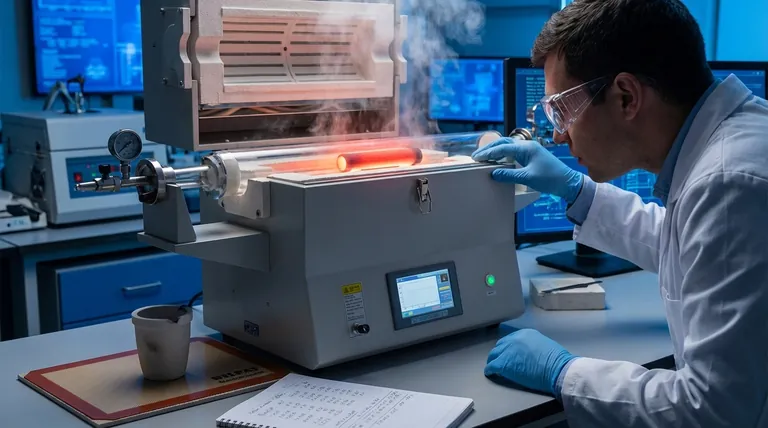
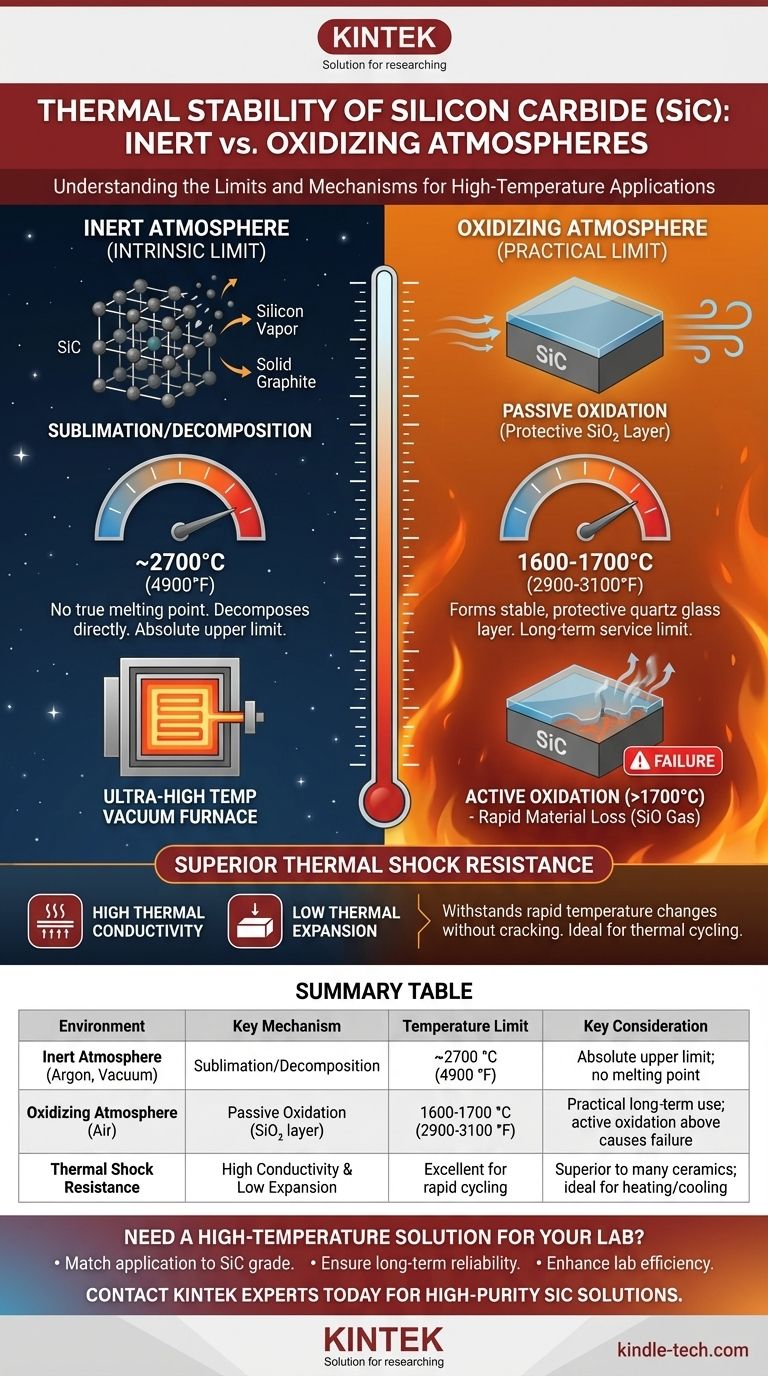
In short, Silicon Carbide (SiC) possesses exceptional thermal stability, but its performance limit is fundamentally determined by the surrounding atmosphere. In an inert environment, it does not melt at atmospheric pressure but instead decomposes at temperatures around 2700 °C (4900 °F). In the presence of oxygen, its practical long-term use is limited to about 1600-1700 °C (2900-3100 °F) due to oxidation.
Silicon Carbide's true value is not a single melting point but its dual nature: it withstands extreme heat through decomposition in inert environments and protects itself via a silica layer in oxidizing environments, making the application's atmosphere the most critical factor.

The Two Regimes of Thermal Stability
To understand if SiC is right for your application, you must distinguish between its intrinsic stability in a vacuum or inert gas and its practical stability in air. These are two very different scenarios with different temperature limits.
Stability in an Inert Atmosphere (Intrinsic Limit)
Under inert conditions (like argon or a vacuum), Silicon Carbide does not have a true melting point at standard pressures.
Instead, it undergoes sublimation or decomposition. This process begins at approximately 2700 °C, where the SiC breaks down directly into silicon vapor and solid graphite (carbon). This temperature represents the absolute upper limit of the material itself.
Stability in an Oxidizing Atmosphere (Practical Limit)
For most real-world applications, such as furnace elements, heat exchangers, or turbine components, SiC is exposed to air (oxygen). This fundamentally changes its behavior.
In an oxygen-rich environment, SiC exhibits what is known as passive oxidation. The surface of the material reacts with oxygen to form a thin, highly stable, and non-porous layer of silicon dioxide (SiO₂), which is essentially quartz glass.
The Role of the Passivation Layer (SiO₂)
This self-forming SiO₂ layer is the key to SiC's success in high-temperature air exposure. It acts as a protective barrier that dramatically slows further oxidation of the underlying SiC.
This passivation layer remains stable and effective for long-term service at temperatures up to approximately 1600 °C. This is why 1600 °C is often cited as the practical operational ceiling for SiC components in air.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Failure Modes
While incredibly robust, SiC is not without its limits. Understanding how and when it fails is critical for reliable system design.
Active vs. Passive Oxidation
Above approximately 1700 °C (or at lower temperatures in low-oxygen-pressure environments), the protective mechanism changes. The process shifts from "passive" to "active" oxidation.
In this regime, the reaction no longer produces a stable SiO₂ layer. Instead, it forms a volatile silicon monoxide (SiO) gas. This leads to rapid material loss, pitting, and ultimately, component failure. Designing for use in air above this temperature is not recommended.
Superior Thermal Shock Resistance
A key advantage of SiC is its exceptional thermal shock resistance. This is its ability to withstand rapid and extreme temperature changes without cracking.
This property is a direct result of two other factors: its high thermal conductivity (it moves heat efficiently, preventing localized hot spots) and its low coefficient of thermal expansion (it expands and contracts very little when heated or cooled). This makes it far superior to many other ceramics in applications involving thermal cycling.
The Impact of Purity and Density
The thermal stability figures cited are for high-purity, fully dense SiC. The presence of impurities (like free silicon or metallic binders) or porosity within the ceramic body can significantly reduce its effective operating temperature. These impurities can create weak points or interfere with the formation of a uniform, protective SiO₂ layer.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting SiC requires you to match its properties to your specific operational environment.
- If your primary focus is ultra-high temperature in a vacuum or inert gas: You can design toward the intrinsic decomposition limit of ~2700 °C, making SiC one of the few viable materials.
- If your primary focus is long-term stability in air or combustion gases: Your safe, practical design ceiling is around 1600 °C, relying on the protective passive oxidation layer.
- If your primary focus is withstanding rapid heating and cooling cycles: SiC's excellent thermal shock resistance makes it a premier choice over other materials that might crack under similar stress.
Ultimately, harnessing the power of Silicon Carbide depends on a clear understanding of your application's atmosphere and thermal demands.
Summary Table:
| Environment | Key Mechanism | Temperature Limit | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inert Atmosphere (Argon, Vacuum) | Sublimation/Decomposition | ~2700 °C (4900 °F) | Absolute upper limit; no melting point |
| Oxidizing Atmosphere (Air) | Passive Oxidation (forms protective SiO₂ layer) | 1600-1700 °C (2900-3100 °F) | Practical long-term use limit; active oxidation above 1700°C causes failure |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | High thermal conductivity & low thermal expansion | Excellent for rapid cycling | Superior to many ceramics; ideal for heating/cooling cycles |
Need a high-temperature solution for your lab?
Silicon Carbide's exceptional thermal stability makes it ideal for demanding applications like furnace elements, heat exchangers, and high-temperature components. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-purity, fully dense SiC lab equipment and consumables tailored to your specific thermal and atmospheric requirements.
Let us help you harness the power of SiC:
- Match your application to the right SiC grade for optimal performance.
- Ensure long-term reliability with materials designed for your operational environment.
- Enhance your lab's efficiency with components built to withstand extreme conditions.
Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK's SiC solutions can solve your high-temperature challenges!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What tube is used for tubular furnace? Choose the Right Material for Temperature & Atmosphere
- What is the function of alumina tubes and alumina wool in a pyrolysis furnace? Optimize Your Biochar Production Quality
- What is the difference between a tubular furnace and a muffle furnace? Choose the Right Tool for Your Application
- How do you clean a tube furnace tube? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe and Effective Cleaning
- What is the pressure on a tube furnace? Essential Safety Limits for Your Lab



















