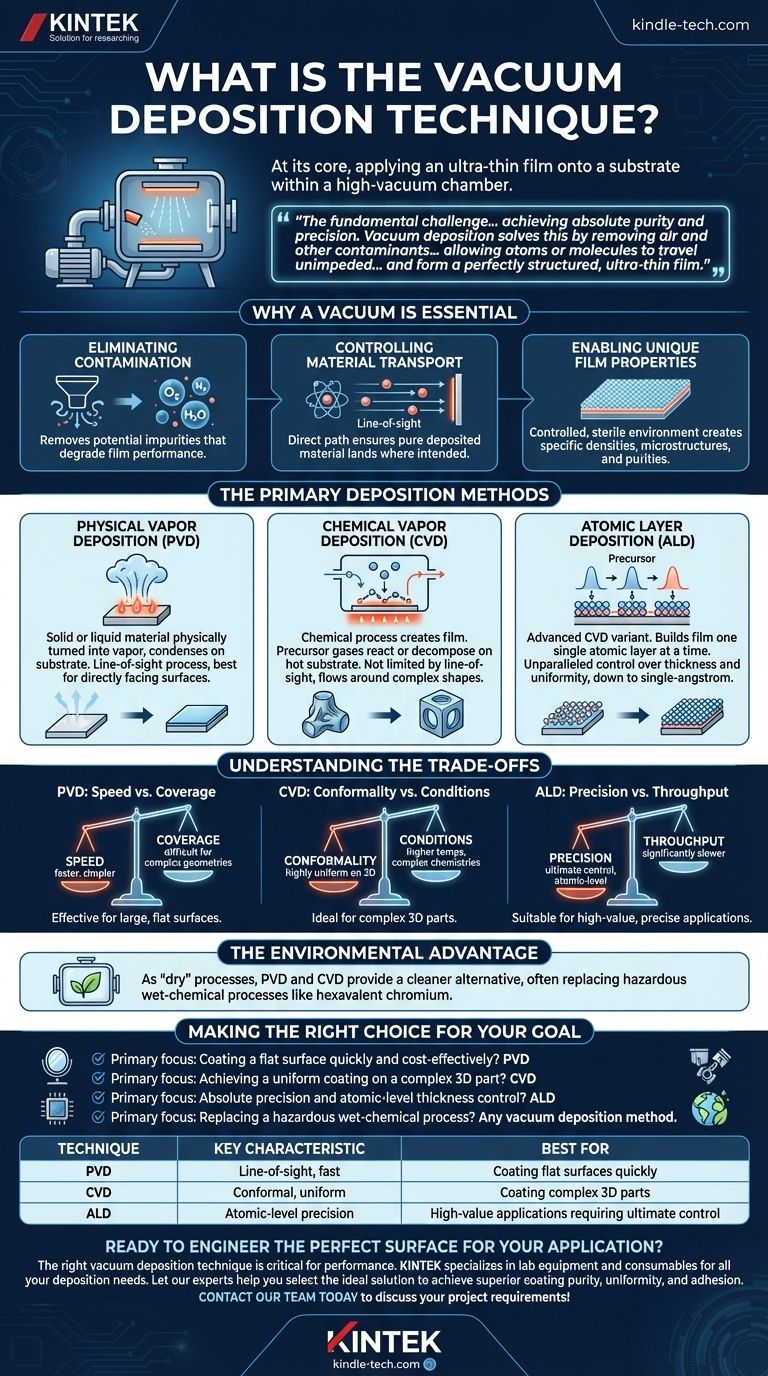
At its core, vacuum deposition is a family of processes used to apply an ultra-thin film of material onto a surface, known as a substrate. This is all done inside a high-vacuum chamber, which is the key to the entire technique. The goal is to build a new surface layer, sometimes only a few atoms thick, with specific optical, electrical, or mechanical properties that the original substrate lacks.
The fundamental challenge in creating high-performance coatings is achieving absolute purity and precision. Vacuum deposition solves this by removing air and other contaminants from the environment, allowing atoms or molecules to travel unimpeded from a source to a target and form a perfectly structured, ultra-thin film.

Why a Vacuum is Essential
Creating a vacuum is not an incidental step; it is the defining characteristic of the process. The low-pressure environment is critical for several reasons.
Eliminating Contamination
The air around us is filled with particles like oxygen, nitrogen, and water vapor. If these particles were present during deposition, they would become embedded in the thin film, creating impurities that degrade its performance. A vacuum removes these potential contaminants.
Controlling Material Transport
In a vacuum, atoms and molecules from the source material can travel in a straight line to the substrate without colliding with air molecules. This direct path, known as "line-of-sight" travel, is crucial for ensuring the deposited material is pure and lands where intended.
Enabling Unique Film Properties
The controlled, sterile environment of a vacuum allows for the creation of film structures with specific densities, microstructures, and purities that would be impossible to achieve in open air.
The Primary Deposition Methods
While there are many specific techniques, they generally fall into two main families: Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) and Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD).
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD)
PVD is a process where a solid or liquid material is physically turned into a vapor, which then condenses onto the substrate as a thin film. Think of it as boiling water and watching steam condense on a cool surface, but with solid metals or ceramics. This is often done by heating the material or bombarding it with ions.
PVD is fundamentally a line-of-sight process, meaning it works best on surfaces that are directly facing the material source.
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
CVD uses a chemical process to create the film. Precursor gases are introduced into the vacuum chamber, where they react or decompose on the hot substrate surface, leaving behind the desired material as a solid film.
Unlike PVD, CVD is not limited by line-of-sight. The gases can flow around complex shapes, resulting in a highly conformal coating that covers all surfaces of a three-dimensional object uniformly.
Atomic Layer Deposition (ALD)
ALD is a more advanced, precise variant of CVD. It builds the film one single atomic layer at a time by introducing precursor gases in separate, sequential pulses. This allows for unparalleled control over film thickness and uniformity, down to the single-angstrom level.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The choice between PVD, CVD, and ALD is a matter of engineering trade-offs between speed, coverage, and precision.
PVD: Speed vs. Coverage
PVD processes are generally faster and often simpler than CVD, making them highly effective for coating large, relatively flat surfaces. However, their line-of-sight nature makes it difficult to uniformly coat complex geometries with undercuts or hidden surfaces.
CVD: Conformality vs. Conditions
CVD's strength is its ability to create highly uniform, conformal coatings on complex 3D parts. The trade-off is that it often requires higher substrate temperatures and involves more complex chemistries and precursor gases than PVD.
ALD: Precision vs. Throughput
ALD offers the ultimate level of control, producing perfectly uniform and conformal films with atomic precision. This precision comes at the cost of speed; ALD is a significantly slower process, making it most suitable for high-value applications like microelectronics where absolute control is non-negotiable.
The Environmental Advantage
A major driver for adopting vacuum deposition is environmental concern. As "dry" processes, PVD and CVD provide a cleaner alternative to traditional wet-chemical electroplating, often replacing hazardous materials like hexavalent chromium and cadmium.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right technique depends entirely on the functional requirements of the final product.
- If your primary focus is coating a flat surface quickly and cost-effectively: PVD is often the superior choice for applications like optical mirrors or barrier films on polymer webs.
- If your primary focus is achieving a uniform coating on a complex 3D part: CVD is the better approach for components like engine parts or cutting tools.
- If your primary focus is absolute precision and atomic-level thickness control: ALD is the necessary method for advanced semiconductor devices and nano-structures.
- If your primary focus is replacing a hazardous wet-chemical process: Any vacuum deposition method offers a significant environmental and safety advantage as a 'dry' technology.
By understanding these core principles, you can effectively select the optimal technology to engineer surfaces with precisely the properties you need.
Summary Table:
| Technique | Key Characteristic | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| PVD | Line-of-sight, fast | Coating flat surfaces quickly |
| CVD | Conformal, uniform | Coating complex 3D parts |
| ALD | Atomic-level precision | High-value applications requiring ultimate control |
Ready to engineer the perfect surface for your application? The right vacuum deposition technique is critical for performance. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables for all your deposition needs, from research to production. Let our experts help you select the ideal solution to achieve superior coating purity, uniformity, and adhesion. Contact our team today to discuss your project requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How are thin films deposited? A Guide to PVD vs. CVD Methods for Your Application
- What is the process of vacuum vapor deposition? Mastering CVD and PVD Thin-Film Coating
- How does PECVD work? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What are the different types of thin films? A Guide to Optical, Electrical, and Functional Coatings
- What are the steps of the CVD process? A Guide to Precision Thin Film Deposition



















