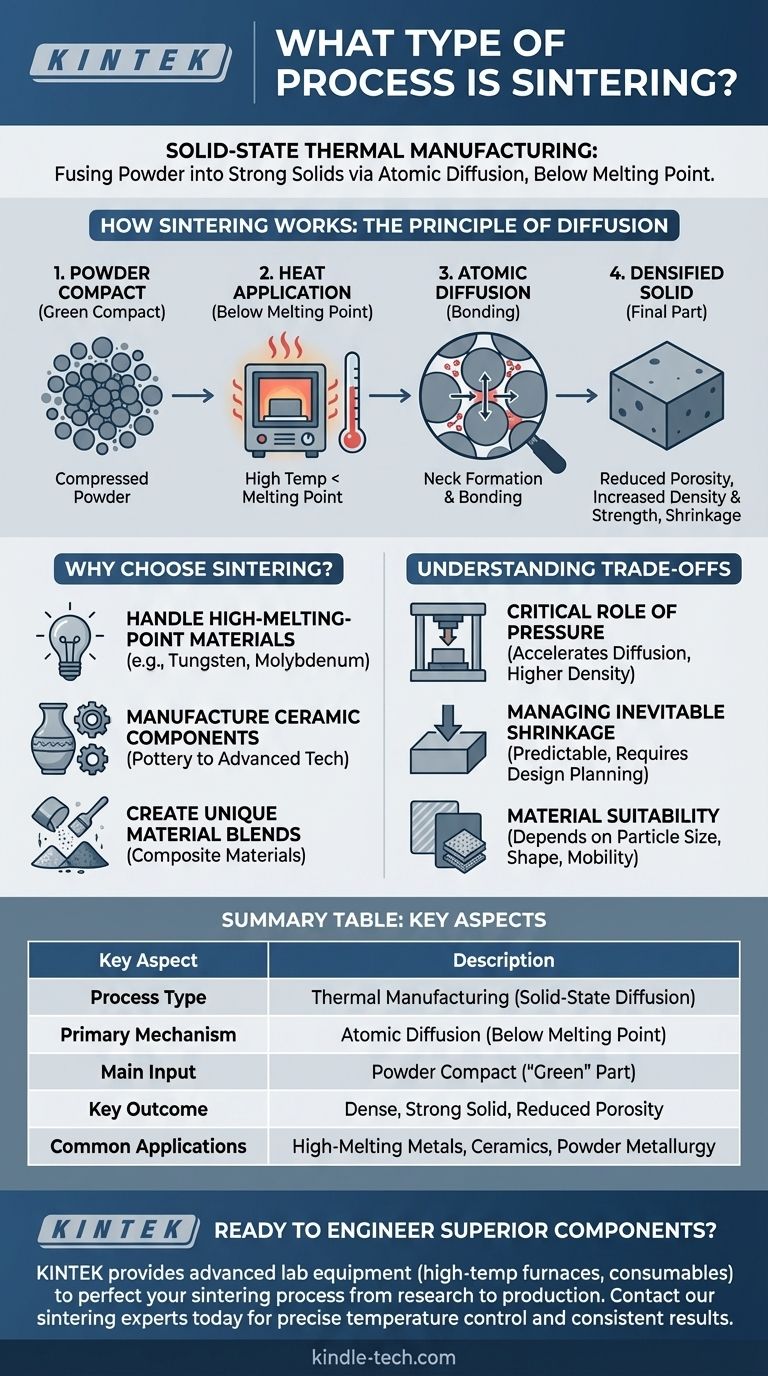
At its core, sintering is a thermal manufacturing process. It uses heat—and often pressure—to compact a powdered material and fuse its individual particles into a single, solid mass. Critically, this is achieved at a temperature below the material's melting point, meaning it never becomes a liquid.
Sintering is not a melting process; it is a solid-state diffusion process. It enables the creation of dense, strong components from powders, which is especially vital for materials with impractically high melting points.
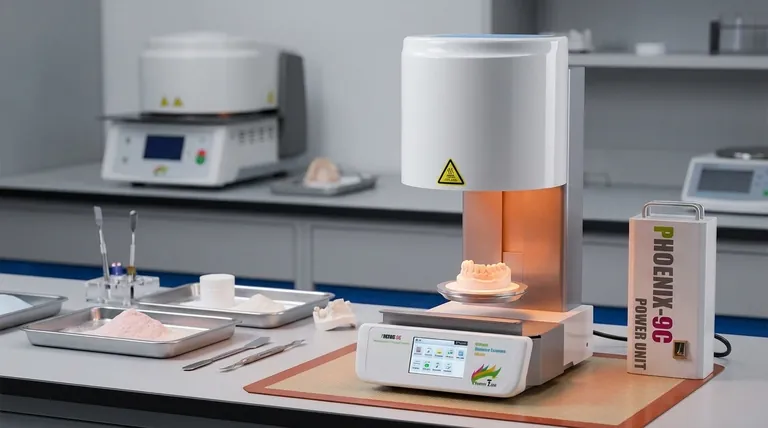

How Sintering Works: The Principle of Diffusion
Sintering transforms a loose powder into a coherent object by encouraging atoms to move and bond across particle boundaries.
The Starting Point: A Powder Compact
The process begins with a fine powder of the desired material, such as a metal or a ceramic. This powder is often first compressed mechanically into a desired shape, a stage known as creating a "green compact."
Applying Heat Below the Melting Point
The green compact is then heated in a controlled furnace. The temperature is raised high enough to energize the atoms within the particles but is kept strictly below the point of liquefaction.
Atomic Diffusion at Particle Boundaries
This applied heat gives the atoms enough energy to migrate, or diffuse, across the surfaces where the individual powder particles touch. As atoms move to fill the microscopic gaps and pores between particles, they form strong metallic or covalent bonds.
The Result: A Densified Solid
This atomic movement effectively "welds" the particles together on a microscopic level. The process eliminates porosity, causing the material to shrink and become significantly more dense, strong, and durable.
Why Choose Sintering Over Melting?
While melting and casting is a common manufacturing method, sintering offers unique advantages that make it essential for specific applications.
Handling High-Melting-Point Materials
Sintering is the go-to process for materials with extremely high melting points, such as tungsten and molybdenum. Melting these metals requires immense energy and specialized equipment, making sintering a far more practical and economical choice.
Manufacturing Ceramic Components
Virtually all modern ceramics, from pottery and porcelain to advanced technical ceramics, are produced via sintering. The process transforms brittle clay or powder preforms into hard, resilient final products.
Creating Unique Material Blends
Powder metallurgy, which relies on sintering, allows manufacturers to combine different types of materials that would not easily mix in a molten state. This makes it possible to create composite materials with tailored properties.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, sintering is a precise process with factors that must be carefully managed for a successful outcome.
The Critical Role of Pressure
While heat drives diffusion, pressure is often applied simultaneously. This pressure increases the contact area between particles, which accelerates the diffusion process and helps achieve higher final density more efficiently.
Managing Inevitable Shrinkage
As the pores between particles are eliminated, the overall component will shrink. This shrinkage is predictable but must be accurately calculated and accounted for in the initial mold design to ensure the final part meets dimensional specifications.
Material Suitability
Not all materials sinter equally well. The effectiveness of the process depends on factors like particle size, shape, and the material's intrinsic atomic mobility.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Sintering is not a universal solution, but it is an indispensable tool when used for the right application.
- If your primary focus is working with high-performance metals like tungsten: Sintering is the most efficient, and often the only, viable method to form dense, solid parts.
- If your primary focus is producing any type of hard ceramic component: Sintering is the fundamental and non-negotiable step that provides structural integrity and hardness.
- If your primary focus is mass-producing complex, small metal parts: Powder metallurgy using sintering is an extremely cost-effective method for creating net-shape components with minimal waste.
By understanding sintering as a process of solid-state fusion, you can engineer robust materials that are simply impossible to form through conventional melting.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Process Type | Thermal manufacturing (solid-state diffusion) |
| Primary Mechanism | Atomic diffusion below the material's melting point |
| Main Input | Powder compact ("green" part) |
| Key Outcome | Dense, strong solid part with reduced porosity |
| Common Applications | High-melting-point metals (tungsten, molybdenum), ceramics, powder metallurgy |
Ready to Engineer Superior Components with Sintering?
Sintering is the key to creating strong, complex parts from high-performance metals and ceramics. KINTEK specializes in providing the advanced lab equipment and consumables you need to perfect your sintering process, from research to production.
We supply high-temperature furnaces and essential materials for laboratories and manufacturers working with powder metallurgy and advanced ceramics. Let our expertise help you achieve precise temperature control and consistent results.
Contact our sintering experts today to discuss how we can support your specific material and application goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
People Also Ask
- How does a rotavap work to remove the solvent? Master Gentle & Efficient Solvent Evaporation
- Why is a high-precision constant temperature stirring reaction device necessary for functionalized BNNS grafting?
- How do you measure ash content? Choose the Right Method for Accurate Results
- Is biomass renewable or non renewable energy? The Truth About Sustainable Power
- What's the difference between melting and smelting? A Guide to Metal Transformation Processes
- What does sintering do to metals? Transform Powder into Durable, Complex Components
- What equipment is needed for pyrolysis? The 4 Core Components for a Successful Plant
- What is the function of a magnetic stirrer during the alkaline etching of nano-silicon carbide? Essential Mixing Guide



















