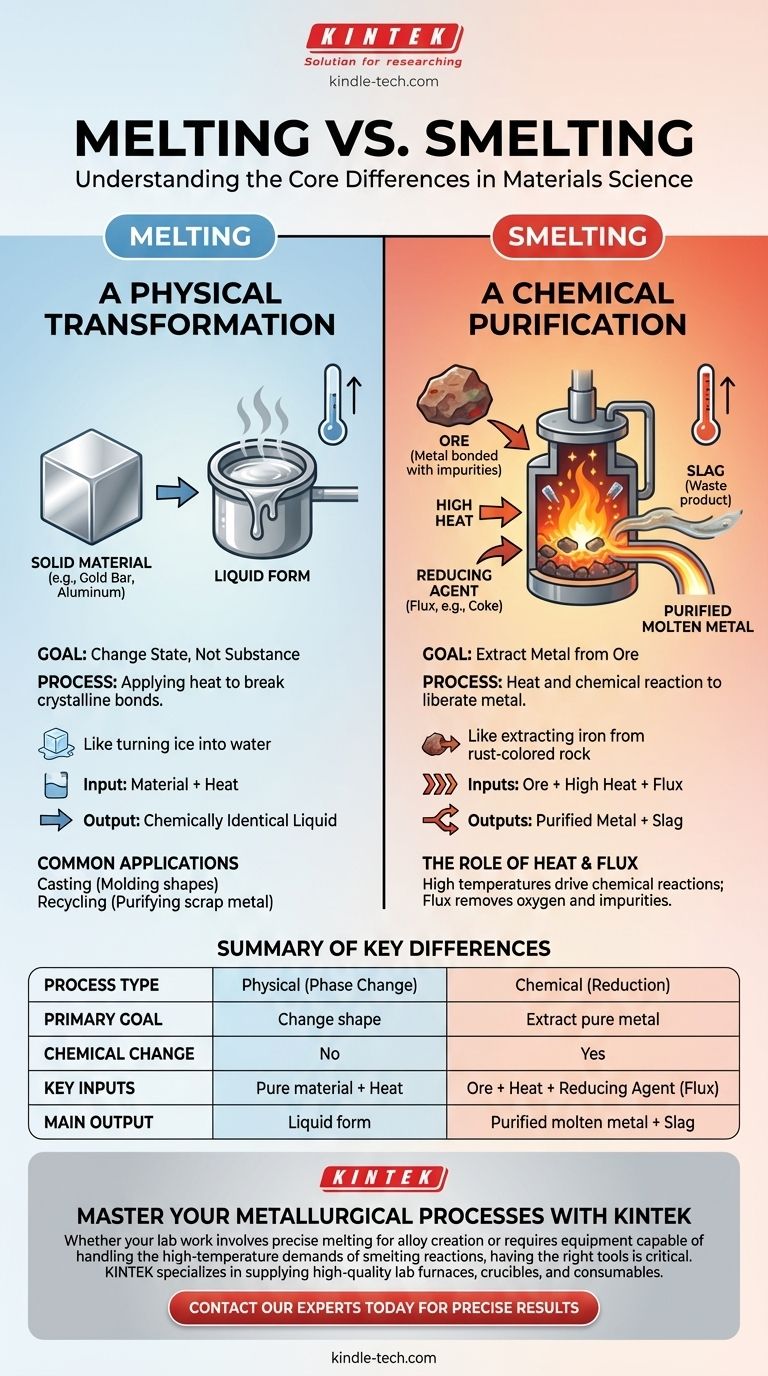
While both processes involve intense heat, melting and smelting are fundamentally different operations with distinct goals. Melting is a purely physical process that changes a substance's state from solid to liquid without altering its chemical identity. Smelting, conversely, is a complex chemical process that uses heat and a reducing agent to extract a pure metal from its ore, fundamentally changing the material's composition.
The core difference is purpose: melting changes a material's form, while smelting changes its substance. Think of melting as turning ice into water, whereas smelting is like extracting iron from rust-colored rock.

The Goal of Melting: A Physical Transformation
Melting is one of the most basic phase transitions in materials science, driven solely by thermal energy. The objective is not to create a new substance but to make an existing one liquid.
Changing State, Not Substance
When you melt an object—be it a gold bar, an aluminum can, or a block of ice—you are simply adding enough heat to break the bonds holding its crystalline structure together. The resulting liquid is chemically identical to the solid it came from.
Common Applications
This process is used for tasks like casting, where molten metal is poured into a mold to create a specific shape. It is also the first step in recycling, where scrap metals are melted down to be purified and reformed into new products.
The Role of Heat
The only necessary input for melting is heat. Once the material reaches its specific melting point, it will begin to transition into a liquid. No chemical reactions are required or intended.
The Goal of Smelting: Chemical Purification
Smelting is a form of extractive metallurgy. Its purpose is to chemically liberate a valuable metal from its natural, impure state within an ore.
Extracting Metal from Ore
Metals like iron, copper, and lead are rarely found in their pure form in nature. They exist as ores, which are minerals where the metal is chemically bonded with other elements, typically oxygen (as an oxide), and mixed with rock and other impurities.
The Chemical Reaction Trio
Smelting relies on a combination of three key inputs to trigger a chemical separation:
- High Heat: Temperatures are raised far above the metal's simple melting point to drive the chemical reaction.
- The Ore: The source of the desired metal.
- A Reducing Agent (Flux): This is the critical ingredient absent in melting. A substance like coke (a form of carbon) is added. At high temperatures, the carbon "steals" the oxygen atoms from the metal oxide, leaving behind a purified, molten metal.
The Byproduct: Slag
During this process, the flux also combines with the other impurities from the ore (like sand and rock). This forms a glassy, liquid waste product called slag. Because slag is less dense than the molten metal, it conveniently floats on top, where it can be skimmed off and removed.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Key Differences
Confusing these two processes can lead to a fundamental misunderstanding of material production. The key is to analyze the inputs and the outputs.
Input Complexity
Melting is simple: you need the material and a heat source. Smelting is complex: you need the ore, a heat source, and a specific chemical reducing agent (flux) to force the desired reaction.
The End Product
The output of melting is the same material you started with, just in a liquid state. The output of smelting is two distinct new substances: the purified molten metal and the waste slag.
Energy and Temperature
Smelting almost always requires significantly higher temperatures than simple melting. This is because the energy is not just changing the material's physical state; it is driving a demanding chemical reaction.
How to Distinguish Them in Practice
To determine which process is being discussed, focus on the ultimate goal and the ingredients involved.
- If your primary focus is to shape or recycle an existing metal: You are dealing with melting.
- If your primary focus is to produce a new, raw metal from a rock-like mineral: You are dealing with smelting.
- If a chemical like coke or limestone is added to facilitate separation: It is a clear indicator of smelting.
- If the process only involves heating a refined material until it liquefies: It is simply melting.
Understanding this distinction is the first step to mastering the fundamentals of materials science and metallurgy.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Melting | Smelting |
|---|---|---|
| Process Type | Physical (Phase Change) | Chemical (Reduction) |
| Primary Goal | Change shape (e.g., casting, recycling) | Extract pure metal from ore |
| Chemical Change | No | Yes |
| Key Inputs | Pure material + Heat | Ore + Heat + Reducing Agent (Flux) |
| Main Output | Liquid form of the input material | Purified molten metal + Slag (waste) |
Master Your Metallurgical Processes with KINTEK
Whether your lab work involves precise melting for alloy creation or requires equipment capable of handling the high-temperature demands of smelting reactions, having the right tools is critical for success and safety.
KINTEK specializes in supplying high-quality lab furnaces, crucibles, and consumables tailored to the exact needs of metallurgy and materials science laboratories. Our equipment ensures precise temperature control, durability, and reliability for both simple melting and complex chemical extraction processes.
Let us help you achieve precise and efficient results. Contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for your specific application.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
People Also Ask
- What is the principle of rotary kiln? Mastering Continuous Thermal Processing
- What are the industrial applications of pyrolysis? Transform Waste into Energy and Valuable Products
- What are the products of pyrolysis of wood? A Guide to Biochar, Bio-oil, and Syngas Yields
- What are the different types of reactors in plastic pyrolysis? Choose the Right System for Your Waste
- What are the types of pyrolysis reactors used in industry? Choose the Right Technology for Your Product



















