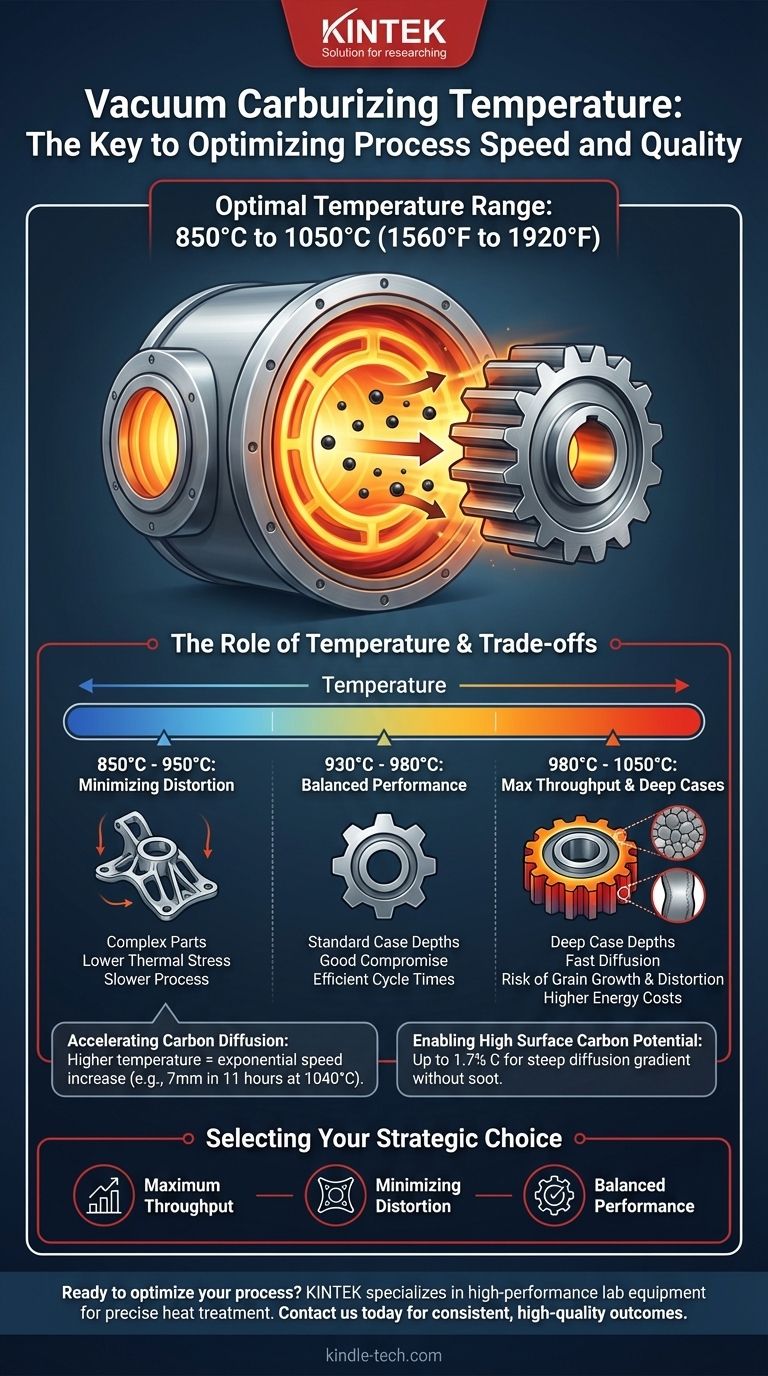
In practice, vacuum carburizing is typically performed within a temperature range of 850°C to 1050°C (1560°F to 1920°F). The specific temperature is a critical process variable chosen to balance processing speed with the final metallurgical properties of the component. While many applications use a moderate range, high temperatures like 1040°C (1900°F) are used to dramatically accelerate the process and achieve very deep case depths that would be impractical with other methods.
The core advantage of vacuum carburizing is its ability to operate cleanly at very high temperatures. This allows for a significant increase in carbon diffusion rates, enabling deeper case hardening in a fraction of the time required by traditional atmospheric gas carburizing.

The Role of Temperature in Process Efficiency
Temperature is the primary driver of diffusion speed in any carburizing process. The unique environment of a vacuum furnace, however, allows for a much more aggressive use of high temperatures to optimize the cycle.
Accelerating Carbon Diffusion
The rate at which carbon atoms diffuse into the surface of steel is exponentially related to temperature. Raising the temperature gives the atoms more energy, allowing them to move through the steel's crystal lattice much faster.
For example, performing vacuum carburizing at a high temperature of 1040°C can achieve a 7 mm case depth in approximately 11 hours. Achieving a similar depth with conventional methods at lower temperatures would take significantly longer, often making it economically unfeasible.
Enabling High Surface Carbon Potential
The clean, oxygen-free vacuum environment allows for the use of a very high surface carbon concentration, sometimes up to 1.7% C, as mentioned in process examples. This high concentration on the surface, combined with the high temperature, creates a steep "gradient" that effectively pushes carbon into the part more rapidly.
In traditional gas carburizing, operating at such high temperatures and carbon potentials would lead to excessive soot formation, causing process variations and significant furnace maintenance challenges.
Understanding the Trade-offs of High-Temperature Processing
While high temperatures offer significant speed advantages, they also introduce critical metallurgical and mechanical trade-offs that must be carefully managed.
Risk of Grain Growth
The most significant metallurgical concern with high-temperature carburizing is grain growth. Holding steel at temperatures above its normal austenitizing range for extended periods can cause its microscopic crystalline grains to coarsen.
Larger grains can negatively impact the final mechanical properties of the part, particularly its toughness and fatigue resistance. This risk must be mitigated by selecting specific "fine-grain practice" steels and carefully controlling the time spent at peak temperature.
Increased Potential for Distortion
Higher processing temperatures create greater thermal gradients, especially during the quenching phase that follows carburizing. This can increase the risk of part distortion, a critical concern for components with complex geometries or tight dimensional tolerances.
Furnace Capability and Energy Costs
Sustained operation at temperatures above 1000°C places significant demands on furnace hardware, including heating elements and insulation. It also naturally consumes more energy. These factors influence the overall cost of the operation and must be weighed against the benefits of shorter cycle times.
Selecting the Right Temperature for Your Goal
The optimal vacuum carburizing temperature is not a single number but a strategic choice based on the desired outcome for a specific component.
- If your primary focus is maximum throughput and deep case depth: Use higher temperatures (980°C to 1040°C), but ensure you are using a suitable fine-grain steel and have a process designed to manage potential distortion.
- If your primary focus is minimizing distortion on complex parts: Use lower, more conventional temperatures (900°C to 950°C) to reduce thermal stresses, accepting that this will result in longer cycle times.
- If your primary focus is a balance of performance and cost: A moderate temperature range (around 930°C to 980°C) often provides an excellent compromise between efficient cycle times and minimal metallurgical risk for standard case depths.
Ultimately, temperature in vacuum carburizing is a powerful lever that, when understood, allows you to precisely control the trade-off between process speed and final part quality.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Range | Common Use Case | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| 850°C - 950°C | Minimizing distortion on complex parts | Slower process, lower thermal stress |
| 930°C - 980°C | Balanced performance and cost | Good compromise for standard case depths |
| 980°C - 1050°C | Maximum throughput and deep case depths | Risk of grain growth, requires fine-grain steels |
Ready to optimize your vacuum carburizing process? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables for precise heat treatment applications. Our expertise helps laboratories achieve superior results with efficient temperature control and process optimization. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your carburizing operations and deliver consistent, high-quality outcomes for your specific laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why do you heat treat in a vacuum? Achieve Perfect Surface Finish and Material Integrity
- What are the three main heat treatments? Mastering Annealing, Hardening & Tempering
- What is the process of vacuum quenching? Achieve Superior Hardness with a Pristine Surface Finish
- What are the five basic heat treatment processes of metals? Master Annealing, Hardening & More
- What is a vacuum heat treatment furnace? The Ultimate Guide to Controlled Atmosphere Processing



















