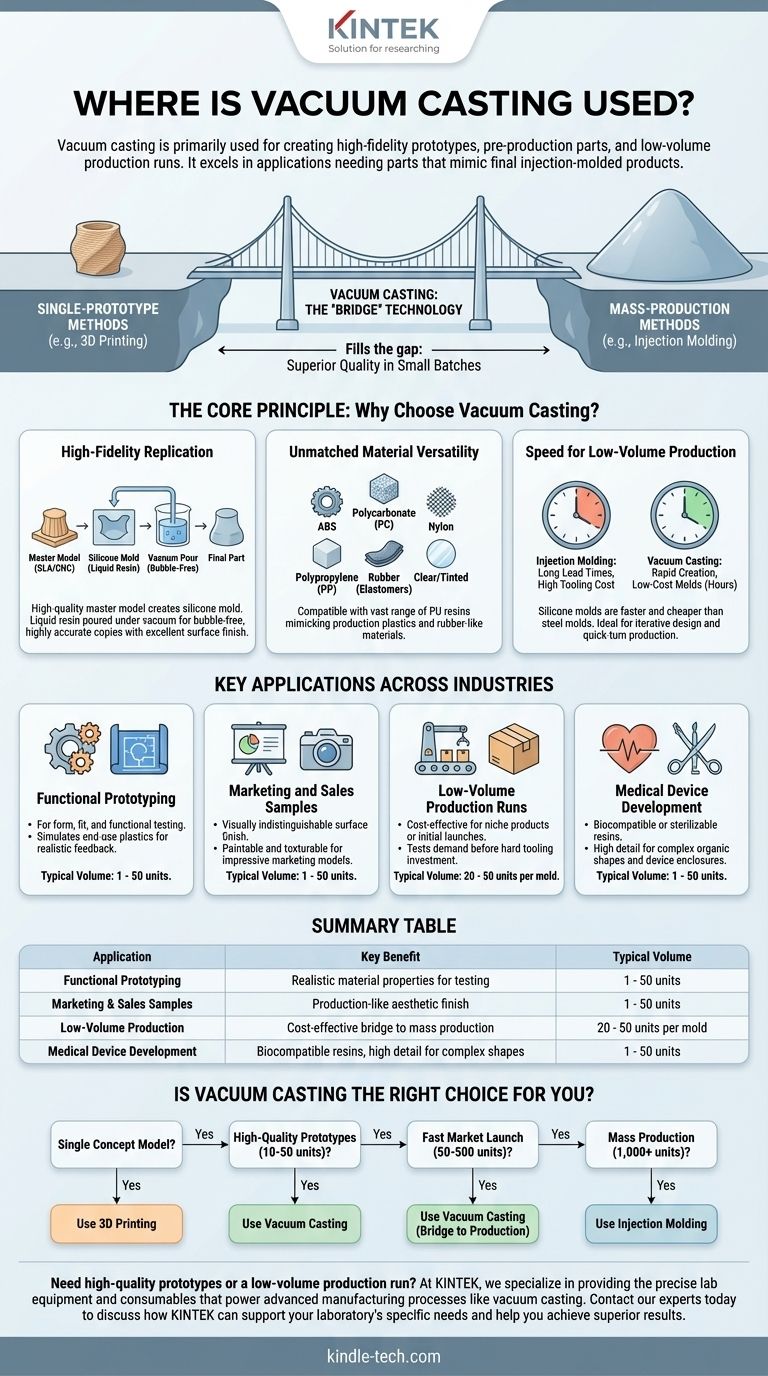
In short, vacuum casting is primarily used for creating high-fidelity prototypes, pre-production parts, and low-volume production runs. It excels in applications where you need parts that closely mimic the look, feel, and performance of final injection-molded products but without the high cost and long lead times of hard tooling.
The core value of vacuum casting is its role as a "bridge" technology. It fills the critical gap between single-prototype methods like 3D printing and mass-production methods like injection molding, offering superior quality in small batches.

The Core Principle: Why Choose Vacuum Casting?
To understand where vacuum casting is used, you must first understand its fundamental strengths. It's not just about what it makes, but how it makes it, which defines its ideal applications.
High-Fidelity Replication
Vacuum casting uses a high-quality master model, often created via 3D printing (SLA) or CNC machining, to create a silicone mold.
Liquid polyurethane resins are then poured into this mold under a vacuum. This process removes air bubbles, ensuring the resin perfectly fills every intricate detail of the mold cavity.
The result is a bubble-free, highly accurate copy of the master model with excellent surface finish.
Unmatched Material Versatility
The process is compatible with a vast range of polyurethane (PU) resins.
These resins can be formulated to mimic the properties of common production plastics, including ABS, polycarbonate (PC), nylon, and polypropylene (PP).
It's also possible to cast parts in soft, rubber-like materials (elastomers) of varying hardness, as well as in clear, transparent, or tinted resins.
Speed for Low-Volume Production
Creating a silicone mold is significantly faster and cheaper than machining a steel or aluminum mold for injection molding.
Once the mold is ready, casting a part takes only a few hours. This allows for the rapid creation of dozens of parts, making it an ideal process for iterative design testing and quick-turn production.
Key Applications Across Industries
The unique combination of quality, speed, and material options makes vacuum casting a critical tool in many sectors.
Functional Prototyping
This is the most common application. Engineers and designers use vacuum casting to create prototypes for form, fit, and functional testing.
Because the parts can be made from materials that simulate end-use plastics, these prototypes provide far more realistic feedback than a simple 3D print.
Marketing and Sales Samples
For trade shows, investor pitches, or user testing, appearance is critical.
Vacuum casting produces parts with a surface finish that is visually indistinguishable from a mass-produced product. Parts can be painted, textured, and finished to create impressive marketing models.
Low-Volume Production Runs
For niche products with limited demand or for the initial launch of a new product, vacuum casting is a cost-effective production method.
It allows companies to get a product to market and test demand before committing to the massive capital expense of injection molding tooling. A single silicone mold can typically produce 20 to 50 parts, depending on the complexity and material.
Medical Device Development
The ability to use biocompatible or sterilizable resins makes vacuum casting invaluable for prototyping medical device enclosures, surgical guides, and anatomical models.
The high level of detail is crucial for replicating complex organic shapes.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No manufacturing process is perfect for every situation. Trustworthy decisions come from understanding the limitations.
The Advantage: Avoiding Hard Tooling Costs
The primary benefit is economic. Vacuum casting avoids the tens of thousands of dollars and months of lead time required for injection mold tooling. This dramatically lowers the barrier to entry for creating high-quality plastic parts.
The Limitation: Mold Lifespan
A silicone mold is not permanent. It degrades with each casting due to chemical reactions and thermal stress.
After approximately 20-50 castings, the mold loses its fine detail and dimensional accuracy, requiring a new mold to be made from the master pattern. This is why the process is not suitable for high-volume production.
The Limitation: Per-Part Cost at Volume
While the initial setup is cheap, the cost per part is higher than injection molding.
The manual labor involved in casting and the limited mold life mean that as your volume increases, injection molding quickly becomes the more economical choice.
Is Vacuum Casting the Right Choice for You?
Use this framework to determine if the process aligns with your project goals.
- If your primary focus is a single concept model: 3D printing is almost always faster and more cost-effective.
- If your primary focus is high-quality prototypes (10-50 units) for testing: Vacuum casting is the ideal choice for its production-like materials and finish.
- If your primary focus is a fast market launch (50-500 units): Vacuum casting is an excellent bridge-to-production tool to satisfy early demand before investing in hard tooling.
- If your primary focus is mass production (1,000+ units): You must invest in injection molding for the lowest possible cost-per-part.
By understanding its specific strengths and limitations, you can leverage vacuum casting as a powerful tool for innovation and efficient product development.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Benefit | Typical Volume |
|---|---|---|
| Functional Prototyping | Realistic material properties for testing | 1 - 50 units |
| Marketing & Sales Samples | Production-like aesthetic finish | 1 - 50 units |
| Low-Volume Production | Cost-effective bridge to mass production | 20 - 50 units per mold |
| Medical Device Development | Biocompatible resins, high detail for complex shapes | 1 - 50 units |
Need high-quality prototypes or a low-volume production run?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the precise lab equipment and consumables that power advanced manufacturing processes like vacuum casting. Whether you're in R&D, medical device development, or product design, having the right tools is crucial for success.
Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK can support your laboratory's specific needs and help you achieve superior results in your prototyping and production workflows.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab Plastic PVC Calender Stretch Film Casting Machine for Film Testing
- Touchscreen Automatic Vacuum Heat Press
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Powerful Plastic Crusher Machine
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine for Dry and Wet Three-Dimensional Sieving
People Also Ask
- What is the meaning of blowing film? A Guide to Biaxial Orientation and Stronger Plastic Films
- What is the difference between calendaring and calendering? Master the Key Spelling and Context
- What are the advantages of blown film extrusion? Boost Your Film Production Efficiency
- What are the disadvantages of the extrusion process? High Costs and Geometric Limits Explained
- What is the process of double extrusion? Create Integrated Multi-Material Components



















