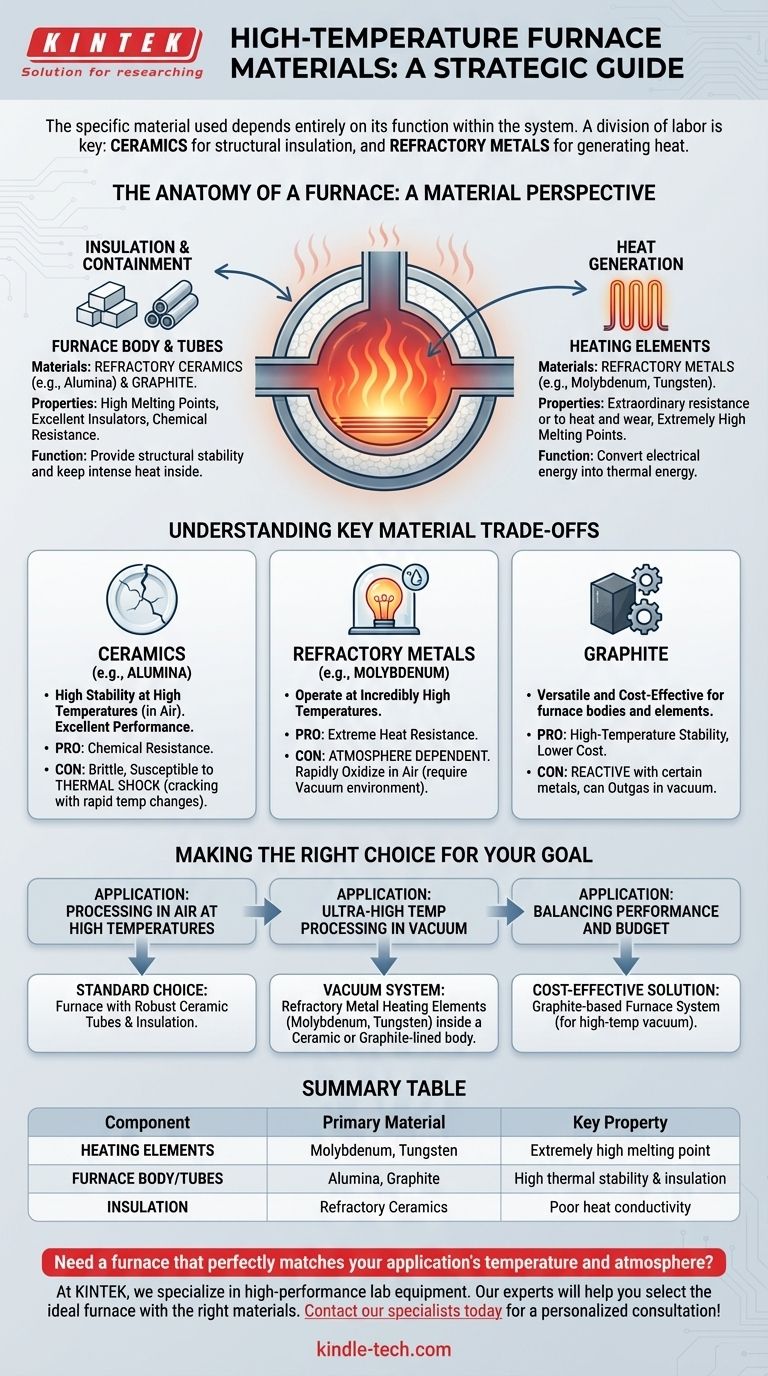
For a high-temperature furnace, the specific material used depends entirely on its function within the system. The furnace body and insulation are typically constructed from refractory ceramics like alumina or graphite, which are chosen for their stability and poor heat conductivity. The heating elements, which must generate the extreme heat, are made from refractory metals like molybdenum and tungsten due to their exceptionally high melting points.
The core principle is a division of labor: ceramics are used for structural insulation and containment, while specialized refractory metals are used to generate the heat itself, especially in vacuum environments. The ideal material is always a function of the required temperature, the furnace atmosphere, and the specific component's role.
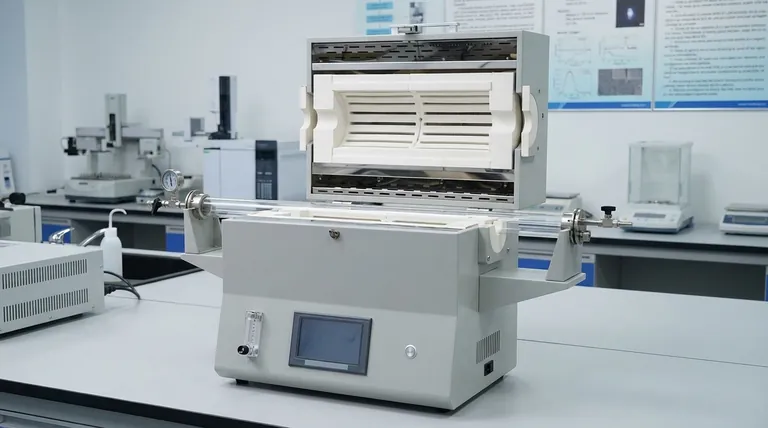

The Anatomy of a Furnace: A Material Perspective
A high-temperature furnace isn't made of a single material but is an assembly of specialized components, each with a material chosen for its unique properties under extreme stress.
The Furnace Body and Tubes: Containing the Heat
The primary role of the furnace body and any internal process tubes is to provide structural stability and thermal insulation.
The materials of choice here are refractory ceramics and graphite. These materials have very high melting points and, critically, are excellent insulators, keeping the intense heat inside the furnace.
Alumina is a common ceramic used for furnace tubes, valued for its high-temperature stability and chemical resistance.
The Heating System: Generating Extreme Temperatures
The heating elements are the heart of the furnace, responsible for converting electrical energy into thermal energy.
These components are typically made from refractory metals, which are defined by their extraordinary resistance to heat and wear.
The most common metals are molybdenum (and its alloys like TZM and molybdenum-lanthanum) and tungsten. These are selected because their melting points are far higher than the operating temperatures of the furnace.
Understanding Key Material Trade-offs
Selecting a material is never about finding a single "best" option; it's about balancing performance, cost, and operational constraints.
Ceramics (e.g., Alumina): High Stability, Low Shock Resistance
Alumina and other ceramics offer excellent performance at high temperatures and in the presence of oxygen.
However, they are brittle and highly susceptible to thermal shock. Rapid heating or cooling can cause them to crack, a risk that increases with the material's thickness and diameter.
Refractory Metals (e.g., Molybdenum): High Temperature, Atmosphere Dependent
Molybdenum and tungsten can operate at incredibly high temperatures, but they will rapidly oxidize and fail if heated in the presence of air.
This is why these metals are almost exclusively used as heating elements inside vacuum furnaces, where the oxygen-free environment protects them from degradation.
Graphite: Versatile and Cost-Effective, but Reactive
Graphite is a common refractory material for furnace bodies, insulation, and even some heating elements due to its high-temperature stability and lower cost.
However, it can react with certain metals and can outgas in a vacuum, requiring careful consideration based on the materials being processed.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your application's specific requirements—temperature, atmosphere, and the material being processed—will dictate the ideal furnace construction.
- If your primary focus is processing in air at high temperatures: A furnace with robust ceramic (e.g., alumina) tubes and insulation is the standard choice.
- If your primary focus is ultra-high temperature processing in a vacuum: Your system will require refractory metal (molybdenum, tungsten) heating elements within a ceramic or graphite-lined furnace body.
- If your primary focus is balancing performance and budget: A graphite-based furnace system is often the most cost-effective solution for high-temperature vacuum applications.
Understanding these core materials and their trade-offs empowers you to select a furnace that precisely matches your thermal processing needs.
Summary Table:
| Component | Primary Material | Key Property |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Elements | Molybdenum, Tungsten | Extremely high melting point |
| Furnace Body/Tubes | Alumina, Graphite | High thermal stability & insulation |
| Insulation | Refractory Ceramics | Poor heat conductivity |
Need a furnace that perfectly matches your application's temperature and atmosphere?
At KINTEK, we specialize in high-performance lab equipment. Our experts will help you select the ideal furnace with the right materials—whether you need refractory metal heating for a vacuum environment or robust ceramic insulation for air-based processes.
Contact our specialists today for a personalized consultation and ensure your thermal processing is a success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How do furnaces contribute to sodium battery cathode performance? Mastering Solid-State Synthesis for Energy Storage
- What is the process of vacuum hardening? Achieve Superior Hardness with a Pristine Surface Finish
- What is a laboratory furnace? The Essential Guide to High-Temperature Precision
- What are the core capabilities of a fast pyrolysis furnace in producing lignin-derived bio-oil? Maximize Your Yield
- How does a high-temperature calcination furnace contribute to the formation of Si-RuO2 catalysts? Optimize Your Synthesis
- What is physical Vapour deposition in crystal growth? Master Atomic-Level Thin Film Fabrication
- What is the primary use of furnace in the chemical industry? Master Thermal Treatment for Material Transformation
- What is the difference between liquid and gas carburizing? Precision, Safety & Environmental Impact



















