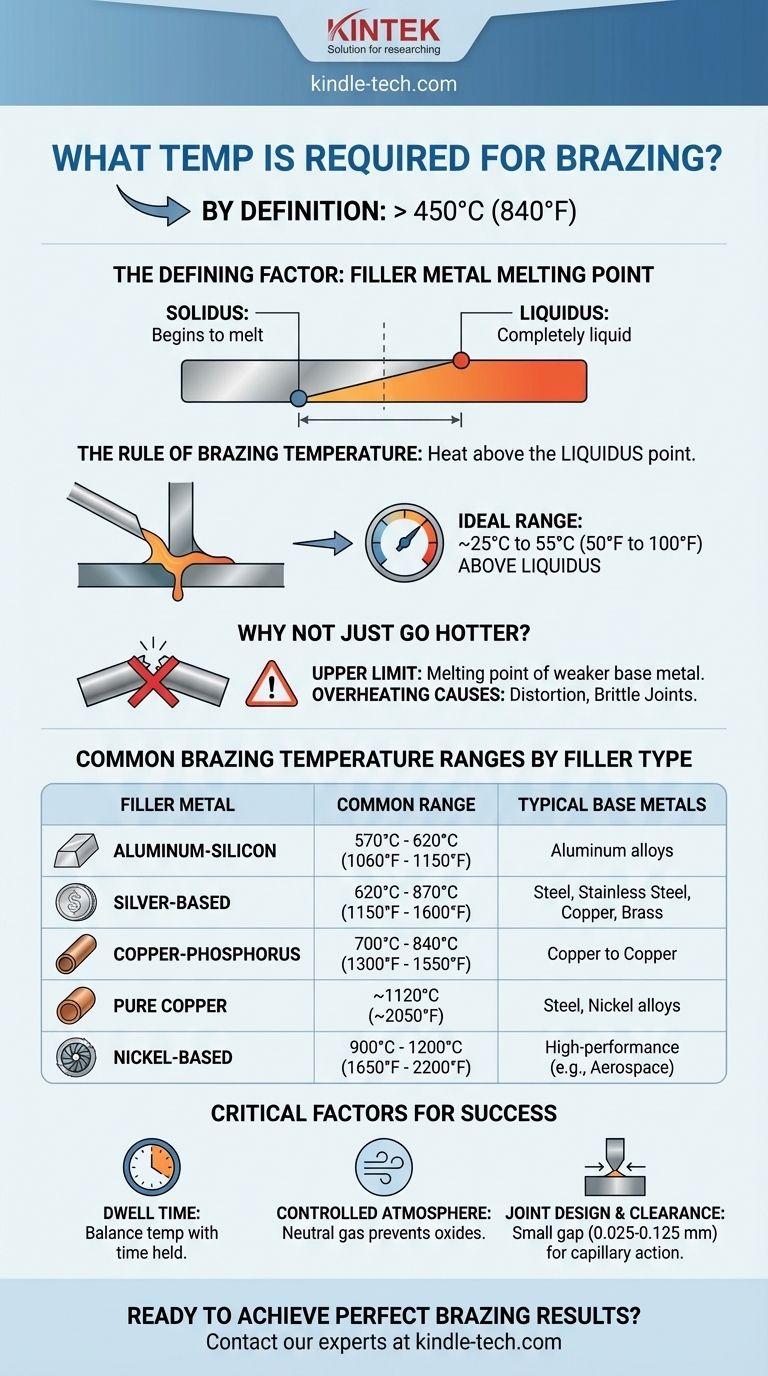
By definition, brazing is a metal-joining process that takes place above 450°C (840°F). However, the precise temperature required for a specific job is not a single number; it is entirely determined by the melting point of the filler metal you use, and it must always be below the melting point of the base metals being joined.
The core principle is not to aim for a generic "brazing temperature," but to heat the assembly to a temperature slightly above the full melting point of your chosen filler metal. This ensures the filler flows correctly without damaging the components you intend to join.
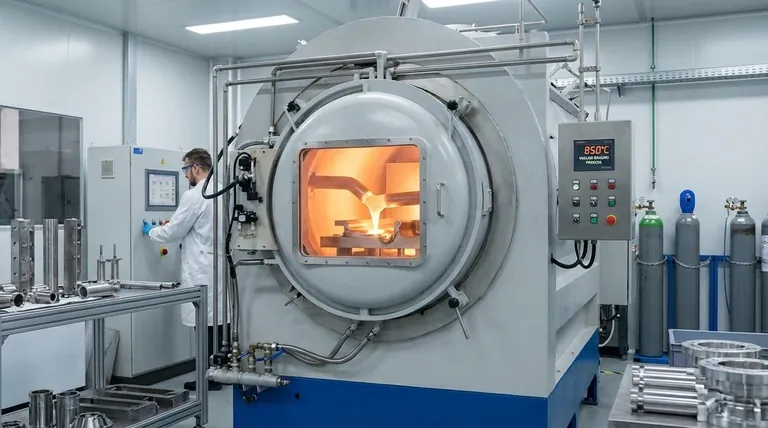

The Defining Factor: Filler Metal Melting Point
The entire brazing process revolves around the properties of the filler metal, also known as the brazing alloy. Understanding its behavior is the key to selecting the correct temperature.
What is a Filler Metal?
A filler metal is an alloy designed to melt at a lower temperature than the base metals it is joining. When it melts, it is drawn into the tight-fitting joint by capillary action, creating a strong metallurgical bond upon cooling.
The "Liquidus" and "Solidus" Temperatures
Filler metals don't melt instantly at one temperature. They have a melting range defined by two points:
- Solidus: The temperature at which the filler alloy begins to melt.
- Liquidus: The temperature at which the filler alloy is completely liquid.
The Rule of Brazing Temperature
For a successful braze, the base metals must be heated to a temperature above the liquidus point of the filler metal. A common industry practice is to set the process temperature approximately 25°C to 55°C (50°F to 100°F) above the liquidus temperature to ensure the filler flows freely and quickly throughout the joint.
Why Not Just Go Hotter? The Role of Base Metals
While you must exceed the filler's liquidus temperature, using excessive heat can be detrimental. The upper temperature limit of your process is always the melting point of the weaker of the two base metals.
Avoiding Base Metal Distortion
Overheating can cause the base metals to warp, weaken, or lose critical engineered properties like hardness. This is especially important when working with thin materials or components that have been previously heat-treated.
Preventing Undesirable Metallurgy
Excessive temperatures can cause unwanted interactions between the filler and base metals, leading to brittle joints that are prone to failure. The goal is a clean bond, not a complete alloying at the interface.
Common Brazing Temperature Ranges by Filler Type
The required temperature varies significantly based on the filler metal's composition.
Aluminum-Silicon Fillers
These are used for brazing aluminum alloys and typically operate in a range of 570°C to 620°C (1060°F to 1150°F). This is a narrow window, as some aluminum alloys begin to melt just above this range.
Silver-Based Fillers
Commonly used for joining steel, stainless steel, copper, and brass, silver alloys offer a wide range of temperatures. They typically operate between 620°C and 870°C (1150°F and 1600°F).
Copper and Copper-Phosphorus Fillers
Pure copper is an excellent high-temperature filler for brazing steel and nickel alloys, requiring temperatures around 1120°C (2050°F). Copper-phosphorus alloys are used for joining copper to copper without flux and operate at lower temperatures, typically 700°C to 840°C (1300°F to 1550°F).
Nickel Fillers
For high-performance applications requiring superior strength and corrosion resistance, such as in aerospace, nickel alloys are used. These require very high temperatures, often in the range of 900°C to 1200°C (1650°F to 2200°F).
Understanding the Trade-offs and Critical Factors
Temperature is the primary parameter, but it doesn't work in isolation. A successful braze depends on a balance of several factors.
Temperature vs. Dwell Time
Dwell time is the duration the assembly is held at the brazing temperature. A slightly lower temperature may require a longer dwell time to ensure the filler metal can fully flow into the joint. Conversely, a higher temperature may allow for a shorter time.
The Importance of a Controlled Atmosphere
For most high-quality brazing, the process must occur in an environment devoid of oxygen. As your references note, a neutral gas atmosphere (like pure nitrogen) with very low oxygen and humidity is essential. This prevents the formation of oxides on the surface of the base metals, which would otherwise inhibit the flow of the filler metal and create a weak bond.
Joint Design and Clearance
Brazing relies on capillary action. This physical phenomenon only works when the gap between the two base metals is very small—typically 0.025 to 0.125 mm (0.001 to 0.005 inches). If the gap is too large, the filler won't be drawn in, regardless of how perfect your temperature control is.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To determine the correct brazing temperature, you must first select the right filler metal for your base materials and performance requirements.
- If your primary focus is joining steel or copper for general applications: A silver-based filler is likely your best choice, placing your required temperature in the 620°C to 870°C range.
- If your primary focus is joining heat-sensitive aluminum parts: You must use a low-temperature aluminum-silicon filler and maintain precise control within the 570°C to 620°C window.
- If your primary focus is high-strength joints for demanding environments: A nickel or high-temperature copper filler is necessary, requiring a furnace capable of reaching 900°C or higher and a controlled atmosphere.
Ultimately, matching the temperature to your chosen filler metal is the foundation of a successful and reliable braze.
Summary Table:
| Filler Metal Type | Common Brazing Temperature Range | Typical Base Metals Joined |
|---|---|---|
| Aluminum-Silicon | 570°C - 620°C (1060°F - 1150°F) | Aluminum alloys |
| Silver-Based | 620°C - 870°C (1150°F - 1600°F) | Steel, Stainless Steel, Copper, Brass |
| Copper-Phosphorus | 700°C - 840°C (1300°F - 1550°F) | Copper to Copper |
| Pure Copper | ~1120°C (~2050°F) | Steel, Nickel alloys |
| Nickel-Based | 900°C - 1200°C (1650°F - 2200°F) | High-performance applications (Aerospace, etc.) |
Ready to achieve perfect brazing results? The right temperature is just the start. For laboratories and manufacturing facilities, KINTEK provides the high-quality brazing furnaces, controlled atmosphere systems, and expert support you need to ensure consistent, strong, and reliable joints every time.
Let's discuss your specific brazing application and material requirements. Contact our experts today to find the ideal solution for your lab's metal-joining challenges.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the most important factor influencing the strength of the brazed joint? Master Joint Clearance for Maximum Strength
- Can dissimilar metals be brazed or braze welded? A Guide to Strong, Reliable Joints
- What is the cost of a vacuum brazing furnace? A guide to key factors and investment strategy
- How is the greatest joint strength obtained in brazing? Master the 3 Keys to Superior Metallurgical Bonds
- What are vacuum furnaces used for? Unlock Ultimate Material Purity and Performance



















