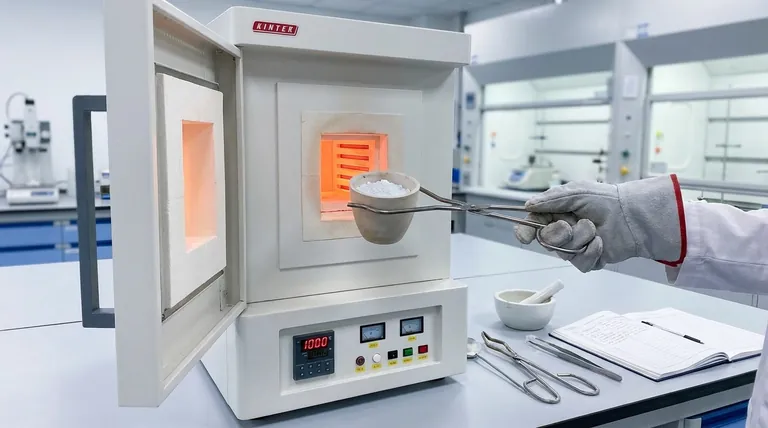
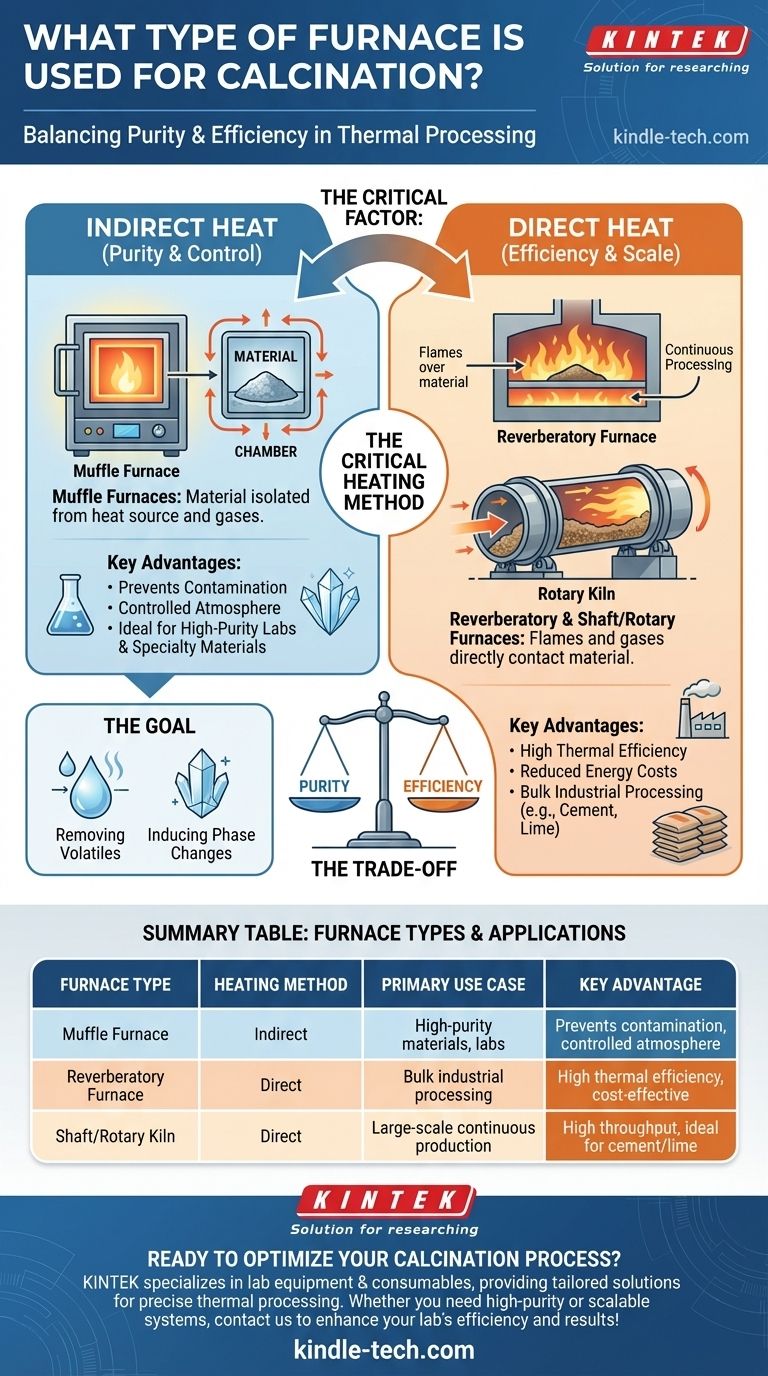
For calcination, the most common types of furnaces are muffle furnaces, reverberatory furnaces, and shaft furnaces or kilns. Each design serves a specific purpose, distinguished primarily by whether the material being heated comes into direct contact with the heat source and its combustion gases.
The critical factor in choosing a calcination furnace is not the furnace type itself, but the underlying heating method. Your choice depends on whether your process requires indirect heat for purity or can tolerate direct heat for maximum thermal efficiency.

The Goal of Calcination
Before selecting a furnace, it's essential to understand the core objective of the calcination process. It is a thermal treatment used to induce a chemical or physical change in a material.
### Removing Volatiles
A primary function of calcination is to heat a substance to drive off volatile components. This commonly includes removing absorbed moisture, carbon dioxide (as in cement production), or sulfur dioxide.
### Inducing Phase Changes
Heating can also be used to change the crystalline structure of a material or to oxidize all or part of the substance being treated. This is crucial for preparing materials for subsequent industrial processes.
Core Furnace Designs for Calcination
While various configurations exist, the technology boils down to a few fundamental designs, each defined by how heat is transferred to the material.
### Muffle Furnaces (Indirect Heating)
In a muffle furnace, the material is placed in a chamber, or "muffle," which is heated from the outside. The heat source and its combustion byproducts do not come into contact with the sample.
This design is constructed from materials like fire-clay or brickwork and is ideal for processes where purity is paramount.
### Reverberatory Furnaces (Direct Heating)
In contrast, a reverberatory furnace allows the flames and hot gases from the heat source to pass directly over the material.
This direct contact allows for very efficient heat transfer, but it also means the material is exposed to the byproducts of combustion.
### Shaft Furnaces & Rotary Kilns (Continuous Processing)
These are large, cylindrical structures often referred to as calciners. They are the workhorses of large-scale industrial applications like cement manufacturing.
Material is fed into one end and moves continuously through the heated cylinder, allowing for high-throughput processing. Heating in these systems is typically direct.
Understanding the Trade-off: Purity vs. Efficiency
The decision between furnace types is fundamentally a trade-off between process control and operational efficiency.
### The Case for Indirect Heat (Purity and Control)
A muffle furnace is the superior choice when the chemical integrity of the final product is the top priority.
Because the material is isolated from combustion gases, you can maintain a controlled atmosphere. This is essential for applications in laboratories or for producing high-purity specialty materials.
### The Case for Direct Heat (Efficiency and Scale)
Reverberatory and shaft furnaces excel in thermal efficiency and scale. Direct contact transfers heat far more effectively, reducing energy costs and processing time.
This makes them the standard for bulk industrial processes where the material is not negatively affected by contact with combustion gases, such as in the production of cement or lime.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the appropriate equipment, you must align the furnace's heating mechanism with your primary process objective.
- If your primary focus is process purity or controlled atmospheres: A muffle furnace is the correct choice, as its indirect heating method prevents contamination.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, cost-effective production: A reverberatory furnace or a rotary kiln is ideal, as direct heating maximizes thermal efficiency for bulk materials.
Ultimately, understanding how heat is delivered to your material is the key to mastering the calcination process.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Type | Heating Method | Primary Use Case | Key Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Muffle Furnace | Indirect | High-purity materials, labs | Prevents contamination, controlled atmosphere |
| Reverberatory Furnace | Direct | Bulk industrial processing | High thermal efficiency, cost-effective |
| Shaft/Rotary Kiln | Direct | Large-scale continuous production | High throughput, ideal for cement/lime |
Ready to optimize your calcination process? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing tailored solutions for laboratories requiring precise thermal processing. Whether you need a high-purity muffle furnace or scalable industrial systems, our expertise ensures you get the right equipment for your goals. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your lab's efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is a furnace used in a chemistry lab? A Guide to High-Temperature Material Transformation
- Why is air and water vapor introduced during pre-oxidation? Master Surface Passivation for Coking Experiments
- How do you measure ash content? Choose the Right Method for Accurate Results
- What is the muffle furnace used to estimate? Measure Ash Content and Volatile Matter Precisely
- What is the significance of the muffle furnace? Achieve Purity and Precision in High-Temperature Processing



















