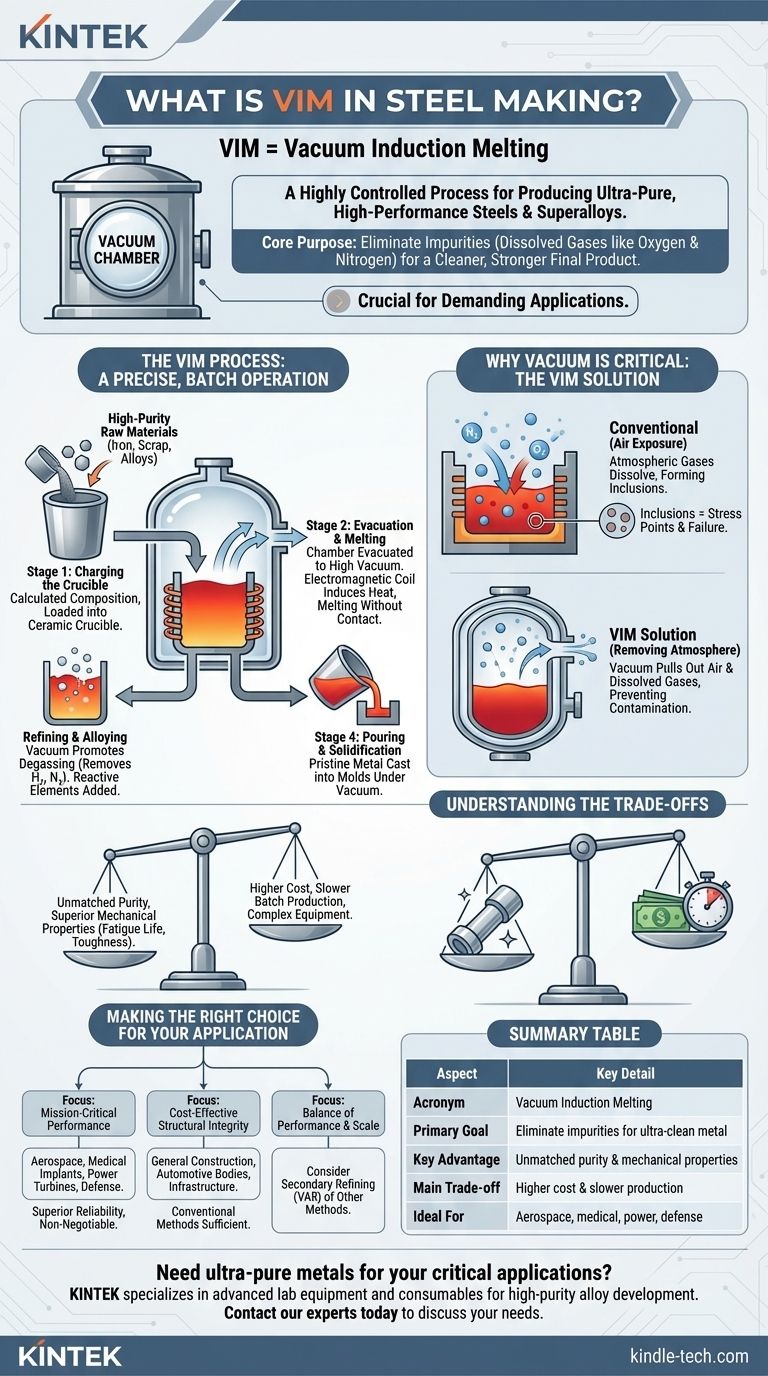
In the context of steelmaking, VIM is not a word but an acronym. It stands for Vacuum Induction Melting, a highly controlled and specialized process for producing extremely clean, high-purity, and high-performance steels and superalloys. Unlike conventional melting, which occurs in open air, VIM takes place entirely within a sealed, vacuum-tight chamber to prevent contamination from atmospheric gases.
The core purpose of Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) is to eliminate impurities, particularly dissolved gases like oxygen and nitrogen, from molten metal. This produces a cleaner, stronger, and more reliable final product suitable for the most demanding applications.
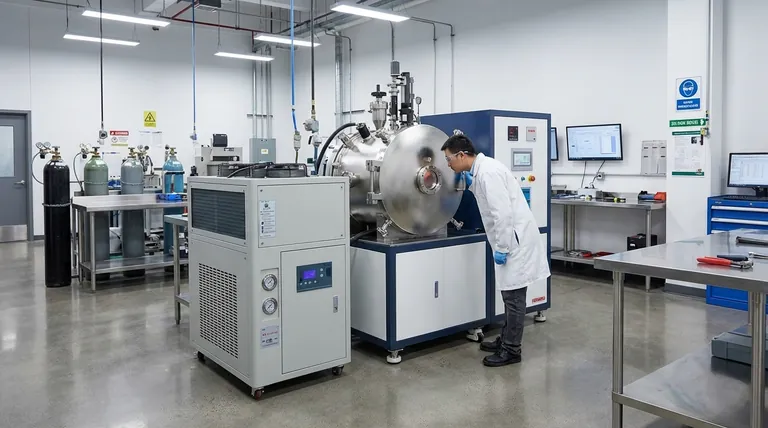

Why Vacuum is the Critical Factor
In conventional steelmaking, molten metal is constantly exposed to the atmosphere. This exposure is the primary source of contamination that can compromise the final material's properties.
The Problem with Air Exposure
Air consists primarily of nitrogen (~78%) and oxygen (~21%). When these gases dissolve in molten steel, they form undesirable compounds called inclusions.
These microscopic inclusions, such as oxides and nitrides, act as stress points within the metal's crystal structure. They are the starting points for cracks and material failure.
The VIM Solution: Removing the Atmosphere
By placing the entire melting process inside a vacuum chamber, VIM physically removes the source of this contamination.
Pulling a strong vacuum evacuates the air, preventing oxygen and nitrogen from ever coming into contact with the molten metal. The vacuum also helps draw out any dissolved gases already present in the solid raw materials, further purifying the melt.
Deconstructing the VIM Process
The VIM process is a precise, batch-oriented operation that involves several key stages, all performed without breaking the vacuum seal.
Stage 1: Charging the Crucible
High-purity raw materials, including iron, scrap, and primary alloying elements, are loaded into a ceramic crucible. The composition is calculated with extreme precision.
Stage 2: Evacuation and Melting
The chamber is sealed, and powerful pumps create a high vacuum. An electromagnetic coil surrounding the crucible is then energized, inducing a powerful electrical current within the metal charge. This current generates intense heat, melting the materials without any direct contact or flame.
Stage 3: Refining and Alloying
Once molten, the vacuum environment promotes degassing, pulling unwanted elements like hydrogen and nitrogen out of the liquid metal. At this stage, highly reactive alloying elements (like aluminum and titanium), which would instantly oxidize in air, can be added with precise control.
Stage 4: Pouring and Solidification
The entire crucible is tilted within the vacuum chamber to pour the purified molten metal into molds, a process known as casting. This ensures the metal remains pristine until it solidifies.
Understanding the Trade-offs
VIM produces exceptional materials, but it is not the standard for all steel production. The decision to use it is a direct trade-off between material quality and production cost.
Key Advantage: Unmatched Purity
The primary benefit of VIM is the production of exceptionally clean steel. This cleanliness directly translates to superior mechanical properties, including improved fatigue life, toughness, and fracture resistance.
The High Cost of Quality
VIM is a batch process, not a continuous one, which limits production volume. The equipment is complex and expensive to build and maintain.
Slower Production Cycles
Achieving and maintaining a high vacuum, followed by the controlled melting and refining stages, makes the process significantly slower than conventional air-melting techniques. This lower throughput increases the cost per ton.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The choice to specify a VIM-produced material depends entirely on the performance requirements and budget of your project.
- If your primary focus is mission-critical performance: For applications in aerospace, medical implants, power generation turbines, or defense, the superior fatigue life and reliability of VIM steel are non-negotiable.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective structural integrity: For general construction, automotive bodies, or infrastructure, the high cost of VIM is unnecessary. Conventional steelmaking processes provide the required performance at a fraction of the cost.
- If your primary focus is a balance of high performance and production scale: You may consider materials produced by other methods, sometimes followed by a secondary vacuum refining process like Vacuum Arc Remelting (VAR), which further purifies an already-cast ingot.
Ultimately, understanding VIM is understanding the fundamental principle that controlling a material's environment during its creation dictates its final quality.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Acronym | Vacuum Induction Melting |
| Primary Goal | Eliminate impurities (gases like O₂, N₂) for ultra-clean metal |
| Key Advantage | Unmatched material purity and superior mechanical properties |
| Main Trade-off | Higher cost and slower production vs. conventional methods |
| Ideal For | Aerospace, medical implants, power generation, defense |
Need ultra-pure metals for your critical applications? The exceptional cleanliness and reliability of VIM-produced materials are essential for mission-critical performance in aerospace, medical, and energy sectors. KINTEK specializes in providing the advanced lab equipment and consumables needed to support the development and quality control of these high-performance alloys. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your high-purity metal production and testing needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Induction Melting Spinning System Arc Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is vacuum arc melting technique? Discover the Precision of Vacuum Induction Melting
- What is VIM in metallurgy? A Guide to Vacuum Induction Melting for High-Performance Alloys
- What principle is used to generate heat in a vacuum induction melting furnace? Achieve Clean, Efficient Metal Melting
- What is the difference between induction melting and vacuum induction melting? Choosing the Right Process for Purity
- What is the primary function of a vacuum induction melting furnace? Melt High-Purity Metals with Precision



















