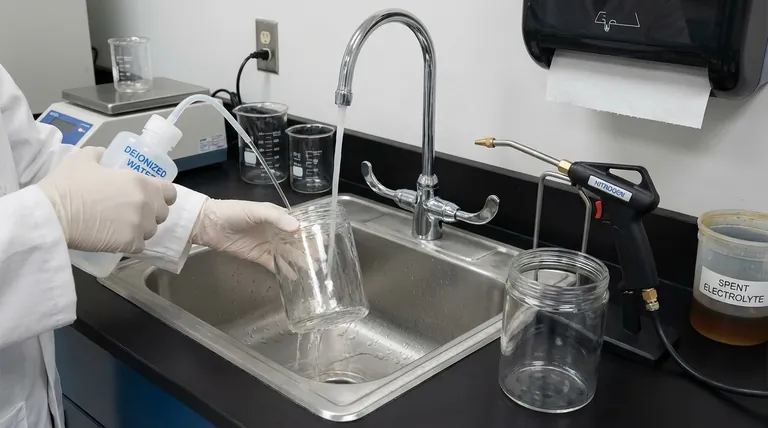
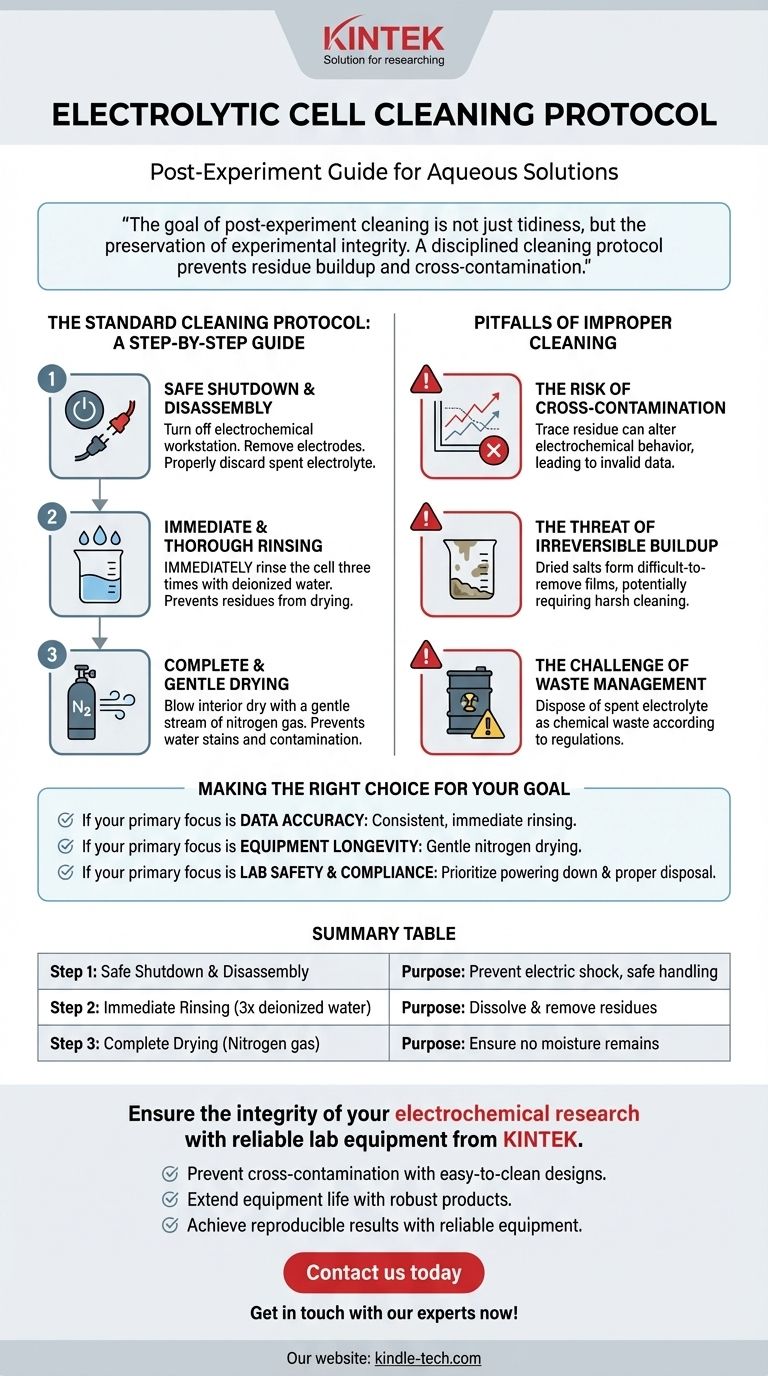
For experiments using aqueous solutions, the standard procedure is to first safely power down the equipment, remove the electrodes, and properly discard the electrolyte. You must then immediately rinse the electrolytic cell thoroughly with deionized water at least three times before drying it completely with a stream of nitrogen gas.
The goal of post-experiment cleaning is not just tidiness, but the preservation of experimental integrity. A disciplined cleaning protocol prevents residue buildup and cross-contamination, which are common sources of inaccurate and unreliable data in future experiments.

The Standard Cleaning Protocol: A Step-by-Step Guide
Following a consistent, methodical process after every experiment is critical for maintaining your equipment and ensuring the validity of your research. Each step serves a specific purpose, from safety to preventing contamination.
Step 1: Safe Shutdown and Disassembly
Before handling the cell, you must turn off the electrochemical workstation or power supply. This crucial first step prevents the risk of electric shock or the creation of electrical arcs when disconnecting components.
Once the system is powered down, you can safely remove the electrodes and any other attachments. Finally, pour out the spent electrolyte into an appropriate waste container.
Step 2: Immediate and Thorough Rinsing
This is the most critical step for preventing contamination. As soon as the electrolyte is removed, immediately rinse the cell three times with deionized water.
Do not delay this step. Waiting allows residues and salts to dry on the cell walls, where they can solidify and become extremely difficult to remove without aggressive cleaning agents. An immediate rinse dissolves and removes these potential contaminants while they are still in solution.
Step 3: Complete and Gentle Drying
After rinsing, the cell must be dried completely. The standard method is to blow the interior dry with a gentle stream of nitrogen gas.
Nitrogen is an inert gas that rapidly displaces water without leaving behind any residue. This method is vastly superior to air drying, which is slow and can introduce dust or other airborne contaminants. Proper drying prevents water stains and ensures that any remaining moisture does not dilute the electrolyte in your next experiment.
Understanding the Pitfalls of Improper Cleaning
Cutting corners during the cleaning process may seem like a minor time-saver, but it introduces significant risks that can compromise your work. Understanding these consequences reinforces the importance of a rigorous protocol.
The Risk of Cross-Contamination
Even trace amounts of residue from a previous experiment can interfere with your next one. Leftover ions can alter the electrochemical behavior of your new system, leading to skewed measurements, shifted potentials, and ultimately, invalid data.
The Threat of Irreversible Buildup
When electrolyte residues are allowed to dry, they form a solid film on the glass. This film may not be removable with a simple water rinse and can require harsh methods like scrubbing or sonication in acid baths, which can physically damage or etch the cell over time.
The Challenge of Waste Management
The cleaning process extends to how you handle the waste. Spent electrolytes are chemical waste and must be disposed of according to safety and environmental regulations. Never pour them directly down the drain unless you are certain they are benign. Proper neutralization and collection are part of a complete and responsible experimental workflow.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Adhering to this protocol is not just about following rules; it is about actively ensuring the quality and reliability of your work. Your approach should be guided by the high standards of scientific research.
- If your primary focus is data accuracy: Consistent, immediate rinsing with deionized water is the most critical step to prevent cross-contamination between runs.
- If your primary focus is equipment longevity: Gentle nitrogen drying and avoiding the need for harsh cleaning agents will preserve the integrity of your electrolytic cell for years.
- If your primary focus is lab safety and compliance: Always prioritize powering down the system before disassembly and handling all chemical waste according to established protocols.
This disciplined approach to cleaning is a foundational practice that enables reliable and reproducible electrochemical research.
Summary Table:
| Step | Key Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Safe Shutdown & Disassembly | Prevent electric shock and safely handle components |
| 2 | Immediate Rinsing (3x with deionized water) | Dissolve and remove residues to prevent cross-contamination |
| 3 | Complete Drying (Nitrogen gas) | Ensure no moisture remains, prevent dilution and contamination |
Ensure the integrity of your electrochemical research with reliable lab equipment from KINTEK.
Proper cleaning is essential, but it starts with using a high-quality electrolytic cell designed for easy maintenance and long-term performance. KINTEK specializes in durable lab equipment and consumables that support precise, contamination-free experiments.
✅ Prevent cross-contamination with equipment designed for thorough cleaning.
✅ Extend the life of your investment with robust, easy-to-maintain cells.
✅ Achieve reproducible results by pairing our reliable products with your disciplined protocols.
Contact us today to find the perfect electrolytic cell and accessories for your laboratory needs. Let’s enhance the accuracy and longevity of your research together.
Get in touch with our experts now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell with Five-Port
- Double Layer Five-Port Water Bath Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell
- H-Type Double-Layer Optical Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell with Water Bath
- H Type Electrolytic Cell Triple Electrochemical Cell
- Double-Layer Water Bath Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of using a three-electrode electrolytic cell system? Precision Screening for AEMWE Electrodes
- What is the core function of a laboratory-scale single-chamber circulating electrolytic reactor? Optimize Al Recovery
- How should the electrical circuit for the electrolytic cell be set up? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe & Accurate Electrolysis
- What is the function of a three-electrode electrochemical cell? Enhance Precision in Alloy Passivation Research
- How does a three-electrode electrochemical cell configuration ensure accurate 904L stainless steel corrosion measurement?
- How are electrolytic etching devices used to characterize duplex stainless steels? Master Microstructure Analysis
- What is the purpose of electrolytic polishing and etching for LFR materials? Reveal True Microstructure Precision
- What is the overall structure of the H-type double-layer optical water bath electrolytic cell? Precision Design for Controlled Experiments