In short, resistive thermal evaporation is primarily used for depositing thin films of materials with relatively low melting and boiling points. This includes a wide range of common metals like gold (Au), aluminum (Al), and indium (In), as well as some non-metallic compounds.
The core principle of resistive evaporation is heating a source until it vaporizes. Therefore, the ideal materials are those that can be evaporated at temperatures that are easily and economically achieved without damaging the heating equipment itself.
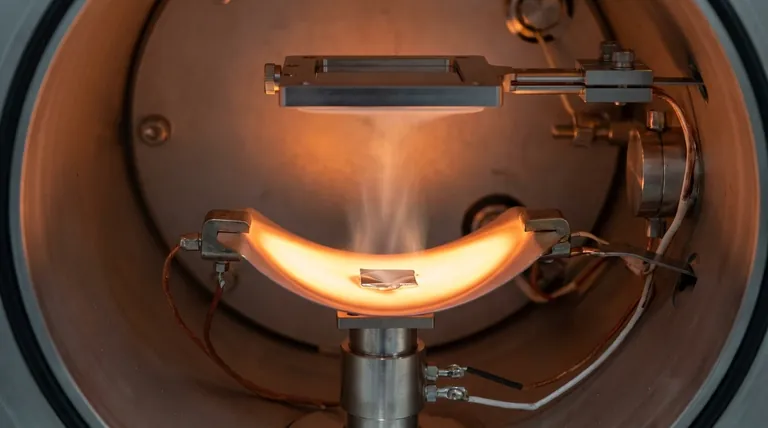

The Guiding Principle: Evaporation Temperature
Resistive evaporation is a straightforward form of Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD). Its simplicity is its greatest strength and also defines its material limitations.
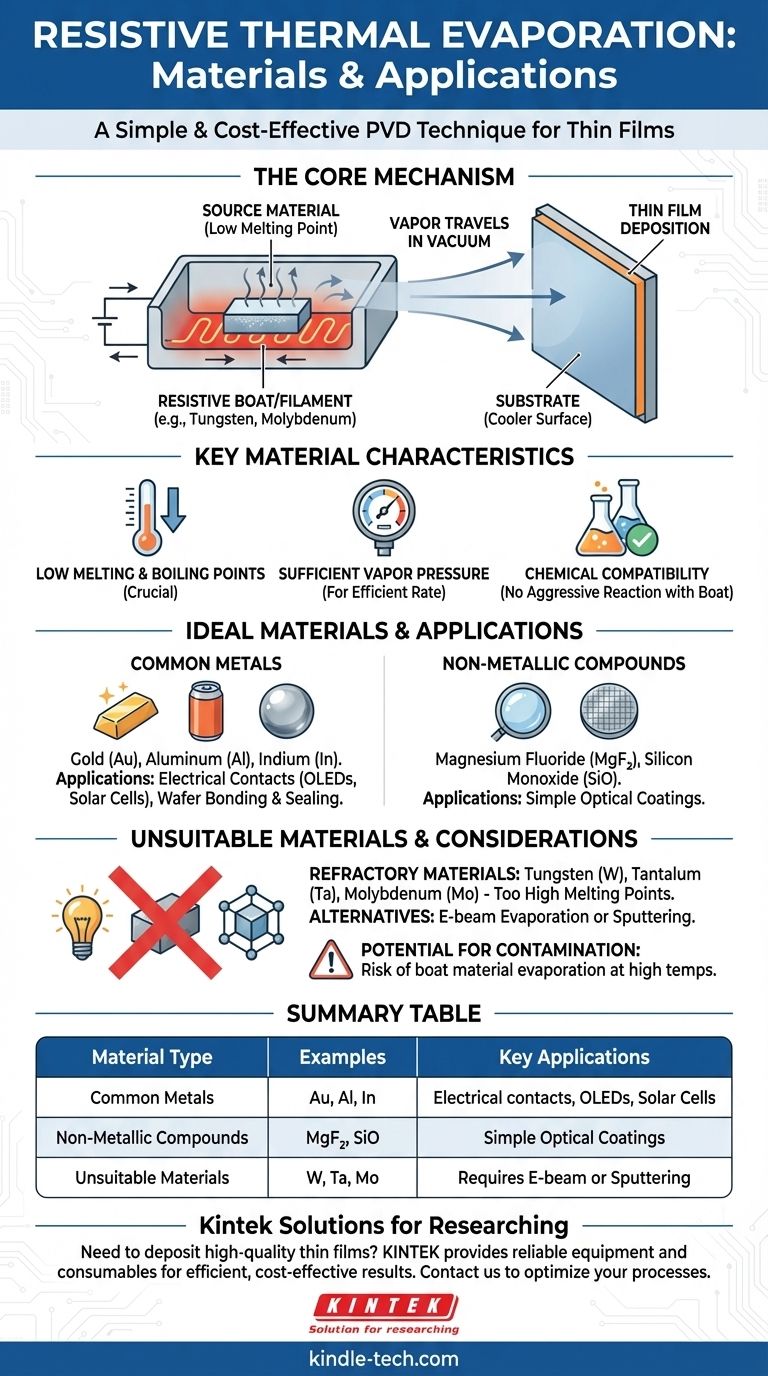
The Core Mechanism
A high electrical current is passed through a resistive source, often a small "boat" or filament made of a high-temperature metal like tungsten or molybdenum. This causes the boat to heat up rapidly due to its electrical resistance.
The Evaporation Process
The material you wish to deposit is placed inside this boat. As the boat's temperature rises, it transfers heat to the source material, causing it to first melt and then evaporate, turning into a vapor.
Film Deposition
This vapor travels in a straight line through the vacuum chamber until it condenses on a cooler surface, which is the substrate (e.g., a silicon wafer or glass slide), forming a thin film.
Key Material Characteristics
Not every material is a good candidate for this process. The selection is governed by a few key physical properties.
Low Melting and Boiling Points
This is the single most important factor. The source material must evaporate at a temperature that is well below the melting point of the resistive boat. For example, aluminum evaporates effectively around 1200°C, which a tungsten boat (melting point >3400°C) can handle easily.
Attempting to evaporate materials with very high melting points, like tungsten itself, is impractical with this method as you would likely melt the heating element first.
Sufficient Vapor Pressure
A material must achieve a high enough vapor pressure at a reasonable temperature to produce an efficient deposition rate. Materials that require extremely high temperatures to generate vapor are poor candidates for this technique.
Chemical Compatibility
The molten source material should not aggressively alloy with or corrode the heating boat. Such a reaction can destroy the boat and, more critically, introduce impurities from the boat material into your thin film.
Common Applications and Material Choices
The combination of low cost and high deposition rates makes resistive evaporation ideal for specific, high-volume applications.
Metallic Contacts
The most common use is creating conductive metal layers. Aluminum and gold are frequently deposited for electrical contacts in devices like OLEDs, thin-film transistors, and solar cells.
Wafer Bonding and Sealing
Indium is often used for creating bumps or layers for wafer bonding. Its very low melting point makes it easy to work with and an ideal hermetic sealant in certain microelectronic packages.
Optical Coatings
Simple optical layers using materials like magnesium fluoride (MgF₂) or silicon monoxide (SiO) can also be deposited, although other methods are often preferred for more complex optical stacks.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While simple and cost-effective, resistive evaporation has clear limitations you must consider.
Not for Refractory Materials
This method is unsuitable for refractory metals—materials with very high melting points like tungsten (W), tantalum (Ta), or molybdenum (Mo). For these, electron-beam evaporation or sputtering are required.
Potential for Contamination
Because you are heating a boat to high temperatures, there is always a small risk that the boat material itself will evaporate and contaminate the film. This is why selecting a boat material with a very low vapor pressure (like tungsten) is critical.
Limited Control Over Co-Deposition
While multiple sources can be used to co-deposit materials, precisely controlling the stoichiometry (the exact ratio of elements) of a complex compound film is very difficult compared to a technique like sputtering.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Use this technique when its strengths align with your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective deposition of simple metals: Resistive evaporation is an excellent choice for materials like aluminum, gold, chromium, or indium for conductive layers.
- If your primary focus is depositing high-purity or complex alloys: You should consider sputtering or electron-beam evaporation for better control over film composition and lower contamination risk.
- If your primary focus is depositing high-temperature or refractory materials: Resistive evaporation is not the correct tool; you must use a higher-energy process like e-beam evaporation.
Ultimately, resistive evaporation excels at its intended purpose: the simple, rapid, and economical deposition of low-melting-point materials.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Examples | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Common Metals | Gold (Au), Aluminum (Al), Indium (In) | Electrical contacts, OLEDs, solar cells |
| Non-Metallic Compounds | Magnesium Fluoride (MgF₂), Silicon Monoxide (SiO) | Simple optical coatings |
| Unsuitable Materials | Tungsten (W), Tantalum (Ta), Molybdenum (Mo) | Requires e-beam evaporation or sputtering |
Need to deposit high-quality thin films for your lab? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing reliable solutions for resistive thermal evaporation and other deposition techniques. Our expertise ensures you achieve efficient, cost-effective results with materials like gold, aluminum, and more. Contact us today to optimize your thin-film processes and enhance your research or production outcomes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Evaporation Boat for High Temperature Applications
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Evaporation Boat for Organic Matter
- Hemispherical Bottom Tungsten Molybdenum Evaporation Boat
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
People Also Ask
- What is thermal evaporation technique thin film deposition? A Guide to Simple, Cost-Effective PVD
- What is the thermal evaporation technique? A Guide to Thin-Film Deposition for Your Lab
- What is vacuum thermal evaporation? A Guide to High-Purity Thin Film Deposition
- What is thermal effect via evaporation? A Simple Guide to Thin-Film Deposition
- What is the meaning of thermal evaporation? A Guide to Simple, Cost-Effective Thin Film Coating



















