At its core, an electric arc is a high-current discharge of electricity across a normally non-conductive medium, such as a gas or a vacuum. Arcing occurs when the electric field between two points becomes too strong for the insulating medium to withstand, causing it to break down and become a conductive plasma channel. This breakdown is often triggered by factors like surface contaminants, material defects, or the inherent properties of the materials involved.
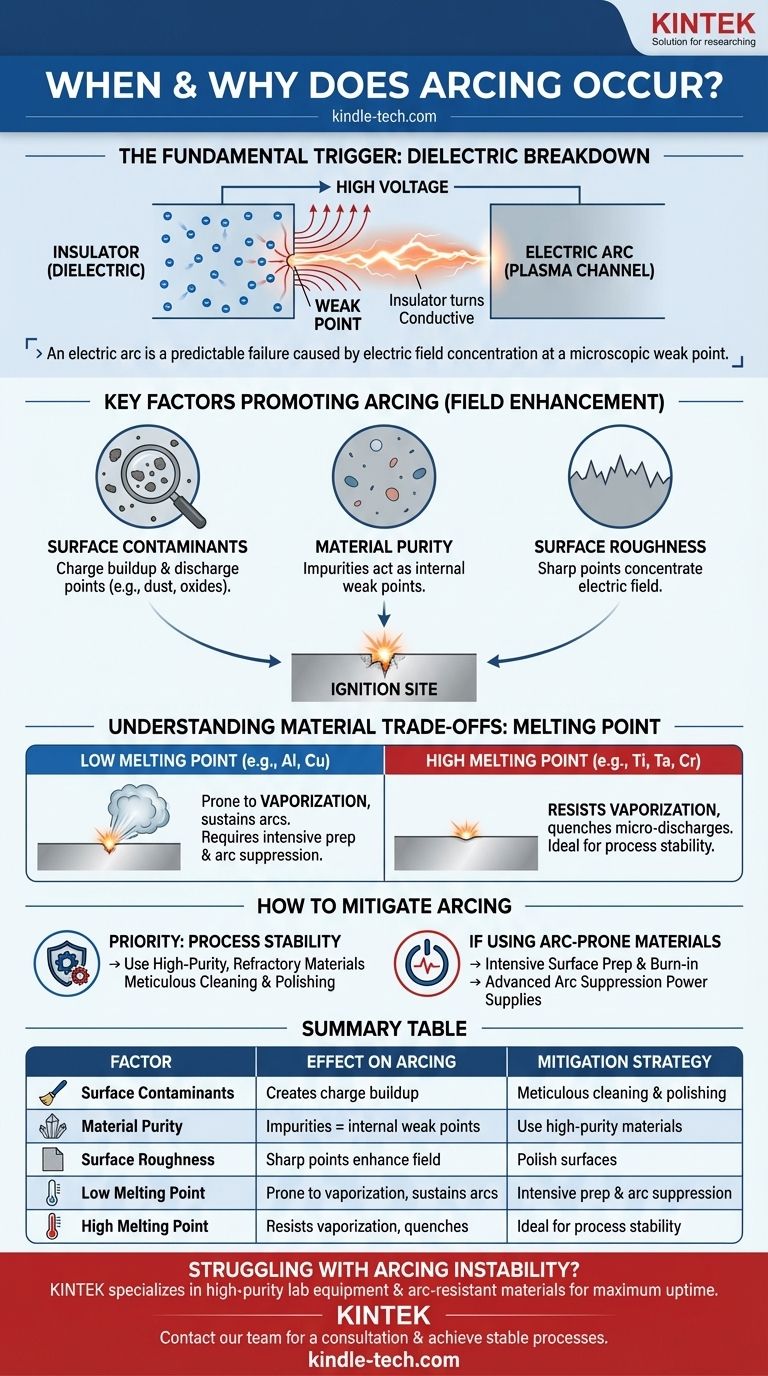
An electric arc is not a random event. It is a predictable failure caused by the concentration of an electric field at a microscopic weak point on a material's surface, leading to a catastrophic discharge of energy.

The Fundamental Trigger: Electric Field Breakdown
To prevent arcing, we must first understand the underlying physics. The entire process hinges on the concept of dielectric breakdown, where an insulator is forced to become a conductor.
What Is an Electric Arc?
An electric arc is essentially a tiny, self-sustaining bolt of lightning. It appears as a bright, intensely hot plasma channel that carries a very high electrical current.
This is not a simple spark; an arc is a continuous discharge that can transfer significant energy, often melting or vaporizing the material at its connection points.
The Role of Dielectric Breakdown
Materials like gases, ceramics, or even a vacuum are insulators (dielectrics), meaning they resist the flow of electricity. However, their insulating ability has a limit, known as dielectric strength.
When the voltage across a gap is high enough, the resulting electric field can rip electrons from the atoms of the insulating medium. This creates a cascade effect, rapidly turning the insulator into a conductive plasma and initiating an arc.
Field Enhancement at Imperfections
An electric field is not always uniform. It will concentrate intensely around any sharp points, microscopic debris, or structural defects on a surface.
This phenomenon, known as field enhancement, means that a microscopic point can experience an electric field hundreds of times stronger than the average field. This localized spot becomes the weak point where an arc is most likely to ignite, even at otherwise safe operating voltages.
Key Factors That Promote Arcing
The principles of breakdown and field enhancement manifest through several practical factors, particularly in high-voltage processes like physical vapor deposition (PVD).
Surface Contaminants and Dielectrics
Insulating (dielectric) particles, such as dust or oxides on a metal surface, are a primary cause of arcing.
These particles allow electrical charge to accumulate on their surface, acting like tiny capacitors. When they accumulate enough charge, they discharge violently to the underlying conductive material, providing the initial energy to trigger a large-scale arc.
Target Material Purity
Impurities within a material can create microscopic regions with different electrical or thermal properties.
These spots act as internal defects that can initiate breakdown under a strong electric field, making lower-purity materials more susceptible to arcing.
Surface Structure and Roughness
A perfectly smooth surface is ideal for preventing arcs. In reality, surfaces have scratches, pores, and microscopic peaks and valleys from the manufacturing process.
Each of these imperfections acts as a sharp point for field enhancement, creating a multitude of potential ignition sites for an arc.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Material Properties
The material itself plays a defining role in arc resistance. This choice often involves a trade-off between the material's desired properties for the application and its inherent stability against arcing.
Low vs. High Melting Point Materials
Materials with a lower melting point, such as Aluminum (Al) and Copper (Cu), are notoriously prone to arcing.
A small, localized discharge can easily generate enough heat to melt or vaporize a tiny amount of the material. This vaporized metal provides a highly conductive medium, making it easy for the small discharge to erupt into a full, high-current arc.
The Stability of Refractory Metals
In contrast, materials with a high melting point, like Titanium (Ti), Chromium (Cr), and Tantalum (Ta), are much more resistant to arcing.
When a small discharge occurs on their surface, their high melting point allows them to absorb the energy without vaporizing. The material remains solid, effectively "quenching" the micro-discharge before it can escalate into a damaging arc.
How to Mitigate Arcing in Your Process
Controlling arcs is a matter of controlling the surface condition and managing material properties. Your strategy will depend on the constraints of your application.
- If your primary focus is process stability: Prioritize using high-purity, high-melting-point (refractory) materials and ensure surfaces are meticulously cleaned and polished to remove contaminants and reduce roughness.
- If you must use arc-prone materials (like Aluminum): Focus intensely on surface preparation, implement a pre-process "burn-in" to condition the surface, and utilize a power supply with advanced arc detection and suppression capabilities.
By understanding these principles, you can transform arc management from a reactive problem into a controlled and predictable aspect of your process.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Effect on Arcing | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Surface Contaminants | Creates charge buildup & discharge points | Meticulous cleaning & polishing |
| Material Purity | Impurities act as internal weak points | Use high-purity target materials |
| Surface Roughness | Sharp points enhance electric field | Polish surfaces to reduce imperfections |
| Low Melting Point (e.g., Al, Cu) | Prone to vaporization, sustaining arcs | Intensive surface prep & arc suppression power supplies |
| High Melting Point (e.g., Ti, Ta) | Resists vaporization, quenches micro-discharges | Ideal for process stability |
Struggling with process instability from arcing? KINTEK specializes in high-purity lab equipment and consumables, including arc-resistant target materials and PVD systems designed for maximum uptime. Our experts can help you select the right materials and implement strategies to prevent arcing, protecting your equipment and ensuring consistent results. Contact our team today for a consultation and let us help you achieve a more stable, productive process.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Oxygen-Free Copper Crucible and Evaporation Boat
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
People Also Ask
- What are the process capabilities of ICPCVD systems? Achieve Low-Damage Film Deposition at Ultra-Low Temperatures
- What are different types of thin films? A Guide to Function, Material, and Deposition Methods
- How are thin films deposited? A Guide to PVD vs. CVD Methods for Your Application
- Why is a Matching Network Indispensable in RF-PECVD for Siloxane Films? Ensure Stable Plasma and Uniform Deposition
- What is the difference between plasma CVD and thermal CVD? Choose the Right Method for Your Substrate


















