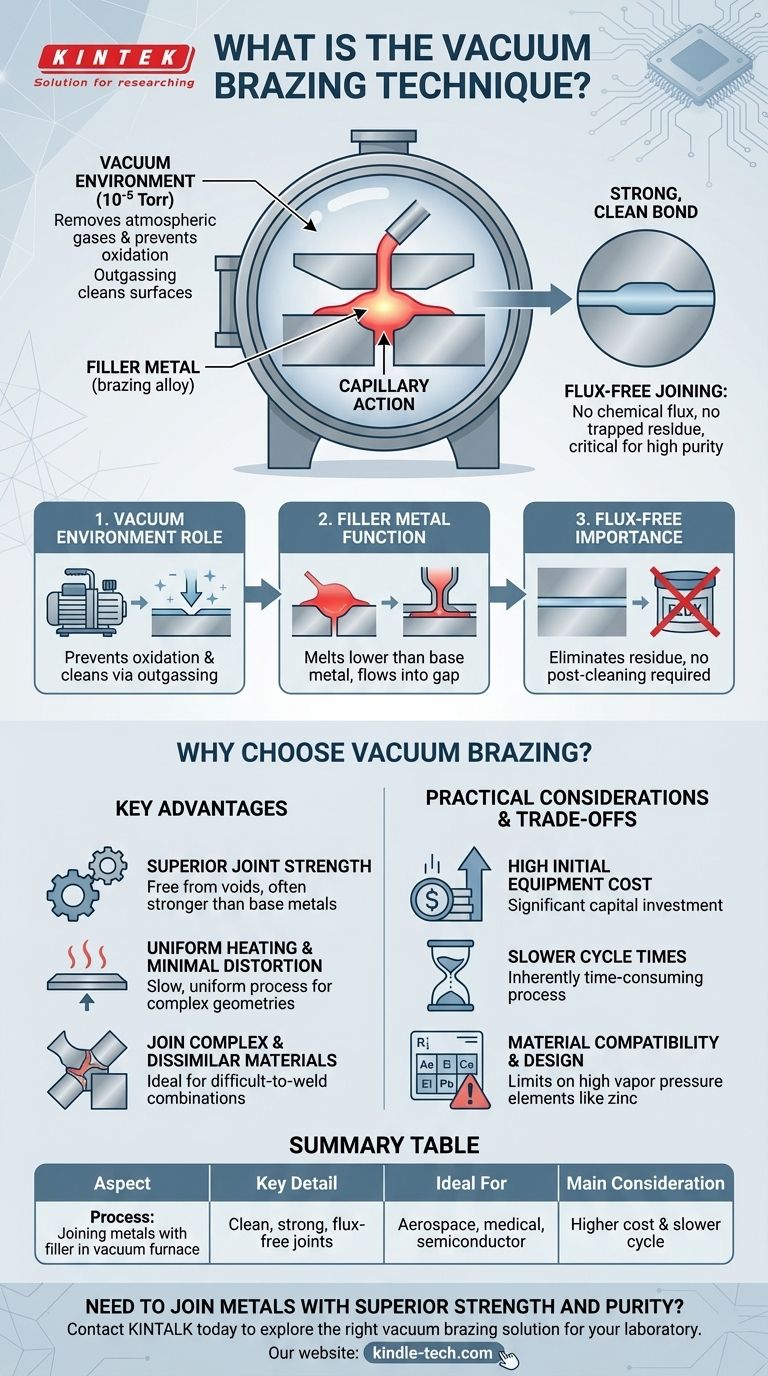
In essence, vacuum brazing is a high-purity joining process that uses a specialized filler metal to form a strong, clean bond between two or more base metals inside a vacuum furnace. The heat of the furnace melts the filler metal, which has a lower melting point than the base metals, allowing it to flow into the tight-fitting joint through capillary action and create a seamless connection upon cooling.
The critical insight is that a vacuum is not just an empty space; it's an active environment. By removing atmospheric gases, the vacuum prevents oxidation and cleans the metal surfaces during heating, resulting in superior, flux-free joints that are impossible to achieve with many other methods.

The Fundamental Mechanism of Vacuum Brazing
Vacuum brazing is a precise thermal process that relies on a controlled environment to achieve a perfect metallurgical bond. Understanding each component of the process is key to appreciating its value.
The Role of the Vacuum Environment
The process takes place in a vacuum furnace, which pumps out air and other gases to create a low-pressure environment, typically around 10⁻⁵ Torr.
This vacuum is not passive. As the temperature rises, the near-absence of oxygen prevents the metal surfaces from oxidizing, which would otherwise inhibit a proper bond.
Furthermore, the vacuum effectively "boils off" surface contaminants and volatile oxides, a phenomenon known as outgassing. This leaves the base metal surfaces exceptionally clean, ensuring the filler metal can properly "wet" and bond with them.
The Function of the Filler Metal
A filler metal, also called a brazing alloy, is selected with a melting point that is lower than the base metals being joined.
During the heating cycle, the assembly is brought to a temperature above the filler's melting point. The molten filler is then drawn into the gap between the workpieces by capillary action.
This liquid metal diffuses into the base metal surfaces, forming a strong, continuous metallurgical bond when the assembly cools and the filler solidifies.
The Importance of Flux-Free Joining
Unlike traditional brazing or soldering, vacuum brazing requires no flux. Flux is a chemical agent used to clean surfaces and prevent oxidation, but it can become trapped in the joint, causing corrosion or weakness.
By eliminating flux, vacuum brazing produces an exceptionally clean joint with no entrapped residue or post-process cleaning required. This is critical for applications in medical, aerospace, and semiconductor industries.
Why Choose Vacuum Brazing? The Key Advantages
The unique environment of the vacuum furnace provides several distinct advantages over other joining techniques, making it the preferred method for demanding applications.
Superior Joint Strength and Integrity
The process produces joints that are free from voids and contaminants. This results in a connection that is often as strong as, or even stronger than, the base metals themselves.
Uniform Heating and Minimal Distortion
Inside a vacuum furnace, the entire assembly is heated and cooled slowly and uniformly. This minimizes thermal stress and distortion, which is crucial when working with complex or delicate geometries.
Ability to Join Complex and Dissimilar Materials
Vacuum brazing is exceptionally well-suited for joining dissimilar metals that may be difficult to weld. It also allows multiple joints on a single complex assembly to be brazed simultaneously, ensuring precision and efficiency.
Understanding the Practical Considerations and Trade-offs
While powerful, vacuum brazing is not the solution for every joining problem. Its benefits must be weighed against its practical limitations.
High Initial Equipment Cost
Vacuum furnaces represent a significant capital investment. The cost and complexity of the equipment make the process more expensive upfront compared to torch brazing or welding.
Slower Cycle Times
The process of pumping down the vacuum, slowly heating the assembly, and then cooling it back to room temperature is inherently time-consuming. This makes vacuum brazing less suitable for high-volume, low-cost production where speed is the priority.
Material Compatibility and Design
Certain elements, such as zinc, cadmium, and lead, have high vapor pressures and will evaporate in a vacuum. These elements cannot be present in either the base metals or the filler alloy, which limits material choices.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct joining method depends entirely on your project's specific requirements for strength, purity, complexity, and cost.
- If your primary focus is ultimate joint purity and strength: Vacuum brazing is the ideal choice, especially for mission-critical components in aerospace, medical, or scientific applications.
- If your primary focus is joining a complex assembly with multiple joints: The uniform heating of vacuum brazing makes it superior for creating stress-free, intricate products.
- If your primary focus is low-cost, high-volume production of simple parts: Other methods like torch brazing, soldering, or welding are likely more economical and efficient.
Ultimately, vacuum brazing is a premier joining technology you leverage when the integrity and cleanliness of the final bond cannot be compromised.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Process | Joining metals with a filler metal in a vacuum furnace |
| Key Advantage | Produces clean, strong, flux-free joints |
| Ideal For | Aerospace, medical, semiconductor, and complex assemblies |
| Main Consideration | Higher initial cost and slower cycle times than some methods |
Need to join metals with superior strength and purity?
Vacuum brazing is the premier choice for mission-critical components where joint integrity is non-negotiable. KINTEK specializes in providing the advanced lab equipment and expert solutions needed for this high-precision process.
We help you:
- Achieve flawless, contaminant-free bonds for complex assemblies.
- Join dissimilar metals that are difficult to weld.
- Ensure minimal part distortion with uniform heating.
If your application in aerospace, medical, or scientific research demands the highest quality, let's discuss how our solutions can meet your needs.
Contact KINTALK today to explore the right vacuum brazing solution for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the major advantage that brazing has over welding? Joining Dissimilar Metals with Ease
- What is the most important factor influencing the strength of the brazed joint? Master Joint Clearance for Maximum Strength
- Can you braze two different metals? Yes, and here’s how to do it successfully.
- What are the factors that affect the strength of a brazed joint? Master the 4 Keys to a Perfect Bond
- What is the difference between welding and vacuum brazing? Choose the Right Joining Method for Your Project



















