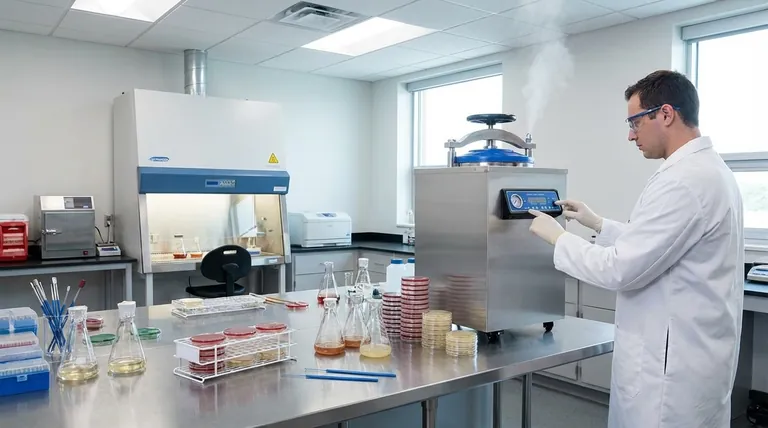
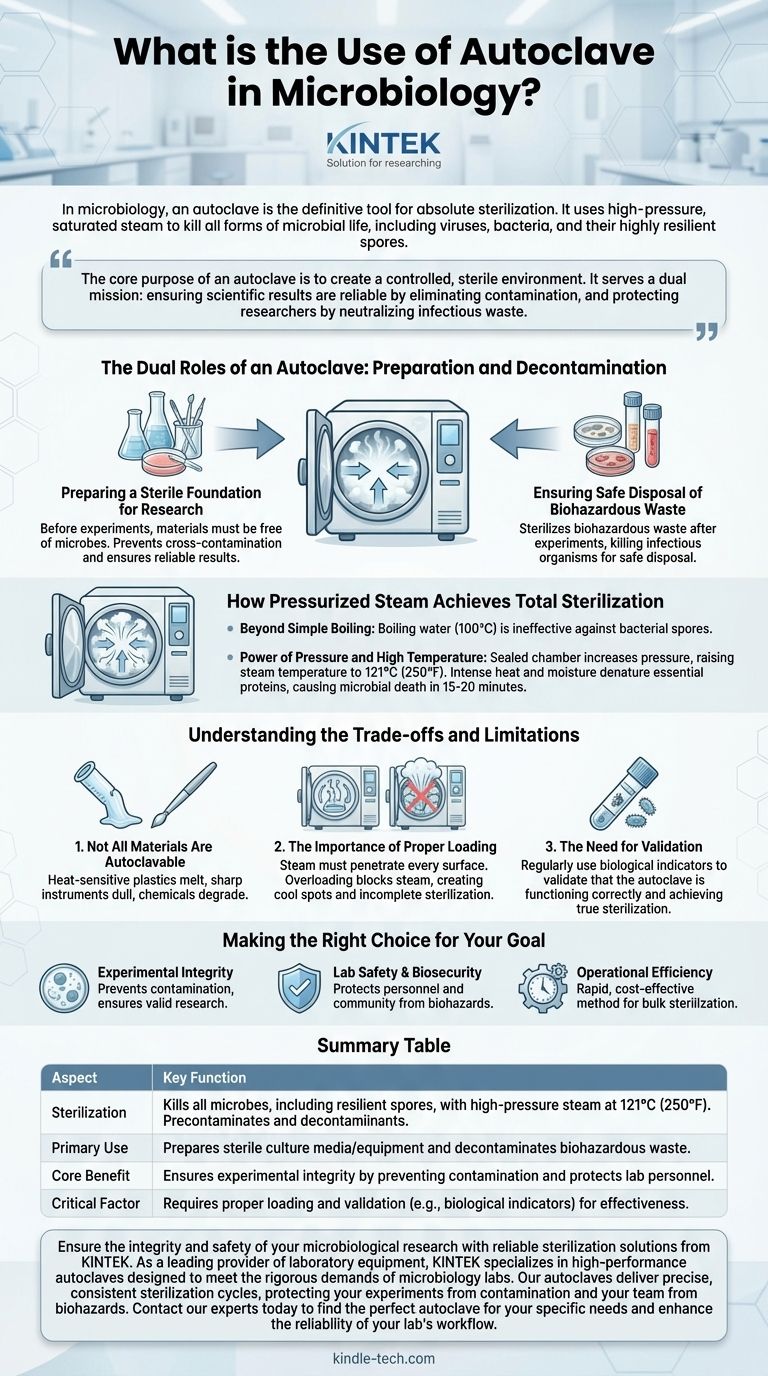
In microbiology, an autoclave is the definitive tool for absolute sterilization. It uses high-pressure, saturated steam to kill all forms of microbial life, including viruses, bacteria, and their highly resilient spores. This process is non-negotiable for preparing sterile culture media and equipment before an experiment and for decontaminating biohazardous materials afterward.
The core purpose of an autoclave is to create a controlled, sterile environment. It serves a dual mission: ensuring scientific results are reliable by eliminating contamination, and protecting researchers by neutralizing infectious waste.

The Dual Roles of an Autoclave: Preparation and Decontamination
An autoclave's function in a microbiology lab can be understood by its role at the beginning and end of the experimental workflow.
Preparing a Sterile Foundation for Research
Before any experiment begins, all materials must be free of foreign microbes. This includes the culture media that microbes grow on, the glassware they are grown in, and the instruments used to handle them.
If these items are not sterile, unwanted bacteria or fungi can grow alongside the organism being studied. This cross-contamination invalidates results, as it becomes impossible to know which microbe is responsible for the observed effects.
Ensuring Safe Disposal of Biohazardous Waste
Once an experiment is complete, the used materials—such as petri dishes, culture tubes, and disposable loops—are considered biohazardous waste. They contain concentrated cultures of microorganisms, which can be infectious.
Simply discarding this waste would pose a significant risk to public health and the environment. The autoclave sterilizes this waste, killing all organisms and rendering it safe for routine disposal.
How Pressurized Steam Achieves Total Sterilization
The effectiveness of an autoclave lies in its ability to harness the combined power of high temperature and pressure, a principle that goes far beyond simple boiling.
Beyond Simple Boiling
Boiling water at 100°C (212°F) can kill many active bacteria, but it is ineffective against bacterial spores. Spores are a dormant, highly protected form of bacteria that can survive extreme conditions and later reactivate.
The Power of Pressure and High Temperature
An autoclave is a sealed chamber that increases pressure. This pressure allows water vapor (steam) to reach temperatures far above boiling, typically 121°C (250°F).
The intense heat, combined with the moisture from the steam, rapidly penetrates materials. This lethal combination denatures the essential proteins and enzymes within all microorganisms, causing their cellular structures to collapse and ensuring their death. The entire cycle is often completed in as little as 15-20 minutes.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While highly effective, an autoclave is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is critical for proper and safe use.
Not All Materials Are Autoclavable
The high heat and pressure will destroy certain materials. Heat-sensitive plastics will melt, sharp instruments can become dulled, and certain chemicals or reagents can degrade or become volatile.
The Importance of Proper Loading
Sterilization depends on steam penetrating every surface. If an autoclave is overloaded or items are packed too tightly, steam penetration can be blocked. This creates cool spots where microorganisms can survive, resulting in incomplete sterilization.
The Need for Validation
You cannot simply assume a cycle was successful. Laboratories regularly use biological indicators, such as vials containing heat-resistant spores. If the spores are killed during the cycle, it validates that the autoclave is functioning correctly and achieving true sterilization.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To apply these principles effectively, align your autoclave procedures with your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is experimental integrity: Autoclaving your media and equipment is the first and most critical step to prevent contamination that invalidates your research.
- If your primary focus is lab safety and biosecurity: Proper autoclaving of all biohazardous waste is a non-negotiable protocol for protecting personnel and the community.
- If your primary focus is operational efficiency: The autoclave provides a rapid, reliable, and cost-effective method for preparing sterile materials in bulk, essential for any high-throughput lab.
Ultimately, mastering the principles and practice of autoclaving is fundamental to conducting responsible and reproducible microbiological research.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Function |
|---|---|
| Sterilization | Kills all microbes, including resilient spores, with high-pressure steam at 121°C (250°F). |
| Primary Use | Prepares sterile culture media/equipment and decontaminates biohazardous waste. |
| Core Benefit | Ensures experimental integrity by preventing contamination and protects lab personnel. |
| Critical Factor | Requires proper loading and validation (e.g., biological indicators) for effectiveness. |
Ensure the integrity and safety of your microbiological research with reliable sterilization solutions from KINTEK.
As a leading provider of laboratory equipment, KINTEK specializes in high-performance autoclaves designed to meet the rigorous demands of microbiology labs. Our autoclaves deliver precise, consistent sterilization cycles, protecting your experiments from contamination and your team from biohazards.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect autoclave for your specific needs and enhance the reliability of your lab's workflow.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory High Pressure Steam Sterilizer Vertical Autoclave for Lab Department
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Portable Digital Display Automatic Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave for Sterilization Pressure
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Herbal Powder Sterilization Machine for Plant
- Desktop Fast High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 16L 24L for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What role does an autoclave play in the acid treatment for microalgae disruption? Unlock High-Yield Cell Pretreatment
- What is the primary function and principle of autoclaving? Master Lab Sterilization with High-Pressure Steam
- What critical environmental conditions does a laboratory autoclave provide for evaluating wear resistance? - KINTEK
- Why is the standard autoclave temperature set to 121? The Science of Effective Sterilization
- What is the life expectancy of an autoclave machine? Maximize Your Investment with Proper Care



















