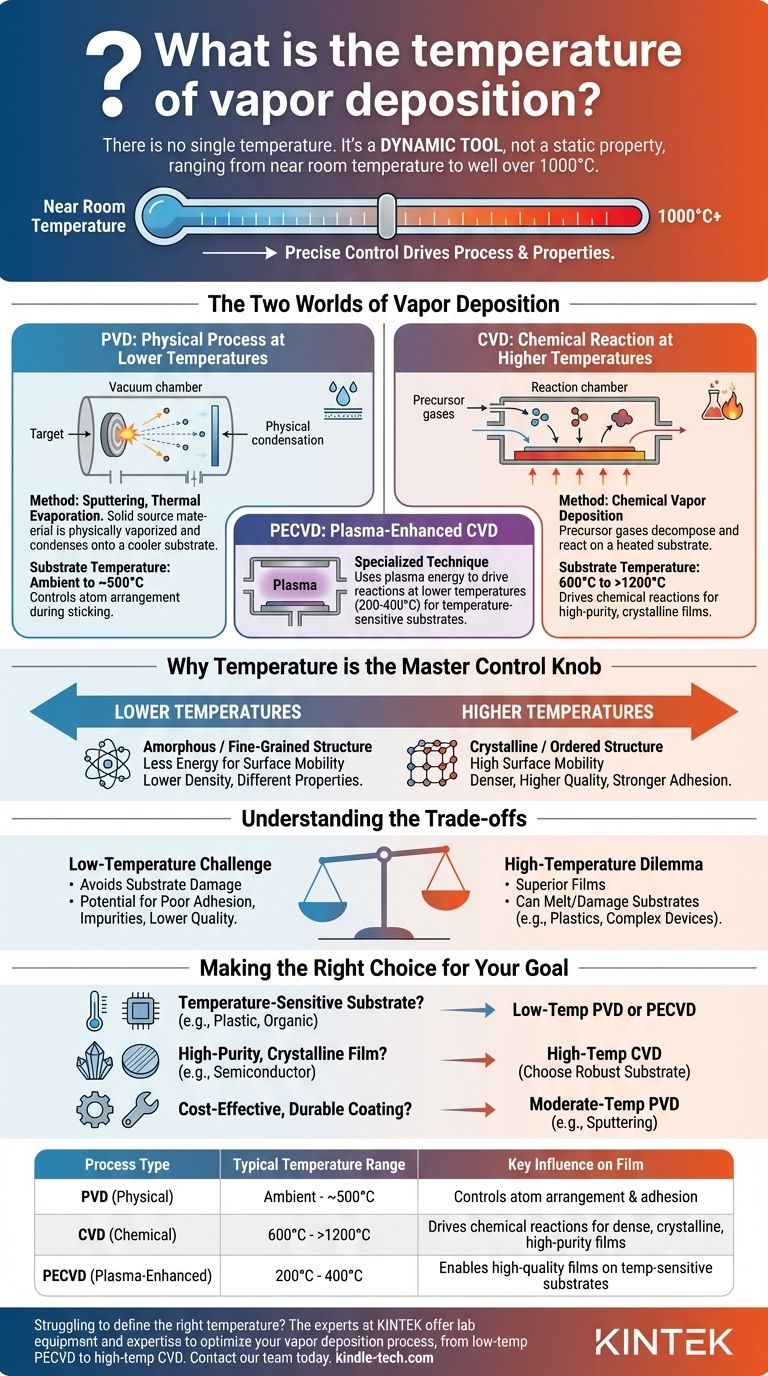
There is no single temperature for vapor deposition. The required temperature is not a fixed number but a critical process parameter that can range from near room temperature to well over 1000°C, depending entirely on the specific technique used and the materials being deposited.
The central concept to grasp is that temperature is not a static property of vapor deposition, but rather a dynamic tool. It is precisely controlled to drive either a physical process (like in PVD) or a chemical reaction (like in CVD) to achieve a film with specific, desired properties.
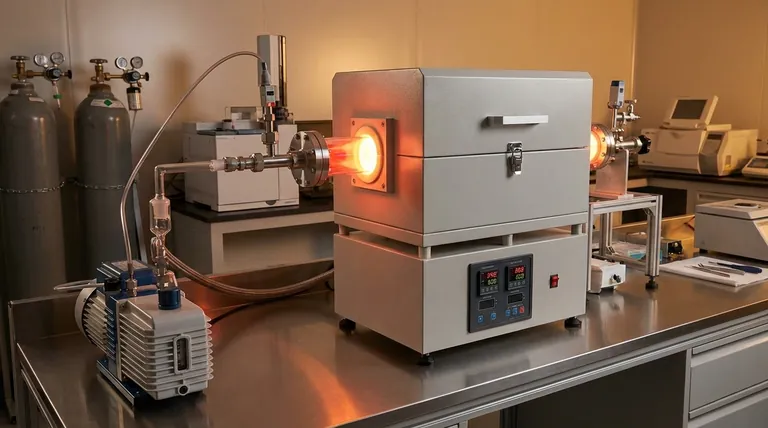

The Two Worlds of Vapor Deposition
To understand the role of temperature, you must first distinguish between the two main families of vapor deposition: Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) and Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD).
PVD: A Physical Process at Lower Temperatures
Physical Vapor Deposition includes methods like sputtering and thermal evaporation. In these processes, a solid source material is bombarded with energy, causing atoms or molecules to be ejected into a vacuum chamber.
These ejected particles travel and physically condense onto a cooler substrate, forming a thin film. The substrate temperature is often kept relatively low—from ambient temperature up to a few hundred degrees Celsius—primarily to control how the atoms arrange themselves as they stick to the surface.
CVD: A Chemical Reaction at Higher Temperatures
Chemical Vapor Deposition is fundamentally different. It involves introducing precursor gases into a reaction chamber where they decompose and react on a heated substrate to form the desired solid film.
This process requires significant thermal energy to break the chemical bonds in the precursor gases and drive the surface reactions. Consequently, CVD temperatures are typically much higher than PVD, often ranging from 600°C to over 1200°C, especially for creating high-purity, crystalline films for industries like semiconductors.
Why Temperature is the Master Control Knob
In both PVD and CVD, the substrate temperature is one of the most powerful levers an engineer has to control the final outcome. It directly influences the microstructure and properties of the deposited film.
Controlling Film Structure and Density
Lower temperatures often lead to an amorphous or fine-grained film structure. The atoms "stick" where they land with little energy to move around, resulting in a less ordered and sometimes less dense film.
Higher temperatures provide the deposited atoms with more surface mobility. This allows them to rearrange into more stable, ordered crystalline structures, resulting in a denser, higher-quality film with different mechanical and electrical properties.
Managing Film Adhesion
Proper temperature control is also critical for ensuring the film adheres strongly to the substrate. A heated substrate can promote better bonding between the first layer of deposited atoms and the surface.
However, a large temperature difference between a hot deposition process and a cool substrate can create internal stresses in the film, potentially causing it to crack or peel off.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a deposition temperature is always a balancing act between achieving the ideal film properties and respecting the limitations of the substrate.
The High-Temperature Dilemma
While high temperatures often produce superior films, they can damage or destroy the underlying substrate. You cannot use a 1000°C CVD process to coat a plastic component, as it would simply melt.
Even with robust substrates like silicon wafers, high temperatures can cause unwanted diffusion of elements or alter previously created structures, posing a significant challenge in complex device fabrication.
The Low-Temperature Challenge
Using a lower temperature avoids damaging the substrate, but it may compromise film quality. Films deposited at low temperatures can suffer from poor adhesion, higher impurity levels, and less desirable structural properties.
To solve this, specialized techniques like Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD) were developed. PECVD uses an energy-rich plasma to help break down precursor gases, allowing the chemical reaction to occur at much lower temperatures (e.g., 200-400°C) while still achieving good film quality.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The optimal temperature is defined by your specific application and constraints.
- If your primary focus is depositing a coating on a temperature-sensitive substrate (like plastic or organic electronics): You will need to investigate low-temperature PVD processes or specialized techniques like Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD).
- If your primary focus is achieving a highly crystalline, dense, and pure film (like for semiconductor manufacturing): You should expect to use a high-temperature CVD process and ensure your substrate material is chosen to withstand it.
- If your primary focus is a cost-effective, durable metal coating on a metal or ceramic part: A PVD process like sputtering at a moderate temperature is often the most practical and widely used solution.
Ultimately, mastering vapor deposition means treating temperature not as a fixed number, but as the most powerful tool for engineering your desired outcome.
Summary Table:
| Process Type | Typical Temperature Range | Key Influence on Film |
|---|---|---|
| PVD (Physical) | Ambient - ~500°C | Controls atom arrangement and adhesion on the substrate surface. |
| CVD (Chemical) | 600°C - >1200°C | Drives chemical reactions for dense, crystalline, high-purity films. |
| PECVD (Plasma-Enhanced) | 200°C - 400°C | Enables high-quality films on temperature-sensitive substrates. |
Struggling to define the right deposition temperature for your substrate and desired film properties? The experts at KINTEK are here to help. We specialize in lab equipment and consumables for vapor deposition, providing the tools and expertise to optimize your process—whether you're working with delicate materials requiring low-temperature PECVD or need high-temperature CVD for semiconductor-grade films. Contact our team today to discuss your specific application and achieve superior results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
People Also Ask
- What is the process of vacuum vapor deposition? Mastering CVD and PVD Thin-Film Coating
- How does PECVD work? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What is PECVD in semiconductor? Enable Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition for ICs
- What is the vapor phase deposition technique? A Guide to PVD & CVD Thin-Film Coating Methods
- What are the methods of deposition? A Guide to PVD and CVD Thin-Film Techniques



















