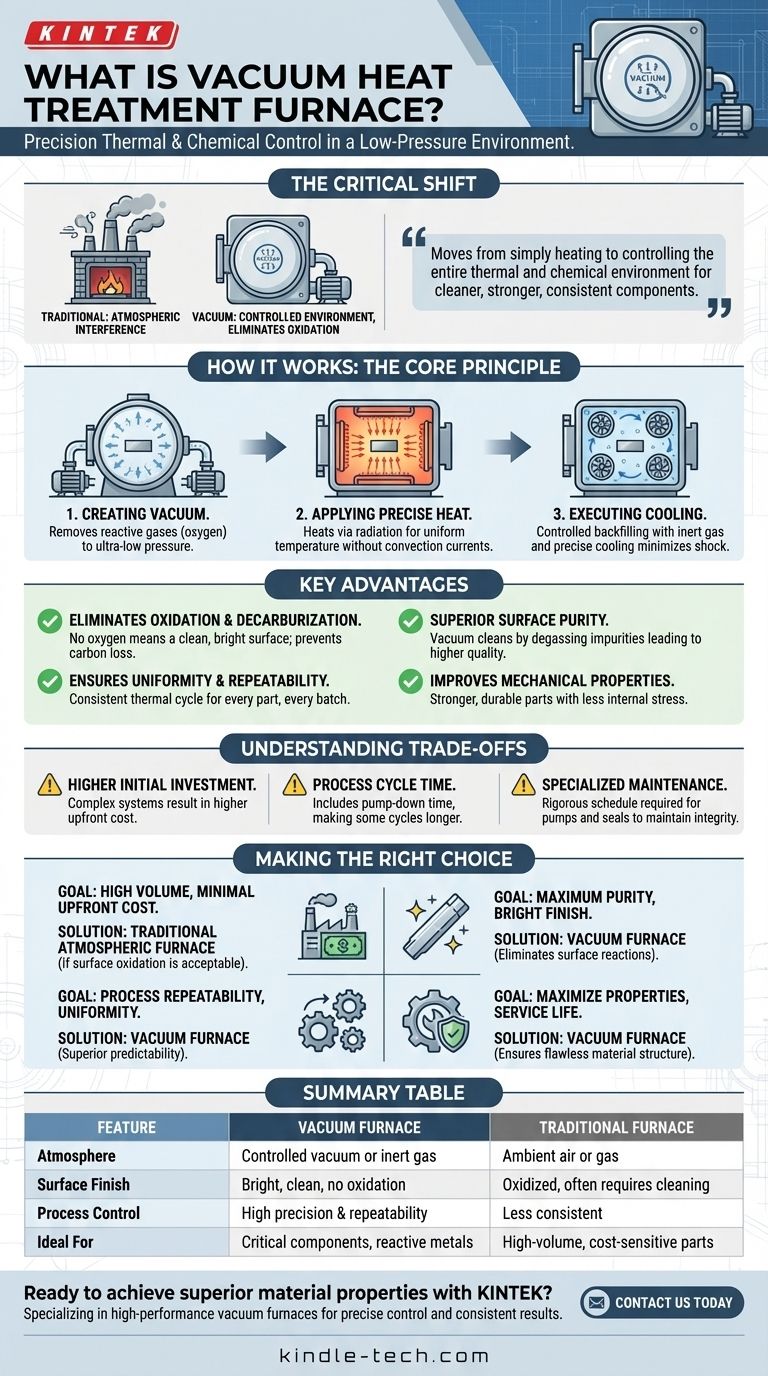
At its core, a vacuum heat treatment furnace is a specialized piece of equipment that heats and cools materials within a controlled, low-pressure environment. Instead of performing these processes in open air, it first removes nearly all of the atmosphere from its chamber. This fundamental difference prevents unwanted chemical reactions, like oxidation, ensuring the material's surface and internal structure are treated with exceptional precision.
The critical shift from traditional to vacuum heat treatment is moving from simply heating a material to precisely controlling its entire thermal and chemical environment. This eliminates atmospheric interference, resulting in cleaner, stronger, and more consistent components.

How a Vacuum Furnace Works: The Core Principle
A vacuum furnace operates by fundamentally changing the environment surrounding the workpiece. This is a deliberate, multi-stage process designed for ultimate control.
Creating the Controlled Environment
First, the assembled workpiece is placed and sealed inside the furnace chamber. A powerful vacuum system, often involving multiple types of pumps, is then used to evacuate the air. The goal is to remove reactive gases, primarily oxygen, to a pressure far below normal atmospheric pressure.
Applying Precise Heat
Once the desired vacuum level is reached, heat is applied. Unlike conventional furnaces that rely on convection (the movement of hot air), a vacuum furnace heats the material primarily through radiation from graphite or ceramic heating elements. This method ensures highly uniform and predictable temperature distribution across the part, without disruptive air currents.
Executing the Cooling Process
Cooling, or quenching, is also meticulously controlled. Instead of dropping the part into an oil or water bath, the furnace is typically backfilled with a high-purity inert gas like nitrogen or argon. Fans then circulate this gas to cool the part at a precise, programmable rate, minimizing thermal shock and distortion.
The Key Advantages of a Vacuum Environment
Operating without an atmosphere is not just a minor tweak; it provides a range of benefits that are impossible to achieve with conventional methods.
Eliminating Oxidation and Decarburization
This is the primary advantage. With virtually no oxygen present, the metal surface cannot oxidize, resulting in a clean, bright finish that requires no subsequent cleaning. For high-carbon steels, it also prevents decarburization—the loss of carbon from the surface, which would otherwise soften the material.
Achieving Superior Surface Purity
The vacuum environment actively cleans the workpiece. Processes like degassing and degreasing occur naturally as impurities on the material's surface vaporize in the low-pressure environment and are removed by the vacuum system. This leads to a purer, higher-quality end product.
Ensuring Uniformity and Repeatability
The absence of convection currents and the precision of radiant heating and controlled gas cooling lead to extremely uniform results. Every part in a batch, and every subsequent batch, experiences the exact same thermal cycle, ensuring unparalleled process repeatability.
Improving Mechanical Properties
By preventing surface contamination and ensuring a uniform internal structure, vacuum heat treatment directly improves the final component's mechanical properties and service life. Parts are stronger, more durable, and have less internal stress and deformation.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, vacuum heat treatment is not a universal solution. An objective assessment requires understanding its limitations.
Higher Initial Investment
Vacuum furnaces are complex systems involving sophisticated heating, pumping, and control instrumentation. This results in a significantly higher upfront capital cost compared to traditional atmospheric furnaces.
Process Cycle Time
While the heating and cooling rates can be very rapid, the overall cycle time must include the "pump-down" phase required to achieve the necessary vacuum level. For some applications, this can make the total process time longer than conventional methods.
Specialized Maintenance
The integrity of the vacuum is paramount. This requires a rigorous and specialized maintenance schedule for the vacuum pumps, chamber seals, and control sensors to prevent leaks and ensure consistent performance.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the appropriate heat treatment method depends entirely on the required outcome for your component.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production with minimal upfront cost: Traditional atmospheric furnaces may be more suitable, provided surface oxidation is acceptable or can be managed with post-processing.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum component purity and a bright finish: A vacuum furnace is the definitive choice, as it completely eliminates surface reactions like oxidation and decarburization.
- If your primary focus is process repeatability and treating complex geometries uniformly: The controlled environment of a vacuum furnace offers superior predictability and avoids the inconsistencies of convection heating.
- If your primary focus is maximizing the mechanical properties and service life of critical components: Vacuum treatment is essential for removing impurities, preventing contamination, and ensuring a flawless material microstructure.
Ultimately, adopting vacuum heat treatment is a strategic decision to prioritize absolute control and material integrity above all else.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Vacuum Furnace | Traditional Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Atmosphere | Controlled vacuum or inert gas | Ambient air or gas |
| Surface Finish | Bright, clean, no oxidation | Oxidized, often requires cleaning |
| Process Control | High precision and repeatability | Less consistent |
| Ideal For | Critical components, reactive metals | High-volume, cost-sensitive parts |
Ready to achieve superior material properties with a vacuum heat treatment furnace?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-performance lab equipment, including vacuum furnaces, to meet the demanding needs of laboratories and research facilities. Our solutions ensure precise temperature control, eliminate surface contamination, and deliver consistent, repeatable results for your most critical components.
Contact us today to discuss how our vacuum heat treatment technology can enhance your lab's capabilities and drive your research forward. Get in touch with our experts now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why do you heat treat in a vacuum? Achieve Perfect Surface Finish and Material Integrity
- How does heat treatment process work? Tailor Material Properties for Your Application
- What are the different types of heat treatment process for steel? Tailor Strength, Hardness & Toughness
- What are the parts of a vacuum furnace? A Guide to the 5 Core Systems
- What are the three main heat treatments? Mastering Annealing, Hardening & Tempering



















