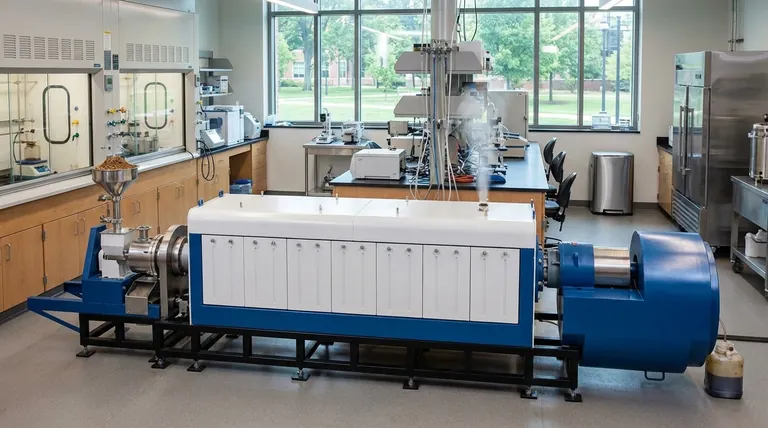
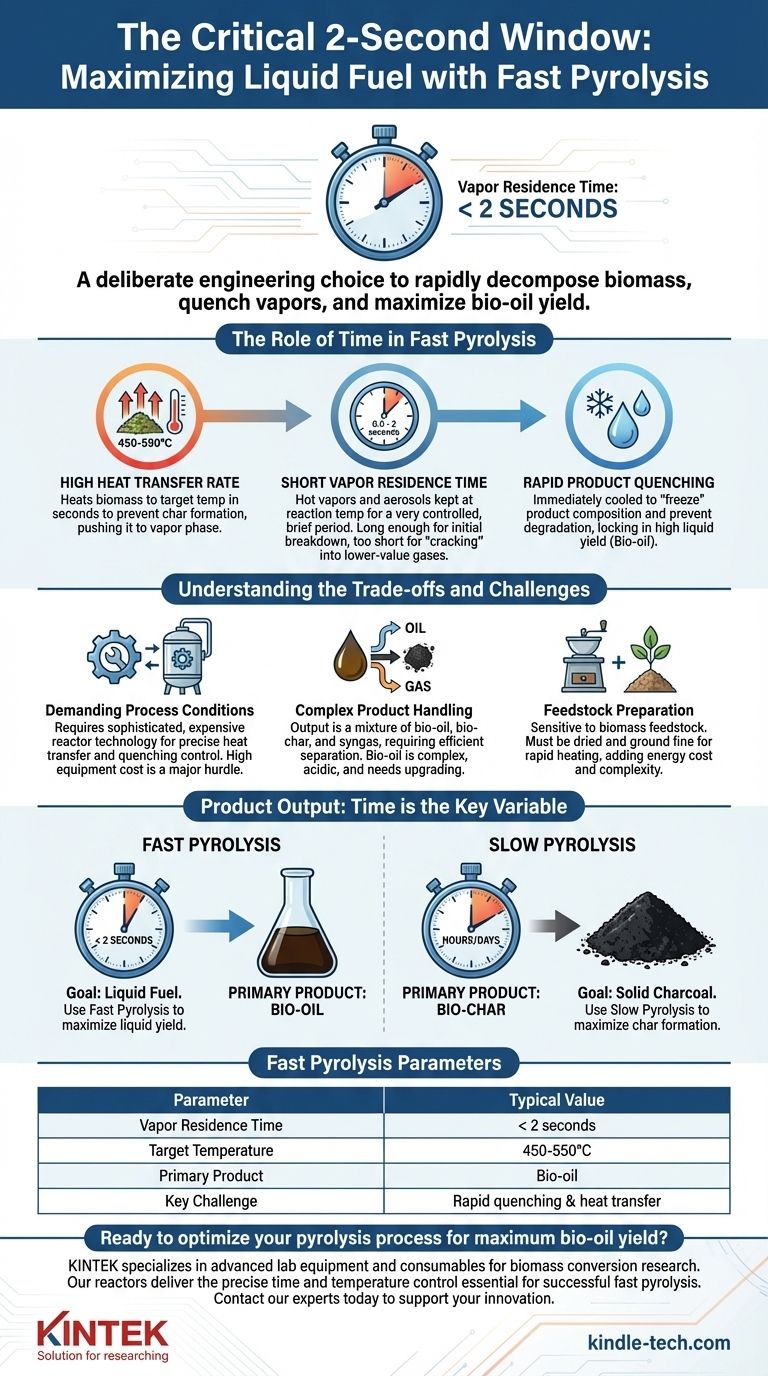
In fast pyrolysis, the actual reaction time, known as the vapor residence time, is exceptionally short. This critical window is typically less than 2 seconds. This brief duration is a deliberate engineering choice designed to rapidly decompose biomass and immediately quench the resulting vapors, maximizing the yield of liquid bio-oil before it can break down into less valuable gases and char.
The core principle of fast pyrolysis is not just speed for its own sake, but precise time control. The extremely short residence time is a targeted strategy to interrupt the chemical breakdown of biomass at the exact moment the yield of liquid bio-oil is highest.

The Role of Time in Fast Pyrolysis
Fast pyrolysis is a thermochemical process engineered around three critical, time-dependent conditions. The goal is to heat the biomass so quickly that it essentially vaporizes, and then cool those vapors before they can undergo secondary reactions.
High Heat Transfer Rate
The process begins with heating the biomass feedstock to a target temperature, typically 450-550°C, as quickly as possible. This requires a reactor designed for very high heat transfer.
The goal is to prevent the slower, char-forming reactions that occur at lower temperatures, pushing the biomass directly into the vapor phase.
Short Vapor Residence Time
This is the answer to the central question. The hot vapors and aerosols produced from the biomass are kept at the reaction temperature for a very controlled, short period—generally between 0.5 and 2 seconds.
This brief window is long enough for the initial breakdown (pyrolysis) to occur but too short for the valuable, condensable vapors to "crack" into lower-value, non-condensable gases.
Rapid Product Quenching
Immediately following the short residence time, the hot gas and vapor mixture is cooled rapidly. This "quenches" the reaction, condensing the vapors into the primary liquid product, known as bio-oil or pyrolysis oil.
This rapid cooling is just as crucial as the rapid heating; it "freezes" the product composition and prevents further degradation, locking in the high liquid yield.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
While fast pyrolysis is an effective method for producing liquid fuel from biomass, it involves significant technical and economic hurdles directly related to its speed.
Demanding Process Conditions
Achieving the required high heat transfer and rapid quenching demands sophisticated and often expensive reactor technology. Simple designs cannot provide the necessary control over time and temperature.
This high equipment cost is a primary challenge to widespread commercial adoption.
Complex Product Handling
The process does not yield a single, pure product. The output is a mixture of bio-oil, solid bio-char, and flammable gases (syngas).
These products must be efficiently separated. Furthermore, the bio-oil itself is a complex, acidic, and unstable mixture that requires significant upgrading before it can be used as a transportation fuel.
Feedstock Preparation
The need for extremely fast heat transfer means the process is sensitive to the biomass feedstock. It must typically be dried and ground into fine particles to ensure it can be heated through in a matter of seconds.
This pre-processing step adds energy cost and complexity to the overall facility.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The "speed" of pyrolysis is not a universal good; it is a tool selected to achieve a specific outcome. Your choice of process time directly determines your primary product.
- If your primary focus is liquid fuel (bio-oil): You must use fast pyrolysis, ensuring a vapor residence time of less than 2 seconds to maximize liquid yield.
- If your primary focus is solid charcoal (bio-char): You should use slow pyrolysis, where residence times can be several hours or even days, which maximizes char formation.
Ultimately, controlling time is the single most important variable in determining the output of any pyrolysis process.
Summary Table:
| Fast Pyrolysis Parameter | Typical Value |
|---|---|
| Vapor Residence Time | < 2 seconds |
| Target Temperature | 450-550°C |
| Primary Product | Bio-oil |
| Key Challenge | Rapid quenching & heat transfer |
Ready to optimize your pyrolysis process for maximum bio-oil yield? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables for biomass conversion research. Our reactors and systems are designed to deliver the precise time and temperature control essential for successful fast pyrolysis. Whether you're scaling up from lab to pilot or need reliable consumables for your experiments, we provide the tools for efficient, high-yield results. Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK can support your laboratory's pyrolysis and bioenergy innovation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Mini SS High Pressure Autoclave Reactor for Laboratory Use
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
- Stainless High Pressure Autoclave Reactor Laboratory Pressure Reactor
People Also Ask
- Is pyrolysis viable? A Guide to Economic, Technological, and Environmental Success
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis technology? Turn Waste into Profit and Reduce Emissions
- What are the reactions involved in pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock the Chemistry for Tailored Bio-Products
- What are the products of pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock Bio-Char, Bio-Oil, and Syngas



















