At its core, vacuum hardening is a high-performance heat treatment process that strengthens metal parts by heating them in a controlled vacuum environment and then rapidly cooling them with a high-pressure inert gas. This method achieves the desired hardness and mechanical properties while producing an exceptionally clean, bright, and scale-free surface finish, eliminating the need for subsequent cleaning operations typical of traditional hardening methods.
The true value of vacuum hardening lies not just in strengthening the material, but in achieving this transformation with superior control, cleanliness, and repeatability. It replaces conventional oil or salt bath quenching with a precise, high-pressure gas quench, fundamentally changing the quality of the final part.

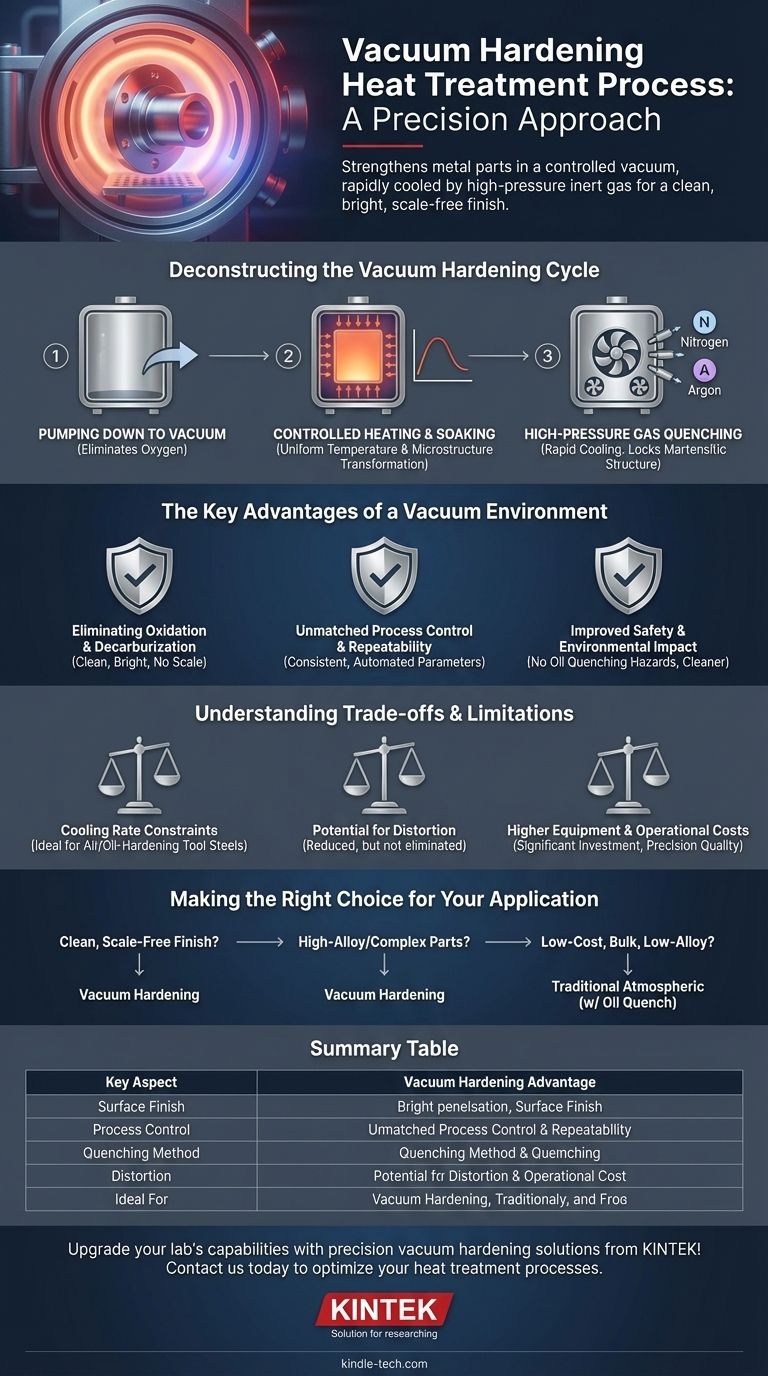
Deconstructing the Vacuum Hardening Cycle
The vacuum hardening process is a meticulously controlled sequence of stages, each critical to achieving the final material properties. It all takes place within a single, highly specialized vacuum furnace.
Step 1: Pumping Down to Vacuum
The cycle begins by placing the workpieces into the furnace chamber and sealing it. A powerful vacuum pumping system then removes the air and other atmospheric gases.
This step is fundamental because it eliminates oxygen. Without oxygen, the part's surface cannot oxidize or form scale during the high-temperature heating phase. The level of vacuum can be precisely controlled, from a low vacuum to a high vacuum (10⁻¹ Pa or lower), depending on the material and desired outcome.
Step 2: Controlled Heating and Soaking
Once the target vacuum level is reached, the parts are heated to a specific austenitizing temperature. This heating is typically done using electrical resistance elements or induction coils inside the furnace.
The parts are then held at this peak temperature for a calculated period, a step known as soaking. This ensures the entire part, including its core, reaches a uniform temperature and its internal microstructure fully transforms. The soaking time is determined by the material type and the effective thickness of the workpiece.
Step 3: High-Pressure Gas Quenching
This is the "hardening" stage. Instead of dropping the parts into a liquid like oil or water, the furnace is rapidly backfilled with a high-purity inert gas, most commonly nitrogen or argon.
Powerful fans or blowers circulate this gas at high velocity and positive pressure (often exceeding atmospheric pressure) to cool the parts rapidly. This rapid cooling, or quenching, locks the desired hard martensitic microstructure into place. The cooling rate can be precisely regulated by adjusting the gas pressure and flow rate.
The Key Advantages of a Vacuum Environment
Choosing vacuum hardening over traditional methods is a decision driven by the need for superior quality and process control.
Eliminating Oxidation and Decarburization
This is the primary benefit. Because the process occurs in a vacuum, there is no oxygen to react with the hot metal surface. The result is a part that emerges from the furnace clean, bright, and free from scale.
This also prevents decarburization, a phenomenon where carbon is lost from the surface layer of the steel, which would otherwise soften the part and reduce its fatigue life.
Unmatched Process Control and Repeatability
Modern vacuum furnaces are fully automated. Critical parameters—including the vacuum level, temperature ramp rates, soaking times, and gas quench pressure—are programmed and precisely controlled.
This digital precision ensures that every part in a batch, and every batch over time, receives an identical treatment cycle. This delivers exceptional consistency and repeatability, which is vital for high-performance applications.
Improved Safety and Environmental Impact
Vacuum hardening eliminates the fire hazards, noxious fumes, and messy residues associated with oil quenching. It creates a cleaner, safer work environment and disposes of the need for hazardous waste management related to used quench oils.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, vacuum hardening is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is crucial for making an informed decision.
Cooling Rate Constraints
While a high-pressure gas quench is very fast, it is generally less severe than an aggressive quench in oil or water. This means vacuum hardening is ideal for air-hardening and oil-hardening tool steels and some stainless steels.
For some low-alloy steels or parts with very large cross-sections, the gas quench may not be fast enough to achieve full hardness throughout the material's core.
Potential for Distortion
All quenching processes introduce thermal stress that can cause distortion. While vacuum gas quenching typically produces less distortion than a liquid quench due to its more uniform cooling, it does not eliminate it entirely.
For extremely delicate parts where minimizing distortion is the absolute priority, alternative low-temperature vacuum processes like nitriding—which does not involve quenching—might be more suitable.
Higher Equipment and Operational Costs
Vacuum furnaces are complex, sophisticated machines that represent a significant capital investment. The cost per cycle can also be higher than traditional atmospheric furnace treatments, making it most suitable for parts where the final quality justifies the expense.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct hardening process depends entirely on your material, part geometry, and final performance requirements.
- If your primary focus is achieving a clean, bright, scale-free finish: Vacuum hardening is the superior choice, as it eliminates the need for post-treatment sandblasting or chemical cleaning.
- If your primary focus is hardening high-alloy tool steels or complex geometries: Vacuum hardening provides the process control and uniform cooling needed to achieve target hardness with reduced risk of distortion compared to oil.
- If your primary focus is hardening low-cost, low-alloy steels in bulk: A traditional atmospheric furnace with an oil quench may be a more cost-effective solution, provided you can accommodate post-process cleaning.
Ultimately, vacuum hardening is a precision manufacturing process chosen when the final quality, consistency, and cleanliness of the component are paramount.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Vacuum Hardening Advantage |
|---|---|
| Surface Finish | Clean, bright, scale-free; no post-cleaning needed |
| Process Control | Precise temperature and vacuum level regulation |
| Quenching Method | High-pressure inert gas (e.g., nitrogen, argon) |
| Distortion | Typically less than liquid quenching methods |
| Ideal For | High-alloy tool steels, complex geometries, stainless steels |
Upgrade your lab's capabilities with precision vacuum hardening solutions from KINTEK!
Are you working with high-performance alloys or intricate components that demand exceptional hardness, cleanliness, and minimal distortion? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment, including vacuum furnace systems, designed to meet the rigorous demands of modern laboratories. Our solutions deliver the process control and repeatability you need for critical applications.
Contact us today via our form to discuss how our expertise in lab equipment and consumables can help you achieve superior results and optimize your heat treatment processes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a vacuum heat treatment work? Achieve Superior Material Properties in a Pristine Environment
- What are the uses of vacuum furnace? Achieve Unmatched Material Purity and Performance
- What materials are used in a vacuum furnace? Selecting the Right Hot Zone for Your Process
- What are vacuum furnaces used for? Unlock Ultimate Material Purity and Performance
- What are vacuum furnace parts? A Guide to the Core Systems for Precision Heat Treatment



















