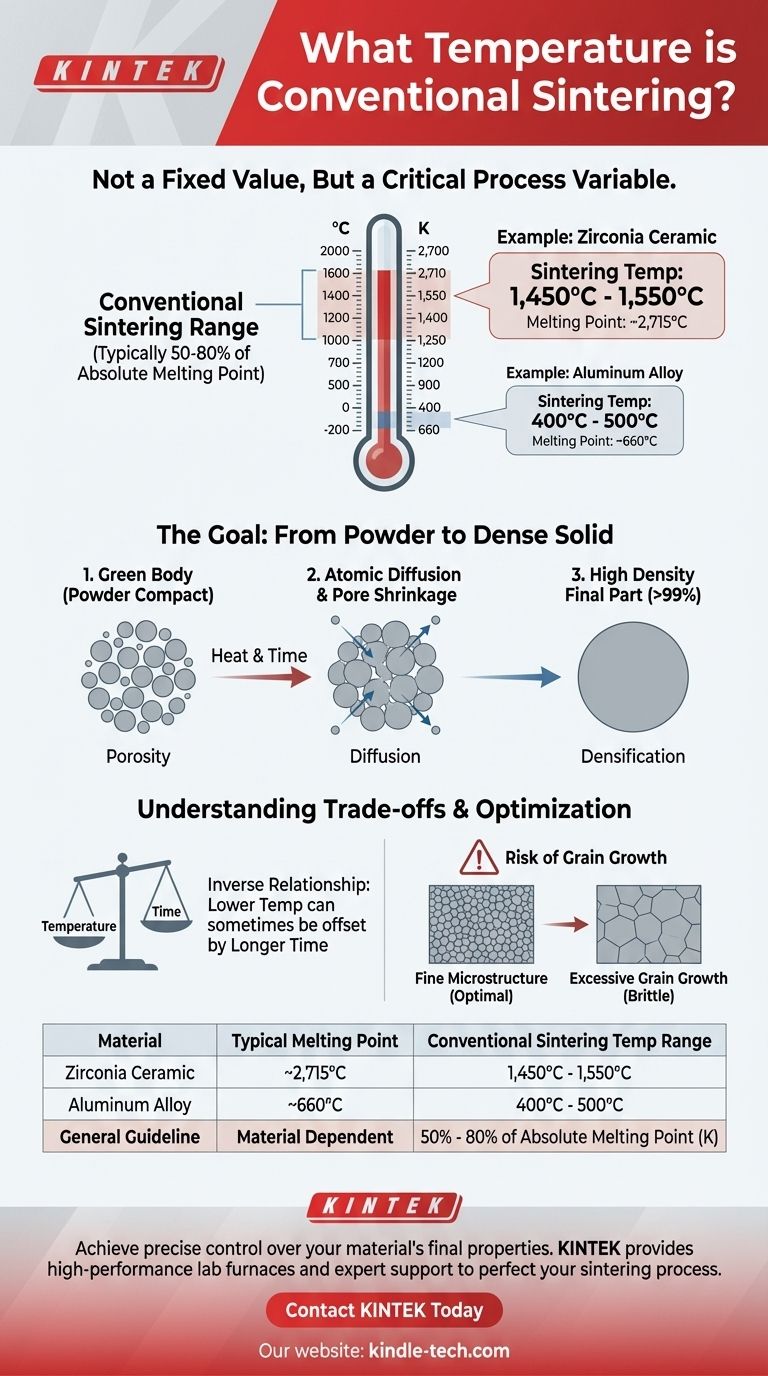
For conventional sintering, the temperature is not a single value but is highly dependent on the material being processed. For a common high-performance ceramic like Zirconia, the firing temperature is typically between 1,450°C and 1,550°C. This is significantly higher than the temperature at which its crystal structure transforms (around 1,170°C) because the primary goal is to achieve maximum density and strength, not just a phase change.
Sintering temperature is best understood not as a fixed number, but as a critical process variable. The correct temperature is one that is high enough to enable atomic diffusion and fuse particles together, yet remains safely below the material's melting point, typically falling within 50-80% of its absolute melting temperature.

The Goal of Sintering: From Powder to Solid
Sintering is a thermal process that converts a powder compact into a dense, solid object. Heat provides the energy needed to fundamentally change the material's structure.
Eliminating Porosity
The starting material is a "green body," a compacted powder with significant empty space, or porosity, between the particles. The primary goal of sintering is to eliminate these pores.
Driving Atomic Diffusion
Heat energizes the atoms within the powder particles. This energy allows atoms to migrate across the boundaries of adjacent particles, filling the voids between them and forming strong metallurgical bonds. This process is known as atomic diffusion.
Achieving High Density
As diffusion progresses, the particles fuse, the pores shrink, and the overall part becomes denser and stronger. For materials like Zirconia, the goal is often to achieve a final density that is over 99% of the theoretical maximum, ensuring superior mechanical properties.
Why Temperature Varies So Drastically
There is no universal sintering temperature because the diffusion process is intrinsically linked to the material's own properties, most importantly its melting point.
The Rule of Thumb: Melting Point is Key
A reliable guideline is that a material's conventional sintering temperature is typically 50% to 80% of its absolute melting temperature (measured in Kelvin). Materials with very high melting points require very high sintering temperatures.
Example: Zirconia
Zirconia has an extremely high melting point of approximately 2,715°C. The common sintering temperature of ~1,500°C falls squarely within the expected range, allowing for effective diffusion without risk of melting.
Example: Metals vs. Ceramics
This principle explains the vast differences across material classes. An aluminum alloy powder (melting point ~660°C) may sinter at temperatures as low as 400-500°C, whereas technical ceramics demand temperatures well over 1,000°C.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a sintering temperature is a balance of competing factors. Simply making it hotter is not always better and can introduce significant problems.
Temperature vs. Time
There is an inverse relationship between temperature and time. You can sometimes achieve similar densification by sintering at a lower temperature for a much longer duration. This is often done to save energy or gain finer control over the final microstructure.
The Risk of Grain Growth
Excessive temperature or time can lead to grain growth, where smaller crystal grains merge into larger ones. While this can help eliminate the last traces of porosity, excessively large grains can often make the final material more brittle and prone to fracture.
The Phase Transformation Point
For a material like Zirconia, reaching the phase transformation temperature (~1,170°C) is a necessary step, but it is not sufficient for full densification. Significant atomic diffusion, which requires the much higher ~1,500°C temperature, is what truly creates a strong, dense final part.
How to Determine the Right Temperature
The ideal sintering temperature depends entirely on your final goal. Always begin with the material supplier's technical data sheet, then adjust based on your specific objective.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength and density: Aim for the upper end of the recommended sintering temperature range to ensure the most complete particle fusion and pore elimination.
- If your primary focus is controlling microstructure or cost: Explore using lower temperatures combined with longer hold times, but verify that you are still achieving the minimum required density for your application.
Ultimately, temperature is the primary lever you can pull to control the final density, grain structure, and mechanical performance of a sintered component.
Summary Table:
| Material | Typical Melting Point | Conventional Sintering Temperature Range |
|---|---|---|
| Zirconia Ceramic | ~2,715°C | 1,450°C - 1,550°C |
| Aluminum Alloy | ~660°C | 400°C - 500°C |
| General Guideline | Material Dependent | 50% - 80% of Absolute Melting Point (K) |
Achieve precise control over your material's final properties.
The correct sintering temperature is critical for achieving maximum density, strength, and the desired microstructure in your ceramic or metal parts. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the high-performance lab furnaces and expert support you need to perfect your sintering process.
Our equipment ensures the precise temperature control and uniform heating essential for repeatable, high-quality results. Let our experts help you optimize your sintering cycle for your specific material and application goals.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your laboratory's sintering needs and discover the right solution for you.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum hot pressing furnace? Achieve 98.9% Density in Al2O3-TiC Laminated Ceramics
- What are the primary advantages of using a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace? Maximize Density in B4C-CeB6 Ceramics
- What is the function of a VHPS system in CoCrFeNiMn alloys? Achieve Near-Theoretical Density and High Purity
- What is the impact factor of powder metallurgy progress? A 2022 Analysis & Context
- What are the advantages of a vacuum hot pressing furnace? Achieve high-density NTC ceramics with superior stability.



















