace? The Ultimate Guide to Controlled Atmosphere Processing
- What is the difference between annealing hardening and tempering? Master Metal Properties for Your Lab
- What are the parts of a vacuum furnace? A Guide to the 5 Core Systems
- How does heat treatment process work? Tailor Material Properties for Your Application



















