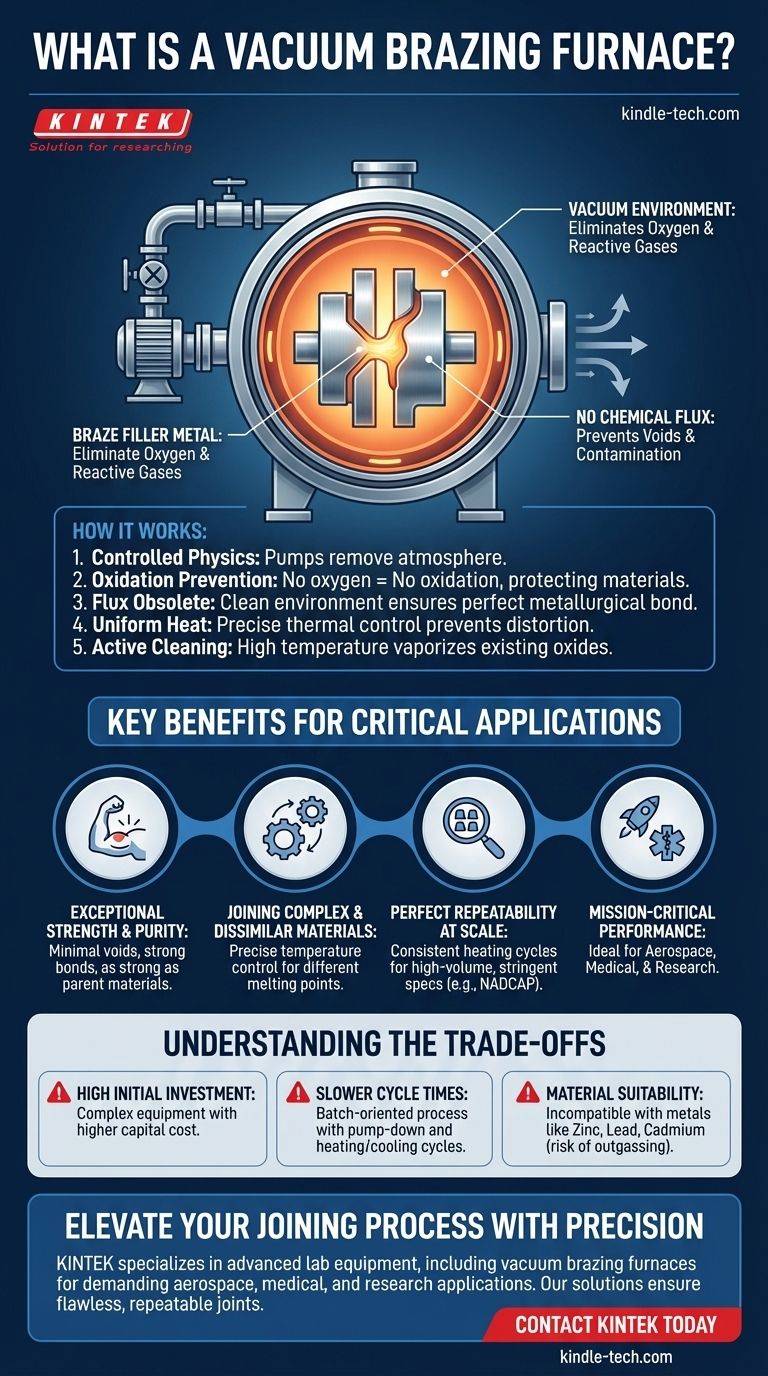
In essence, a vacuum brazing furnace is a highly controlled chamber that joins materials together using a filler metal in a near-total vacuum. By removing reactive gases like oxygen, the furnace creates an ideal environment that prevents oxidation and contamination during the heating process. This results in exceptionally strong, clean, and precise joints without the need for chemical fluxes.
The critical advantage of a vacuum furnace isn't just preventing contamination; it's creating an active environment for perfection. The vacuum actively protects components, can remove existing surface oxides, and provides unparalleled temperature control, making it the definitive choice for joining high-performance, mission-critical parts.

How a Vacuum Furnace Achieves Superior Joints
To understand the value of a vacuum furnace, you must look beyond the simple joining of parts and focus on the controlled physics of the environment it creates.
The Role of the Vacuum Environment
A vacuum system, composed of pumps, valves, and gauges, works to remove the atmosphere from the sealed furnace chamber.
This achieves a critical goal: eliminating oxygen and other reactive gases. Without oxygen, oxidation simply cannot occur, even at the high temperatures required for brazing.
This protects the integrity of both the base materials and the filler metal, ensuring the final joint is pure and free from performance-degrading oxides.
Eliminating Contamination Without Flux
Traditional brazing methods rely on a chemical flux to clean the surfaces and prevent oxidation.
Flux, however, can become trapped in the joint, creating voids and potential points of failure. It also leaves behind a corrosive residue that requires aggressive post-brazing cleaning.
A vacuum furnace makes flux entirely obsolete. The clean environment ensures a perfect metallurgical bond without introducing any foreign contaminants.
Unparalleled Thermal Control
Vacuum furnaces provide extremely uniform heat distribution. This ensures that complex assemblies, regardless of their geometry, are heated evenly.
This precise control prevents thermal distortion, a common problem in other joining processes where localized heat can cause parts to warp.
The furnace can execute pre-programmed heating and cooling cycles with perfect accuracy, ensuring every part is processed under the exact same conditions.
Actively Cleaning the Part Surface
Counterintuitively, a vacuum furnace can operate at temperatures higher than the point of oxide formation.
In the oxygen-free environment, this high heat causes existing, light oxide layers on the components to dissociate and vaporize. The furnace doesn't just prevent new oxides; it can remove old ones, further ensuring a pristine surface for the braze alloy.
Key Benefits for Critical Applications
The controlled environment of a vacuum furnace translates directly into tangible benefits, particularly for industries where failure is not an option.
Exceptional Joint Strength and Purity
By eliminating oxides and flux entrapment, the process produces joints with minimal voids and superior mechanical properties. The final bond is often as strong as the parent materials themselves.
Joining Complex and Dissimilar Materials
The precise temperature control allows for the successful brazing of materials with different melting points or thermal expansion rates. It is an ideal solution for intricate assemblies with complex geometries.
Perfect Repeatability at Scale
Sophisticated control systems, sometimes linked to barcodes, allow the furnace to run identical heating cycles for every batch. This makes it invaluable for high-volume manufacturing where every single part must meet stringent specifications, such as those required by NADCAP for the aerospace industry.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, vacuum furnace brazing is not the solution for every application. Objectivity requires acknowledging its limitations.
High Initial Investment
Vacuum furnaces are complex pieces of equipment. The initial capital cost is significantly higher than that of most other joining equipment.
Slower Cycle Times
The process is inherently batch-oriented. Time is required to load the parts, pump the chamber down to a deep vacuum, run the heating and cooling cycle, and vent the furnace. This makes it less suitable for high-speed, continuous production lines.
Material Suitability
Certain materials are not compatible with a vacuum environment. Metals with a high vapor pressure, such as zinc, lead, or cadmium, can outgas at brazing temperatures, contaminating the furnace and compromising the joint.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting vacuum furnace brazing is a decision based on the required level of precision, purity, and performance of the final assembly.
- If your primary focus is mission-critical performance: This is the standard for aerospace, medical, and research applications where joint failure would have catastrophic consequences.
- If your primary focus is joining complex or dissimilar materials: The furnace's precise thermal management is essential for creating stress-free joints in intricate assemblies.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, high-precision manufacturing: The process's unmatched repeatability ensures every part in a large run meets the exact same quality standard.
- If your primary focus is maintaining absolute part integrity: For components that cannot tolerate any thermal distortion or flux contamination, vacuum brazing is the ideal method.
Ultimately, a vacuum brazing furnace is an investment in certainty, delivering flawless and repeatable joints where precision is paramount.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Oxygen-Free Vacuum Environment | Prevents oxidation and contamination, eliminating the need for chemical flux |
| Precise Thermal Control | Ensures uniform heating, prevents distortion, and handles complex geometries |
| Active Surface Cleaning | Removes existing oxides at high temperatures for pristine bonding surfaces |
| Exceptional Joint Integrity | Produces minimal-void, high-strength bonds often as strong as the base materials |
| Perfect Repeatability | Ideal for high-volume, high-precision manufacturing with consistent results |
Ready to elevate your joining process with precision and reliability?
At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced lab equipment, including vacuum brazing furnaces designed for demanding applications in aerospace, medical, and research. Our solutions ensure flawless, repeatable joints for mission-critical components.
Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can help you achieve superior results — Get in touch via our contact form!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the process of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Purity and Precision in High-Temp Processing
- What are vacuum furnaces used for? Unlock Ultimate Material Purity and Performance
- How is the greatest joint strength obtained in brazing? Master the 3 Keys to Superior Metallurgical Bonds
- What metals can be joined by brazing? Discover the Versatility of Modern Brazing Techniques
- Can you braze two different metals? Yes, and here’s how to do it successfully.



















