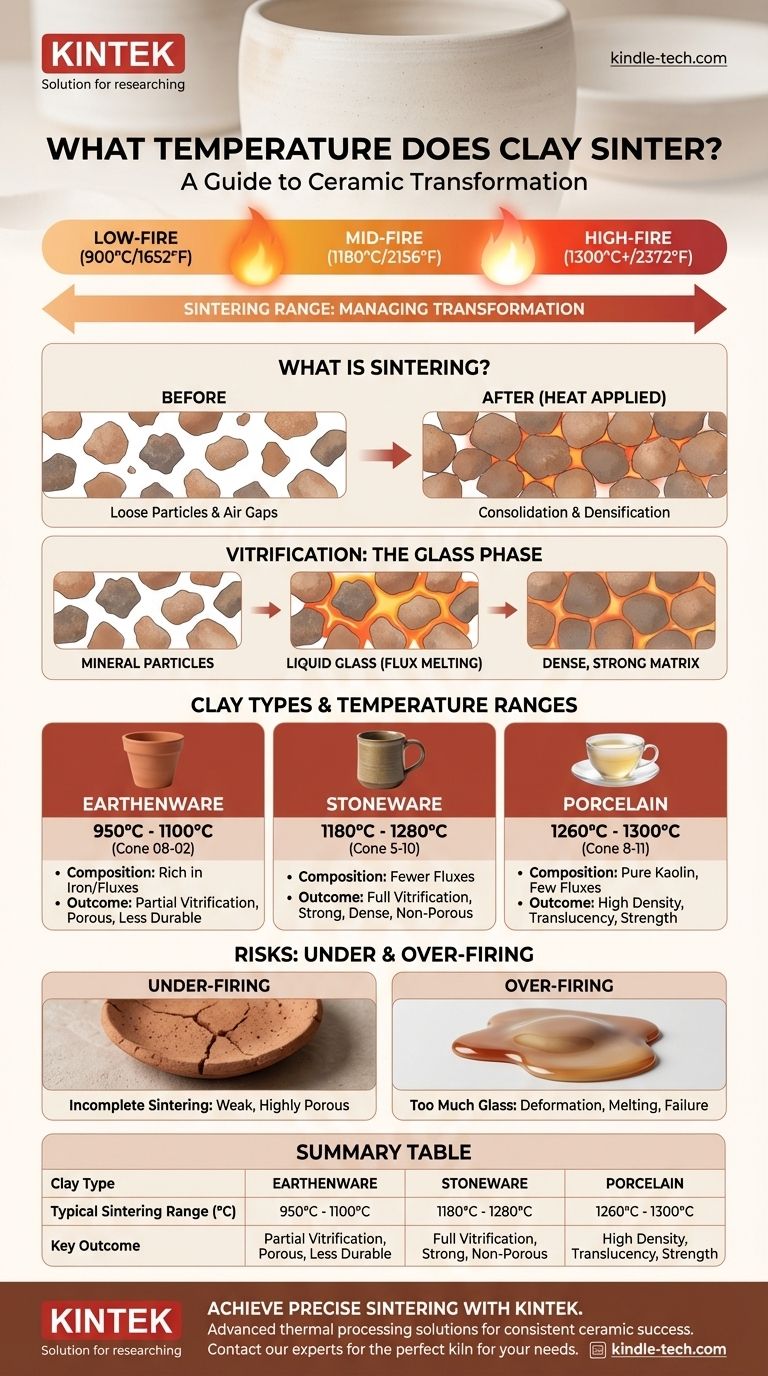
The sintering temperature for clay is not a single value but a wide range that depends entirely on the clay's specific mineral composition. Generally, the process begins around 900°C (1652°F) for low-fire clays and can extend beyond 1300°C (2372°F) for high-fire materials like porcelain. The key is to understand that you are not aiming for one number, but managing a process of transformation.
Sintering is less about reaching a specific temperature and more about managing a physical transformation. The correct temperature is dictated by the clay's composition and the desired final properties, such as strength, density, and porosity.

What is Sintering? A Deeper Look
To control the outcome of your work, you must first understand the fundamental process that occurs inside the kiln. Sintering is a thermal process that turns a collection of loose mineral particles into a solid, coherent mass.
The Fundamental Goal: Consolidation
Imagine the clay as a dense collection of microscopic particles with tiny air gaps between them. As you apply heat, the atoms on the surfaces of these particles become more active. They begin to diffuse, or move, across the particle boundaries, effectively "welding" them together at their points of contact.
This process reduces the total surface area of the particles and shrinks the air gaps, causing the entire clay body to become denser and stronger. This happens well below the material's full melting point.
The Role of Temperature
Heat is the catalyst for this transformation. According to material science principles, significant sintering typically begins at temperatures greater than half of the material's melting point. This thermal energy is what enables atoms to migrate and form new, stronger bonds between particles.
More heat accelerates this process, leading to greater density. However, too much heat can cause the material to fully melt and lose its shape.
Vitrification: The Key Transformation in Clay
In ceramics, sintering drives a critical process called vitrification. Clay isn't made of one pure material; it's a mix. Some minerals in the clay body have a lower melting point than others.
During firing, these minerals (known as fluxes) melt and form a liquid glass. This molten glass flows into the pores between the non-melting particles, like kaolin. Upon cooling, this glass solidifies, acting as a powerful glue that binds everything into a dense, strong, and often waterproof structure.
Factors That Determine Sintering Temperature
The vast temperature range for sintering clay (750°C to 1300°C) is a direct result of different clay compositions and intended outcomes.
Clay Body Composition
This is the single most important factor. Different types of clay contain different minerals and impurities that act as fluxes.
- Earthenware: Rich in mineral impurities like iron oxide, which act as powerful fluxes. This causes it to vitrify at much lower temperatures, typically 950°C to 1100°C.
- Stoneware: Contains fewer fluxes than earthenware, requiring higher temperatures (1180°C to 1280°C) to mature and become vitrified.
- Porcelain: A very pure clay, primarily kaolin, with few natural fluxes. It requires the highest temperatures (1260°C to 1300°C) to achieve its characteristic density and translucence.
Particle Size
Finer clay particles have more surface area relative to their volume. This increased surface energy allows the sintering process to begin at a lower temperature compared to a clay body with coarser particles.
Desired Outcome (Porosity vs. Strength)
The temperature you choose directly impacts the final properties.
- Low-Fire Sintering: Results in partial vitrification, leaving the clay body porous and less durable. This is characteristic of earthenware and terracotta.
- High-Fire Sintering: Leads to complete vitrification, creating a very dense, strong, and non-porous body. This is the goal for functional stoneware and durable porcelain.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Pitfalls
Achieving the correct level of sintering is a balancing act. Deviating from the ideal temperature for your specific clay body will lead to failure.
Under-firing: The Risk of Weakness
If you fire the clay at a temperature that is too low, sintering and vitrification will be incomplete. The resulting piece will be structurally weak, highly porous, and unable to hold water, even if glazed.
Over-firing: The Danger of Deformation
If the temperature is too high, you will create too much liquid glass within the clay body. The piece will lose its structural integrity and begin to slump, warp, or even melt into a puddle in the kiln. This is an irreversible failure.
The Importance of the Firing Schedule
Peak temperature is only part of the equation. The rate of heating and the amount of time spent at peak temperature (the "soak") are also critical. A proper firing schedule ensures the heat penetrates the piece evenly and allows the chemical reactions of sintering to complete fully.
Making the Right Choice for Your Clay
Always refer to the manufacturer's recommendations for your specific clay body. However, understanding the categories will give you a strong technical foundation.
- If you are working with Earthenware: Target a lower temperature range, typically Cone 08 to 02 (around 955°C - 1050°C), to achieve hardness without causing it to melt.
- If you are working with Stoneware: Aim for a mid-to-high fire range, typically Cone 5 to 10 (around 1186°C - 1285°C), to achieve full vitrification and durability.
- If you are working with Porcelain: You must fire at high temperatures, typically Cone 8 to 11 (around 1263°C - 1300°C), to develop its characteristic translucency and strength.
Ultimately, successful sintering comes from knowing your specific material and precisely controlling the heat to achieve your desired transformation.
Summary Table:
| Clay Type | Typical Sintering Range (°C) | Key Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Earthenware | 950°C - 1100°C | Partial vitrification, porous body |
| Stoneware | 1180°C - 1280°C | Full vitrification, strong & durable |
| Porcelain | 1260°C - 1300°C | High density, strength & translucency |
Achieve precise sintering results with the right equipment.
Understanding the correct temperature is just the first step. Precise, reliable kilns and lab furnaces are essential for consistent ceramic success. Whether you're working with earthenware, stoneware, or porcelain, KINTEK's advanced thermal processing solutions provide the exact control you need to avoid under-firing or over-firing.
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, serving the precise heating needs of ceramic artists, researchers, and production facilities. Let our experts help you select the perfect kiln for your specific clay body and desired outcomes.
Contact our thermal experts today to discuss your project and ensure perfect firing every time.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What affects melting range? Understand the Critical Role of Purity and Structure
- What are the applications of muffle furnace in pharmaceutical industry? Ensure Drug Purity and Quality
- Does heat capacity affect melting point? Unraveling the Key Differences in Thermal Properties
- Where is a muffle furnace used? Essential for Clean, High-Temperature Processing
- What precautions you will take while handling the muffle furnace? Ensure Safe and Efficient Operation



















