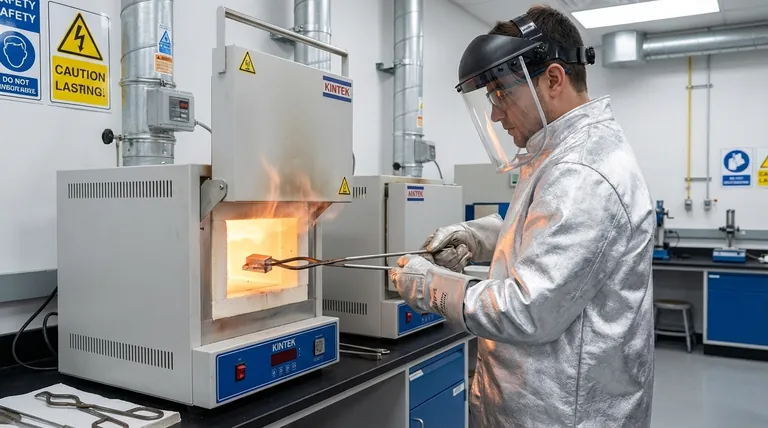
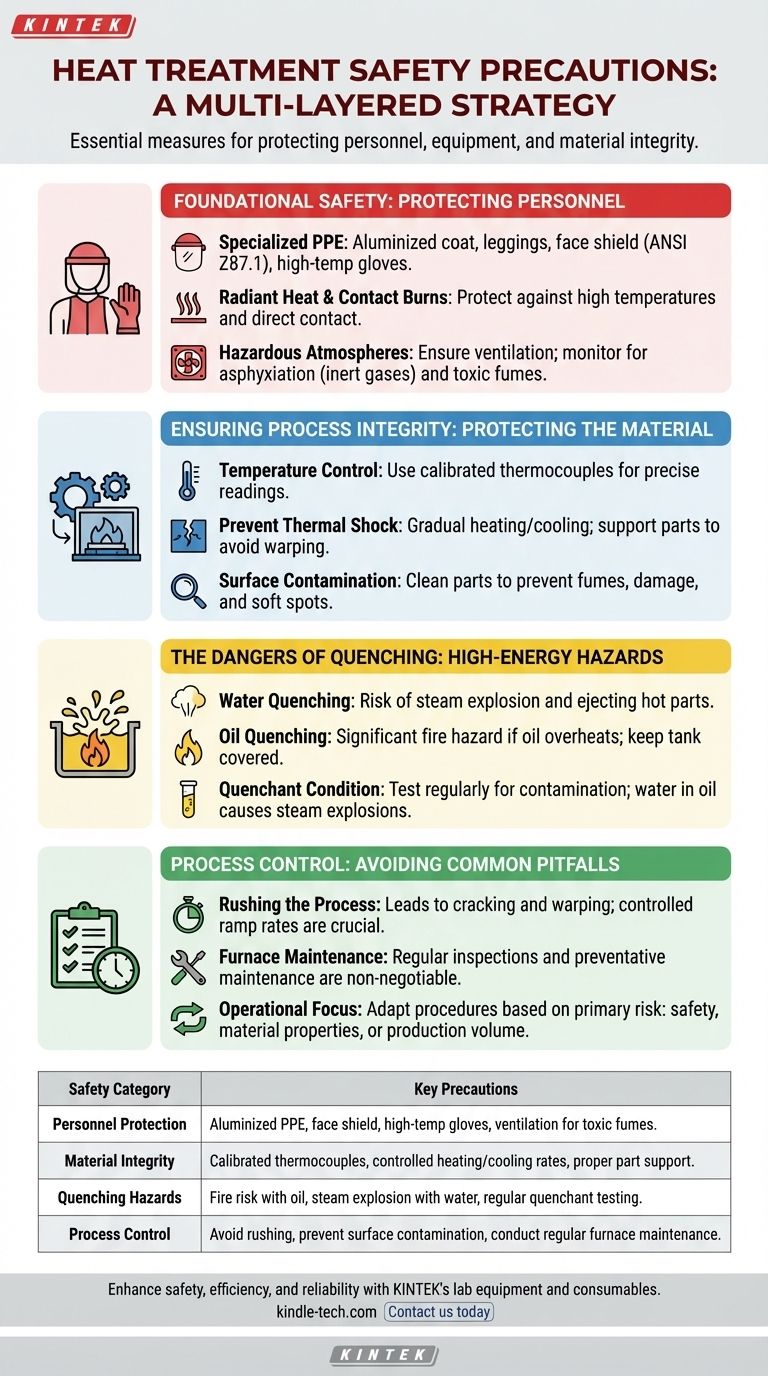
Observing proper precautions during heat treatment is a non-negotiable aspect of metallurgical work. At its core, this means implementing a multi-layered safety strategy that addresses personal, equipment, and material risks. The necessary precautions involve using specific personal protective equipment (PPE), ensuring correct furnace operation, carefully handling materials throughout the process, and understanding the violent reactions that can occur, particularly during quenching.
The primary goal of heat treatment safety extends beyond simply preventing burns; it is about systematically controlling a high-energy process from start to finish. This requires treating every step—from furnace preparation to part quenching—as a critical control point for ensuring personnel safety, material integrity, and equipment longevity.

Foundational Safety: Protecting Personnel
The most immediate risks in heat treatment involve high temperatures and hazardous materials. Protecting the operator is the first priority.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) is the First Line of Defense
Your standard workshop PPE is insufficient. Heat treatment demands specialized gear designed for thermal hazards. This includes an aluminized coat and leggings to reflect radiant heat, a face shield with ANSI Z87.1 rating, and high-temperature gloves. For handling parts at temperature, non-flammable materials like Kevlar or leather are essential.
Understanding Thermal Hazards
Operators face two types of heat risk: contact burns from touching hot parts or furnaces, and radiant heat exposure. Radiant heat can cause serious burns and heat stress even from a distance, which is why reflective aluminized clothing is critical.
Managing Hazardous Atmospheres
Many furnaces use inert gases like nitrogen or argon to prevent oxidation. In an enclosed space, a leak can displace oxygen and create an asphyxiation hazard. Proper ventilation and atmosphere monitoring are crucial. Likewise, the fumes from burning surface contaminants or quenching oil can be toxic and require local exhaust ventilation.
Ensuring Process Integrity: Protecting the Material
Procedural errors not only pose a safety risk but can also destroy the workpiece, wasting significant time and resources.
The Critical Role of Temperature Control
The properties of the final product are dictated by precise temperature and time. Using a properly calibrated thermocouple is essential. An inaccurate temperature reading can mean the difference between a perfectly hardened part and a brittle, cracked, or soft one.
Preventing Thermal Shock and Distortion
Heating or cooling a part too quickly creates internal stresses that can cause it to warp or crack. This is known as thermal shock. Parts should be heated gradually and supported properly within the furnace to prevent sagging at high temperatures.
The Dangers of Quenching
Quenching is often the most hazardous step. Submerging a hot part in a liquid causes an instant, violent reaction.
- Water Quenching: Creates a massive and instantaneous steam bubble that can splash boiling water and potentially eject the part.
- Oil Quenching: Poses a significant fire hazard. If the oil's temperature exceeds its flash point, the hot part can ignite the oil's vapors.
Surface Contamination is a Hidden Risk
Any oil, grease, or cutting fluid left on a part will burn off in the furnace. This creates unwanted fumes, can damage furnace elements, and may even affect the part's surface chemistry, leading to soft spots or inconsistent hardening.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Common Pitfalls
Every decision in heat treatment involves balancing speed, cost, and safety. Recognizing common failure points is key to avoiding them.
Pitfall: Rushing the Process
The most common mistake is attempting to heat or cool parts too quickly to save time. This is the leading cause of cracking and warping. A slow, controlled ramp rate for temperature is almost always safer and produces a better result.
Pitfall: Neglecting Quenchant Condition
Quenching oil degrades over time and can become contaminated with water. Water contamination is extremely dangerous, as it can cause a violent steam explosion when a hot part is introduced. Oil should be tested regularly, and quench tanks must be covered to prevent water entry.
Pitfall: Overlooking Furnace Maintenance
A faulty door seal, a cracked heating element, or a malfunctioning controller can compromise both safety and the quality of the work. Regular inspection and preventative maintenance are not optional; they are a core part of a safe operating procedure.
How to Apply This to Your Operation
Your procedural focus should adapt based on the primary risk factor of your specific operation.
- If your primary focus is operator safety: Your highest priority is rigorous training on PPE, radiant heat hazards, and emergency procedures for quench fires.
- If your primary focus is achieving specific material properties: Unwavering control over furnace calibration, soak times, and quenchant agitation is paramount to prevent scrapped parts.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production: Automating loading/unloading and implementing strict preventative maintenance schedules for furnaces and quench systems are essential for both safety and consistency.
A disciplined, well-informed approach transforms heat treatment from a hazardous art into a predictable and safe science.
Summary Table:
| Safety Category | Key Precautions |
|---|---|
| Personnel Protection | Aluminized PPE, face shield, high-temp gloves, ventilation for toxic fumes. |
| Material Integrity | Calibrated thermocouples, controlled heating/cooling rates, proper part support. |
| Quenching Hazards | Fire risk with oil, steam explosion with water, regular quenchant testing. |
| Process Control | Avoid rushing, prevent surface contamination, conduct regular furnace maintenance. |
Ensure your heat treatment processes are safe, efficient, and reliable with KINTEK.
As specialists in lab equipment and consumables, we understand the critical importance of safety and precision in metallurgical work. Our range of high-quality furnaces, calibrated thermocouples, and safety accessories are designed to help you implement the essential precautions outlined in this article—protecting your team, your materials, and your investment.
Whether you're focused on operator safety, achieving precise material properties, or scaling up production, KINTEK has the solutions to support your laboratory's unique needs.
Contact us today to discuss how our equipment can enhance the safety and success of your heat treatment operations.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- How is a multi-channel potentiostat used in fixed-bed bioelectrochemical systems? Optimize Spatial Mapping & Control
- What are 5 common uses for molybdenum? Enhancing Steel, Alloys, and High-Temp Performance
- What is the energy consumption of conventional ultra-low temperature (ULT) freezers? Managing High Energy Costs
- What temperature is maintained in a bacterial incubator? The 37°C Standard Explained
- Is a filter press better than a clarifier? Choose the Right Tool for Your Separation Goal
- What is the effect of sputtering pressure? Master Atomic Energy for Superior Thin Films
- Why is high-purity nitrogen used for deoxygenation? Ensure Accuracy in HTHP Corrosion Experiments
- How thick is sputter coating for SEM? Achieve Perfect SEM Imaging with Optimal Coating Thickness



















