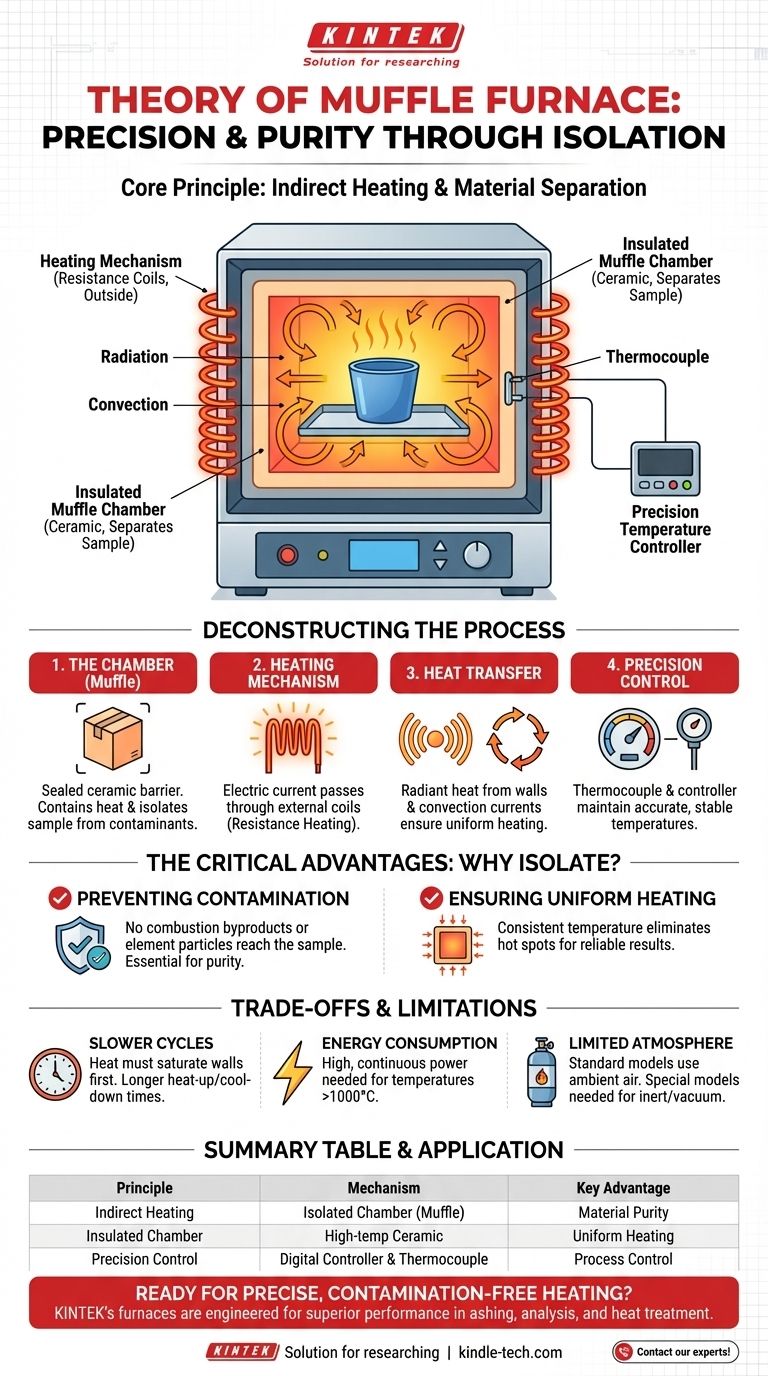
The core principle of a muffle furnace is indirect heating within a controlled environment. It uses a high-temperature chamber—the "muffle"—to heat a material without it ever making direct contact with the source of the heat, such as flames or electric heating elements. Modern muffle furnaces are typically electric, using resistance heating to achieve precise, high temperatures in an atmosphere free from combustion contaminants.
The defining feature of a muffle furnace is not just its ability to reach high temperatures, but its principle of separation. By isolating the heated sample from the energy source and its byproducts, it ensures material purity and enables highly controlled, repeatable thermal processes.

Deconstructing the Working Principle
To understand its theory, it's best to break the furnace down into its fundamental components and processes. This reveals how it achieves both high heat and high purity.
The Insulated Chamber (The "Muffle")
The heart of the furnace is the muffle itself. This is an enclosed chamber, typically rectangular, made from high-temperature refractory materials like dense ceramic.
This chamber serves two functions: it contains the material to be heated and acts as a barrier, isolating it from the outside. Its walls are designed to withstand extreme thermal stress and prevent heat loss.
The Heating Mechanism
While historical muffle furnaces burned fuel like coal or wood, modern versions are almost exclusively electric.
They operate on the principle of resistance heating. Electric current is passed through high-resistance coils (heating elements) often made of materials like Nichrome or Kanthal. As these elements resist the flow of electricity, they convert electrical energy directly into heat, glowing red-hot.
Crucially, these heating elements are located outside the muffle chamber, either wrapped around it or embedded in the furnace's insulated walls.
Heat Transfer: Radiation and Convection
Since the sample does not touch the heating elements, heat must be transferred indirectly. This happens in two main ways:
- Radiation: The hot walls of the muffle chamber radiate thermal energy inward, heating all surfaces of the sample uniformly.
- Convection: The air inside the sealed chamber heats up, creating convection currents that circulate and transfer heat to the sample.
This combined process ensures that the entire sample is heated evenly, avoiding hot spots that could occur with direct flame impingement.
Precision Temperature Control
Modern muffle furnaces include a thermocouple and a digital controller. The thermocouple measures the internal temperature of the chamber in real time.
The controller compares this reading to the user's setpoint and precisely modulates the power sent to the heating elements, allowing for extremely stable and accurate temperature management.
The Critical Advantage: Isolation and Purity
The indirect heating method is not the most energy-efficient way to generate heat, but it provides one overriding advantage that defines the furnace's purpose: purity.
Preventing Contamination
In many scientific and industrial processes, sample contamination is unacceptable. In a fuel-fired furnace, byproducts like soot, ash, and volatile gases would ruin the sample.
By placing the sample inside the muffle, it is completely isolated from these contaminants. Even in electric models, this separation prevents any potential off-gassing or microscopic particles from the heating elements from reaching the sample.
Ensuring Uniform Heating
The enclosed, insulated nature of the muffle creates a highly stable thermal environment. Heat radiates from all walls, ensuring the sample is heated evenly from all sides. This is critical for processes like annealing metals or performing precise chemical analysis.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
No technology is perfect. Acknowledging the trade-offs is key to using a muffle furnace effectively.
Slower Heating Cycles
Because the heat must first saturate the muffle's thick ceramic walls before it can be radiated to the sample, muffle furnaces generally have slower heat-up and cool-down times compared to direct-fire or induction furnaces.
Energy Consumption
Maintaining temperatures of 1000°C or higher requires a significant and continuous input of electrical energy. The insulation is designed to be efficient, but this is inherently an energy-intensive process.
Limited Atmosphere Control (in Basic Models)
A standard muffle furnace heats a sample in ambient air. If a process requires an inert atmosphere (like nitrogen or argon) or a vacuum, a more specialized and expensive furnace with gas ports and vacuum seals is necessary.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To determine if a muffle furnace is the correct tool, consider your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is material purity and analytical precision: A muffle furnace is essential. It is the standard for ashing samples, gravimetric analysis, and heat-treating materials that must remain uncontaminated.
- If your primary focus is rapid, high-volume melting: A direct-fire or large-scale induction furnace might be more time and energy-efficient, as indirect heating is slower.
- If your primary focus is simple high-temperature heat treatment in air: A standard electric muffle furnace is an excellent, reliable, and widely available choice for achieving controlled temperatures.
Ultimately, understanding this principle of separation is the key to leveraging the muffle furnace for precise and reliable results.
Summary Table:
| Principle | Mechanism | Key Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Indirect Heating | Sample is isolated in a chamber (muffle); heat is transferred via radiation/convection. | Material Purity (No contamination from heating elements or combustion byproducts) |
| Insulated Chamber | Made of high-temperature ceramic to contain heat and isolate the sample. | Uniform Heating (Consistent temperature for reliable, repeatable results) |
| Precision Control | Digital controller and thermocouple maintain accurate, stable temperatures. | Process Control (Essential for analytical testing and specific thermal cycles) |
Ready to achieve precise, contamination-free heating in your lab?
KINTEK's muffle furnaces are engineered for superior performance in applications like sample ashing, gravimetric analysis, and heat treatment. Our expertise ensures you get the right equipment for pure, controlled thermal processing.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect muffle furnace for your laboratory's needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between an oven and a muffle furnace? A Guide to Selecting the Right Thermal Equipment
- What is the importance of a muffle? Achieve Purity and Precision in High-Temperature Processes
- Which gas is used in a muffle furnace? Choosing the Right Atmosphere for Your Lab Process
- What is a muffle furnace consist of? A Guide to Its 3 Core Systems for Pure, High-Temp Processing
- What is the mechanism of a muffle furnace? Master Precise, Contaminant-Free Heating



















