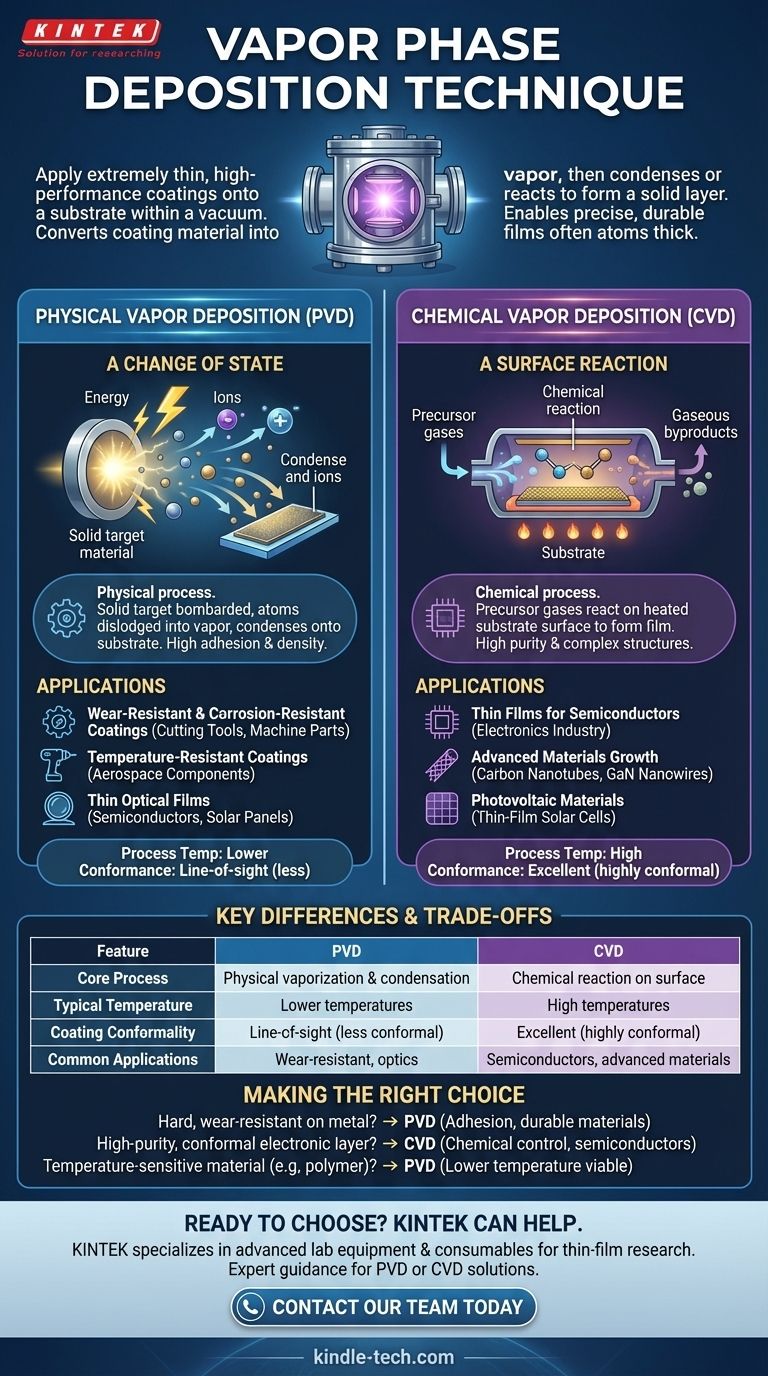
Vapor phase deposition is a family of advanced manufacturing techniques used to apply extremely thin, high-performance coatings or films onto a surface, known as a substrate. These processes all operate within a vacuum and work by converting a coating material into a gaseous state (a vapor), which is then transported to the substrate where it condenses or reacts to form a solid layer.
The core challenge in advanced materials is applying a perfectly uniform, durable film, often just a few atoms thick. Vapor deposition solves this by transforming a material into a gas, allowing it to flow and settle onto a target surface with incredible precision, where it becomes solid through either a physical change of state (PVD) or a chemical reaction (CVD).

The Two Pillars of Vapor Deposition
While "vapor deposition" is the umbrella term, the process is executed through two fundamentally different methods. Understanding their distinction is key to understanding their applications.
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD): A Change of State
Physical Vapor Deposition is fundamentally a physical process, much like water vapor condensing on a cold mirror. A solid source material, or "target," is bombarded with energy inside a vacuum chamber.
This energy physically dislodges atoms from the target, turning them into a vapor. This vapor then travels through the vacuum and condenses onto the cooler substrate, forming a dense and strongly bonded thin film. Common PVD methods include evaporation and sputtering.
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD): A Surface Reaction
Chemical Vapor Deposition is a chemical process. Instead of physically vaporizing a solid target, one or more volatile precursor gases are introduced into a reaction chamber.
When these gases come into contact with the heated substrate, a chemical reaction is triggered directly on its surface. This reaction forms the desired solid film, and the gaseous byproducts of the reaction are removed from the chamber.
Understanding the Practical Applications
The differences in how PVD and CVD work make them suitable for very different engineering goals.
Where PVD Excels
PVD is the go-to method for applying exceptionally hard and durable coatings. Its physical nature allows for the deposition of materials with very high melting points.
Common applications include creating wear-resistant and corrosion-resistant coatings for cutting tools and machine parts, depositing temperature-resistant coatings on aerospace components, and applying thin optical films for semiconductors and solar panels.
Where CVD is Essential
CVD offers a level of chemical precision that PVD cannot. Because it builds the film through a chemical reaction, it is ideal for creating highly pure materials and complex structures.
It is frequently used in the electronics industry for depositing the thin films that form semiconductors. It is also essential for growing advanced materials like carbon nanotubes and GaN nanowires and for applying photovoltaic materials in the manufacturing of thin-film solar cells.
Key Differences and Trade-offs
Choosing between PVD and CVD involves understanding their inherent limitations and advantages.
Process Temperature
CVD typically requires very high substrate temperatures to initiate the necessary chemical reactions. This limits its use to substrates that can withstand extreme heat. PVD can often be performed at much lower temperatures, making it suitable for a wider range of materials.
Film Conformance and Purity
Because the precursor gases in CVD can flow into every microscopic feature of a surface, it excels at creating conformal coatings that uniformly cover complex shapes. It also produces films of very high purity. PVD is more of a "line-of-sight" process, which can make it difficult to evenly coat intricate geometries.
Material Versatility
PVD can deposit a vast range of materials, including pure metals, alloys, and ceramics that are difficult to create as a stable precursor gas for CVD. CVD is superior for depositing specific chemical compounds that cannot be easily created with PVD methods.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The selection of a deposition method is dictated entirely by the desired outcome and the constraints of the material being coated.
- If your primary focus is a hard, wear-resistant coating on a metal component: PVD is the standard choice for its excellent adhesion and ability to deposit durable, high-melting-point materials.
- If your primary focus is creating a highly pure, conformal electronic layer on a silicon wafer: CVD offers the chemical control required to build precise semiconductor films.
- If your primary focus is coating a temperature-sensitive material like a polymer: A lower-temperature PVD process is almost always the more viable option.
Ultimately, selecting the correct vapor deposition technique depends on a clear understanding of your material, your substrate, and the specific properties your final product requires.
Summary Table:
| Feature | PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) | CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) |
|---|---|---|
| Core Process | Physical vaporization & condensation | Chemical reaction on the surface |
| Typical Temperature | Lower temperatures | High temperatures |
| Coating Conformality | Line-of-sight (less conformal) | Excellent (highly conformal) |
| Common Applications | Wear-resistant coatings, optics | Semiconductors, advanced materials |
Ready to choose the right vapor deposition process for your application?
KINTEK specializes in providing advanced lab equipment and consumables for all your thin-film research and development needs. Whether you are developing wear-resistant coatings with PVD or high-purity semiconductor films with CVD, our experts can help you select the ideal solution.
Contact our team today to discuss your project requirements and discover how KINTEK can enhance your laboratory's capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
People Also Ask
- What is the most common method of making graphene? Discover the Industry Standard for High-Quality Production
- What is the purpose of creating thin films? Unlock New Surface Properties for Your Materials
- What are the methods of CVD? A Guide to Choosing the Right Deposition Technique
- What are the main drawbacks of MOCVD technology? Navigate High Costs, Safety Risks, and Impurity Challenges
- What is the process of laser sintering? A Guide to Additive Manufacturing for Complex Parts
- What is the process of LPCVD? Master High-Purity, Uniform Thin-Film Deposition
- How is diamond coating done? A Guide to CVD Methods for Superior Performance
- How is an ultrasonic bath utilized during the diamond seeding phase of substrate preparation? Enhance CVD Nucleation



















