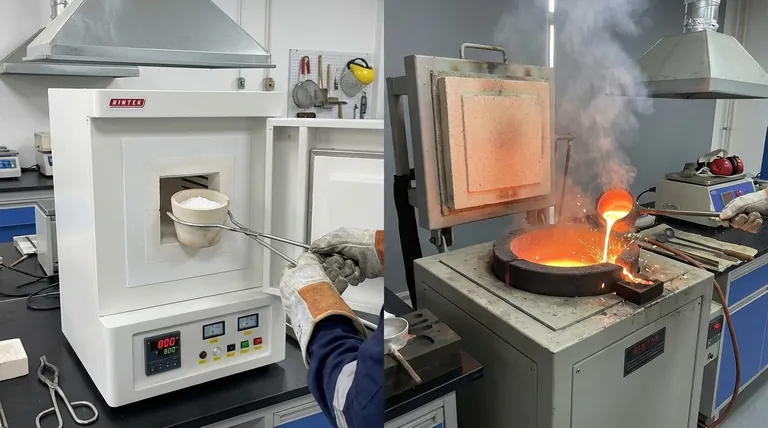
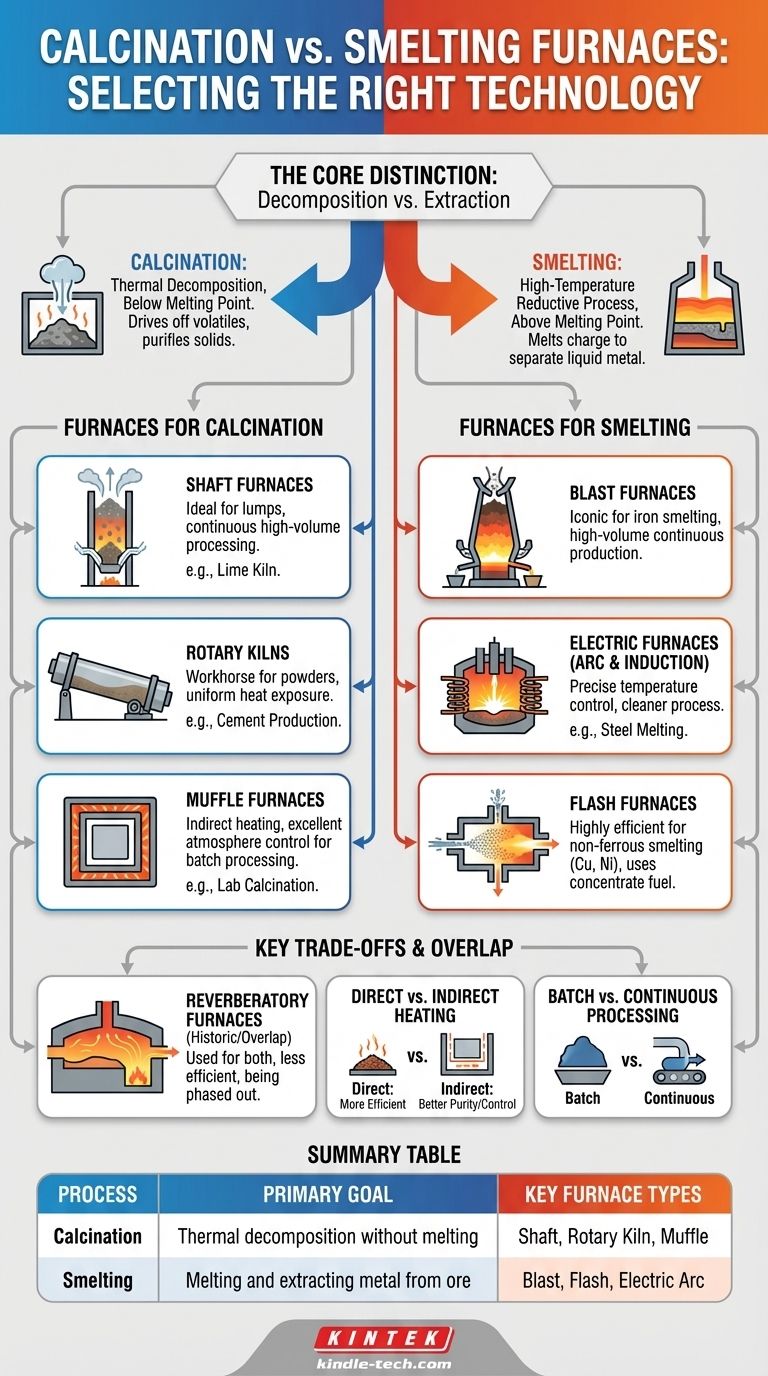
While some furnaces can be adapted for multiple roles, calcination and smelting are fundamentally different processes that typically require distinct furnace technologies. Calcination is a thermal decomposition process that drives off volatiles without melting the material, often using shaft, muffl_e_, or rotary kilns. Smelting, conversely, is a high-temperature reductive process that melts the charge to separate a pure base metal, demanding robust technologies like blast furnaces or flash furnaces.
The core distinction lies in the end goal: calcination uses heat to chemically change and purify a solid, while smelting uses heat and chemical agents to melt and extract a liquid metal from its ore. Your choice of furnace is dictated entirely by which of these transformations you need to achieve.

The Fundamental Difference: Calcination vs. Smelting
To select the right technology, you must first be clear on the underlying process. Though both involve high heat, their objectives are nearly opposite.
What is Calcination?
Calcination is a thermal treatment process applied to ores and other solid materials to bring about a chemical change. This typically involves heating the material to a high temperature, but below its melting point.
The primary goal is to drive off a specific component. Common examples include driving water out of hydrates, carbon dioxide (CO₂) from carbonates (like limestone to produce lime), or other volatile substances.
What is Smelting?
Smelting is a metallurgical process used to extract a base metal from its ore. It involves heating the ore well beyond its melting point in the presence of a reducing agent, such as coke or charcoal, and a fluxing agent, like limestone.
The process creates two separate molten layers: the elemental metal and a waste layer called slag. The slag contains the unwanted rock and impurities, which can then be physically separated from the much denser molten metal.
Furnaces Optimized for Calcination
These furnaces are designed for excellent heat transfer and atmosphere control to process solid materials without melting them.
Shaft Furnaces
A shaft furnace, like a lime kiln, is a tall, vertical chamber. Lump material (like limestone) is fed into the top, and it slowly descends by gravity. Hot gases are forced up from the bottom, efficiently transferring heat in a counter-current flow before exiting. This design is ideal for high-volume, continuous processing.
Rotary Kilns
The rotary kiln is the workhorse for calcining powders and fine-grained materials, most famously in cement production. It is a long, rotating, slightly inclined cylinder. Material is fed into the higher end and tumbles its way to the lower end, ensuring every particle is uniformly exposed to the heat.
Muffle Furnaces
A muffle furnace provides indirect heating. The material is placed inside a sealed chamber (the "muffle"), which is then heated from the outside. This is critical when the combustion gases must not come into contact with the material, preventing contamination and allowing for precise control of the atmosphere inside the chamber.
Furnaces Designed for Smelting
Smelting furnaces must be able to contain extremely hot, corrosive molten materials and facilitate chemical reactions.
The Blast Furnace
The blast furnace is the iconic technology for iron smelting. It is a massive shaft-type furnace continuously charged with iron ore, coke (as fuel and a reducing agent), and limestone (as a flux). A hot "blast" of air is injected into the bottom, driving temperatures high enough to produce molten iron and slag, which are tapped off periodically.
Electric Furnaces (Arc and Induction)
Electric Arc Furnaces (EAF) use high-energy electric arcs to generate intense, concentrated heat, primarily for melting steel scrap. Induction furnaces use electromagnetic fields to heat and melt metal. Both offer excellent temperature control and a cleaner process, as they don't rely on fossil fuel combustion.
Flash Furnaces
A dominant technology in modern non-ferrous smelting (e.g., for copper and nickel), flash smelting is remarkably efficient. Finely ground ore concentrates are injected with oxygen-enriched air into a hot furnace chamber. The sulfide mineral particles combust mid-air, generating their own heat and smelting almost instantaneously.
Understanding the Key Trade-offs
While the processes are distinct, some furnace types have been adapted for both, highlighting important engineering compromises.
The Overlap: Reverberatory Furnaces
A reverberatory furnace heats its charge by radiating energy from the roof and walls. The fuel is burned in a separate area, and the flame and hot gases pass over the material bed.
Historically, they were used for both calcining fine materials and smelting metals like copper. However, they are generally less fuel-efficient than modern shaft or flash furnaces and are being phased out in many large-scale applications.
Direct vs. Indirect Heating
This is a critical decision point. Direct heating (as in a blast furnace or rotary kiln) is more energy-efficient, as the heat source directly contacts the material. Indirect heating (as in a muffle furnace) provides superior purity and atmosphere control at the cost of lower thermal efficiency.
Batch vs. Continuous Processing
Muffle furnaces are typically used for smaller-scale batch operations where precise control is paramount. Shaft furnaces and rotary kilns are built for high-throughput, continuous industrial operations where efficiency and volume are the primary drivers.
Selecting the Right Technology for Your Process
Your final choice depends entirely on your material, desired chemical transformation, and operational scale.
- If your primary focus is high-volume thermal decomposition: A rotary kiln (for powders) or a shaft furnace (for lumps) provides the most efficient continuous solution.
- If your primary focus is purity and atmosphere control during calcination: A muffle furnace is the definitive choice for indirect heating in a controlled environment.
- If your primary focus is large-scale iron extraction from ore: The blast furnace remains the unparalleled industry standard.
- If your primary focus is efficient, modern smelting of sulfide ores: Flash furnace technology offers superior energy efficiency and throughput.
- If your primary focus is melting existing scrap metal or specialty alloys: An electric arc or induction furnace provides the necessary power and control.
Ultimately, you must match the furnace's capabilities—heat transfer method, temperature limits, and material handling—to the specific requirements of your process.
Summary Table:
| Process | Primary Goal | Key Furnace Types | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Calcination | Thermal decomposition without melting | Shaft, Rotary Kiln, Muffle | Driving off volatiles, purifying solids (e.g., lime production) |
| Smelting | Melting and extracting metal from ore | Blast, Flash, Electric Arc | Extracting base metals (e.g., iron, copper) |
Need expert guidance on selecting the right furnace for your lab or industrial process? At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-performance lab equipment and consumables tailored to your specific needs. Whether you're working on calcination for material purification or smelting for metal extraction, our team can help you choose the ideal furnace technology for optimal results. Contact us today to discuss your requirements and enhance your laboratory efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is a muffle furnace used for in a lab? Achieve Clean, High-Temperature Processing
- How is the ash content determined in a muffle furnace? Master the Gravimetric Analysis Method
- How is a muffle furnace used for sample digestion? A Guide to Dry Ashing for Accurate Analysis
- What are the acceptance criteria for muffle furnace? Ensure Safety, Performance & Success
- How long should a furnace take to raise the temperature? Key Factors for Optimal Heating Speed



















