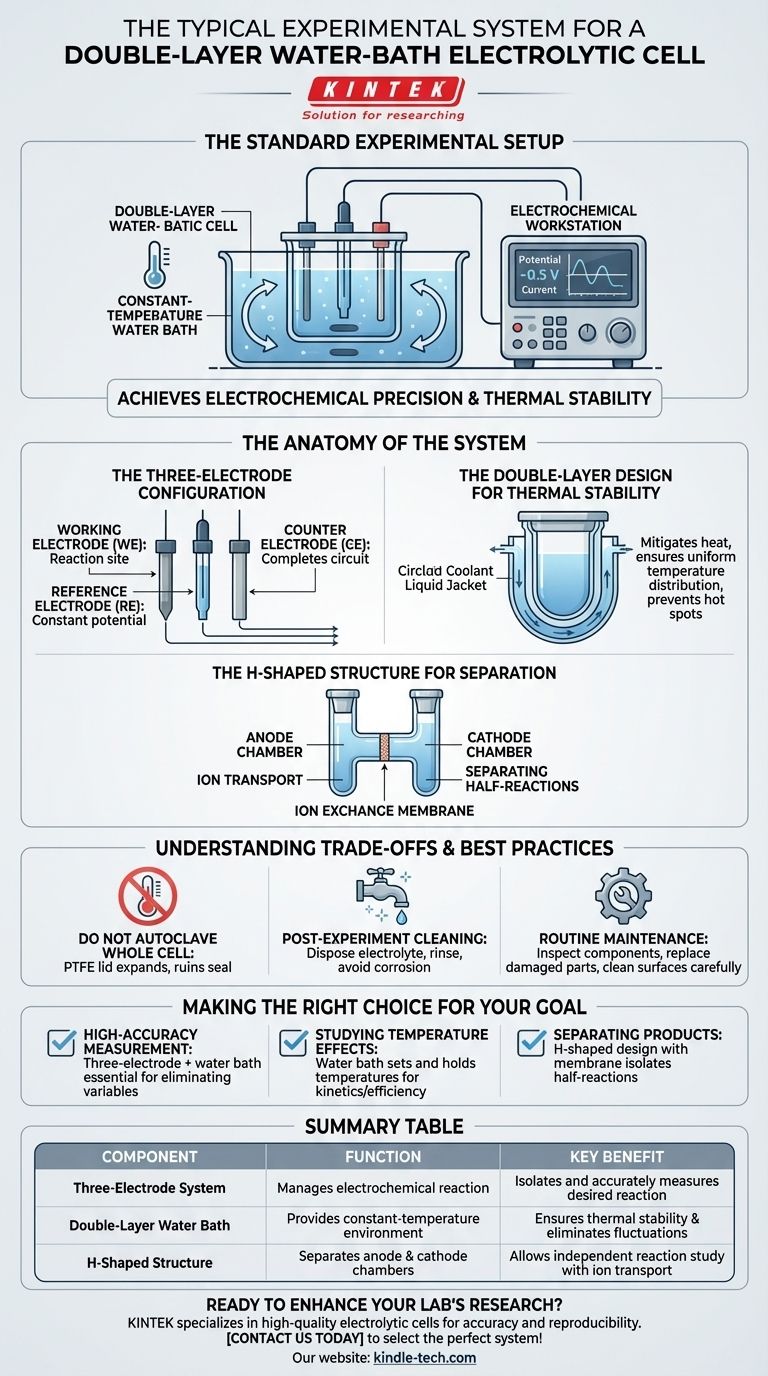
The standard experimental setup for a double-layer water-bath electrolytic cell is a three-electrode system managed by an electrochemical workstation. This system consists of a working electrode where the reaction of interest occurs, a counter electrode to complete the electrical circuit, and a reference electrode to provide a stable potential for accurate measurements. The entire assembly operates within a constant-temperature water bath to ensure thermal stability throughout the experiment.
The core purpose of this system is to achieve both electrochemical precision and thermal stability. The three-electrode setup isolates and accurately measures the desired reaction, while the water bath eliminates temperature fluctuations, leading to highly accurate and repeatable experimental results.

The Anatomy of the System
A double-layer electrolytic cell is more than just a container; it's an integrated system designed for control. Understanding its components reveals its function.
The Three-Electrode Configuration
The heart of the electrochemical measurement is the three-electrode system. Each electrode has a distinct role:
- Working Electrode (WE): This is the surface where the specific electrochemical reaction you are studying takes place.
- Reference Electrode (RE): This electrode maintains a constant, known potential. All voltage measurements of the working electrode are made relative to the reference, ensuring accuracy.
- Counter Electrode (CE): Also called the auxiliary electrode, its function is to pass current to the working electrode, completing the circuit without interfering with the reference electrode's stable potential.
The Double-Layer Design for Thermal Stability
The cell's signature feature is its double-wall construction, which creates a jacket for a constant-temperature liquid. This water bath is not a passive feature; it is critical for control.
The water bath mitigates heat generated by the electrolysis reaction itself or absorbed from the environment. This provides a uniform temperature distribution across the inner cell, preventing local hot spots and ensuring the reaction proceeds consistently.
The H-Shaped Structure for Separation
Many of these cells feature an H-shaped structure, which divides the cell into two distinct chambers (e.g., an anode and a cathode chamber).
These chambers are typically separated by a replaceable ion exchange membrane. This design allows the reactions in each chamber to proceed independently while still enabling the necessary ion transport to maintain charge neutrality, further improving experimental accuracy.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Best Practices
Proper operation and maintenance are critical for achieving reliable data and ensuring the longevity of the equipment. Missteps here can compromise your results or damage the cell.
The Hazard of High-Temperature Sterilization
While the glass components of the cell can be sterilized by autoclaving at 121°C, you must never heat or autoclave the entire assembled cell.
The PTFE (Teflon) lid will expand significantly when heated and may not return to its original shape, ruining its seal and rendering the cell unusable. Always disassemble the cell and sterilize only the glass parts.
Post-Experiment Cleaning Protocol
Residues can contaminate future experiments. Immediately after use, turn off all equipment and carefully remove the electrodes.
Dispose of the electrolyte and rinse the cell multiple times with distilled water. If stubborn residues remain, use a dilute acid or base for cleaning, but first confirm it will not corrode the cell or electrodes.
Routine Maintenance for Longevity
Periodically inspect all components, including the glass body, seals, and electrodes, for any signs of damage or wear. Replace any compromised parts immediately.
Regularly clean the cell's inner and outer surfaces with a soft cloth or brush to remove dirt and deposits, taking care not to scratch the glass.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The double-layer water-bath cell is a versatile tool, but its key features are best leveraged when aligned with a specific experimental objective.
- If your primary focus is high-accuracy measurement: The combination of the three-electrode system and the constant-temperature water bath is non-negotiable for eliminating electrical and thermal variables.
- If your primary focus is studying temperature effects: The water bath is your primary tool, allowing you to systematically set and hold different temperatures to observe their impact on reaction kinetics or efficiency.
- If your primary focus is separating anodic and cathodic products: The H-shaped design with an ion exchange membrane is the critical feature you need to isolate the two half-reactions.
By integrating precise electrochemical control with stable thermal management, this system empowers you to conduct highly reliable and reproducible experiments.
Summary Table:
| Component | Function | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Three-Electrode System | Manages electrochemical reaction | Isolates and accurately measures the desired reaction |
| Double-Layer Water Bath | Provides constant-temperature environment | Ensures thermal stability and eliminates fluctuations |
| H-Shaped Structure | Separates anode and cathode chambers | Allows independent reaction study with ion transport |
Ready to enhance your lab's electrochemical research with precision and thermal stability? KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment, including electrolytic cells and consumables designed for accuracy and reproducibility. Let our experts help you select the perfect system for your specific experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss your requirements and discover the KINTEK difference!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Double Layer Five-Port Water Bath Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell
- H-Type Double-Layer Optical Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell with Water Bath
- Multifunctional Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell Water Bath Single Layer Double Layer
- H Type Electrolytic Cell Triple Electrochemical Cell
- Quartz Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell for Electrochemical Experiments
People Also Ask
- How can the electrochemical reaction be controlled when using this electrolytic cell? Master Voltage, Current & Electrolyte
- What are the standard aperture sizes on the lid of the multifunctional electrolytic cell? Key Ports for Your Electrochemical Setup
- When is professional repair required for a double-layer water-bath electrolytic cell? Protect Your Lab's Precision and Safety
- What are the key features of the five-port water bath electrolytic cell? Precision Control for Electrochemical Experiments
- What are the typical volumes and aperture configurations for a double-layer water-bath electrolytic cell? Optimize Your Electrochemical Setup



















